![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Enzymes |
Make it easier for molecules to react -most enzymes are a protein -catalyze (speed up) chemical reactions by lowering activation energy |
|
|
|
Induced fit |
The hand must fit the glove! -substrate molecule must fit into the active site on the enzyme -the "ose" must match the "ase" -sucrose --> sucrase |
|
|
|
Substrate |
Reactant molecule. -the "ose" |
|
|
|
Specificity |
=different enzymes catalyze different reactions. Diff molecules only fit diff enzymes |
|
|
|
Intolerance (such as lactose) |
Inability to digest lact'ose', due to a deficiency of lact'ase' (no enzyme production) |
|
|
|
Metabolic rate |
Rate at which the body uses energy. - influenced by many factors: Body weight Sex Exercise Genetic makeup |
|
|
|
BMR |
Basal metabolic rate - average is 70 calories per hour (or 1680 per day) of an awake person who is resting. But alert. |
|
|
|
Cellular respiration |
Aerobic. -converts energy from food into energy stored in ATP |
|
|
|
ATP |
ATP consists of adenine, a sugar, and 3 phosphate groups.
A: adenine T: tri P: phosphate
When phosphate is transferred from. ATP to another molecule (phosphorylation), energy is transfered and ADP is what is left -The energy from ATP can power multiple kinds of work in cells/body |
|
|
|
ADP |
A: adenine D: di P: phosphate As ATP is used up, it must be replenished by cell respiration -food energy --> replenishes the phosphate (that was pulled off) to ADP --> making ATP -process: ADP + phosphate, uses oxygen. |
|
|
|
How cell resp. Works |
3 stages: Glycosis Citric acid cycle Electron transport and ATP synthesis |
|
|
|
Stage 1: Glycosis |
-6 carbon glucose molecules broken down into 3 carbon pyruvic acid molecules. -doesn't use O2 -happens outside organelles in fluid cytosol -produces 2 ATP
Also! -removes electrons for use in producing ATP in the final stage of CR -electrons are carried by NAD+ |
|
|
|
NAD+ |
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. - EMPTY taxi cab for electrons -picks up 2 hydrogen atoms (along with the electrons) -releases 1 +charge hydrogen ion (H+) -becomes NADH - FULL taxi cab for electrons -Carries the Etrons to their destination (which is the final step in cell respiration) |
|
|
|
Stage 2: citric acid cycle |
-pyruvic acid is decarboxylated (loses a carbon dioxide molecule) - the 2-carbon molecule enters the citiric acid cycle. -reacts with OAA and proceeds through a series of reactants -takes 8 diff enzymes -produces more carbon dioxide and releases it into the atmosphere
NADH and 2 ATP are also produced here.
|
|
|
|
Why is it it called : citric acid cycle? |
Because every trip around the pathway regenerates the first reactant which is -a 4 carbon molecule called oxaloacetate (OAA) |
What is a cycle? |
|
|
Stage 3: electron transport and ATP synthesis |
Essentially, energy from electrons added to the electron transport chain is used to produce ATP. -electrons harvested during stage 1 & 2 are carried to this stage by the NADH -electron transport chain (of proteins) functions as a conveyor belt for Etrons -moving toward the matrix of the mirochindrion -Etrons combine with oxygen and produce water! %WHY?% -conveyor belt also is moving H+ ions from matrix into the intermembrane space -decreases concentration in matrix -increases concentration in intermembrane diffusion occurs but because charged ions cannot cross the hydrophobic membrane they escape via a protein channel called ATP synthase This enzyme uses the energy made by the rushing H+ ions to synthesize 26 ATP out of ADP+P.
|
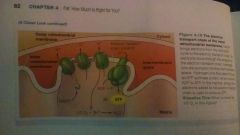
Water rushing thru a turbine to create electricity. |
|
|
Anaerobic respiration |
Cells generating energy with the absence of oxygen. Happens when a body works out really hard and oxygen cant be replenished fast enough. |
|
|
|
Fermentation |
When cells run low on O2 they must get their ATP from glycolysis (stage 1) only because this is the only stage that doesn't use O2
cells run low on NAD+ because it is converted to NADH during glycosis.
Fermentation occurs to regenerate NAD+
Can't be used long cuz it creates lactic acid which also creates 2 ATP. -produced by the actions of NADH, which will have no where to dump its electrons during fermentation because there is no electron transport chain and no oxygen to accept them. -lactic acid is transported to liver where cells use oxygen to convert it back to pyruvic acid
Explains: -heavy breathing after working out has stopped. -"paying back your oxygen debt" to liver - "hitting the wall" -is the accumulation of too much lactic acid in muscles. And muscles shut down until resupplying oxygen rate outpaces the rate of oxygen use |
When we hit the wall |
|
|
BMI |
Body mass index: correlates amount of body fat with risk of illness and death using weight and height data
Healthy body fat indexes: M- 14% W- 22%
|
|
|
|
Healthy range of BMI |
20-25 |
|
|
|
Obesity |
A BMI of 30+ But this is not a perfect scale Ex: Arnold Schwarzenegger had a BMI of 31 So muscle mass has something to do with it as well |
|
|
|
Insulin |
Hormone that triggers cells to take up glucose Made by beta cells in pancreas |
|
|
|
Type 1 diabetes |
Genetic Usually arises in child hood Body cannot produce insulin --> no beta cells Treated daily with insulin injections |
|
|
|
Type 2 diabetese |
Dibesity Associated with obesity Usually arises in adults May be controlled by diet and exercise
|
|
|
|
Hypertension |
High blood pressure Pressure is consistently over 140/90 mmHg Normal is usually 120/80 |
|
|
|
Blood pressure terms |
Systolic Diastolic |
|
|
|
Systolic |
Pressure as the heart contracts "Lub" |
|
|
|
Diastolic |
The pressure while the heart relaxes "Dub" |
|
|
|
Heart attack /stroke |
Sudden loss of blood to heart due to blocked arteries Loss of blood to brain due to blocked arteries |
|
|
|
Cholesterol |
Lipid that CAN build up and cause blockages
When to high, Can also be good Is carried by lipoproteins |
|
|
|
Low density lipoproteins (LDLs) |
Low density : carry cholesterol made in liver and from foods |
|
|
|
High density lipoproteins (HDLs) |
Carry excess cholesterol to liver for excretion as bile
Sat fats! Raise cholesterol |
|
|
|
Anorexia |
Self starvation -can starve heart producing altered rythms Can cause amenorrhea: cessation of menstruation causing sterilization Increases risk of osteoporosis -weak bones |
|
|
|
Bulimea |
Binge eating followed by purging Many of same health effects as anorexia May lead to stomach rupture Dental and gum problems from stomach acid Dehydration... Sometimes fatal |
|
|
|
Inputs and out puts of cell respiration |
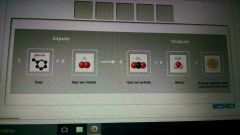
Inputs: 1 Glucose - fuel + 6 Oxygen - gas we inhale
Out puts: (equals) 6 Carbon dioxide- gas exhaled + 6 water -h2o + ATP -energy packets that cells use to do work |
|
|
|
First law of thermodynamics |
Energy cannot be created, or destroyed. It can only be changed from one form to another. |
|
|
|
Exergonic |
Energy releasing reactions |
|
|
|
Endergonic |
Energy consuming reactions |
|

