![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
2 main sources of protein
|
dietary
celluar |
|
|
if amino acids aren't used as building blocks, what happens to them
where does this occur |
NO STORAGE form of amino acids → degraded
(damaged proteins also removed) LIVER |
|
|
why does ammonia need to be converted to urea (in LIVER)
|
ammonia NH3/NH4+ is TOXIC at high concs
|
|
|
where is ammonia formed from
|
some amino acids contain nitrogen in their side chains
→ broken down → NH3 + NH4+ |
|
|
4 major nitrogen-containing excretory molecules
|
UREA
uric acid (gout) CREATININE ammoniom NH4+ |
|
|
what are the 3 steps in the synthesis of urea
|
1) TRANSAMINATION
2) DE-AMINATION 3) UREA CYCLE |
|
|
what's involved in step 1 in the formation of urea (transamination):
- enzyme - substrates - products - location & destination of prods |
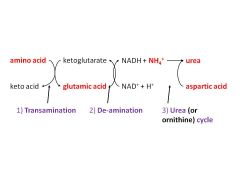
amino acids ----AMINOTRANSFERASES→ keto acids (→ TCA)
gives GLUTAMATE( (nitrogen carrier)→ taken to LIVER occurs in ALL TISSUES |
|
|
step 2) DEAMINATION in urea synthesis;
- loc - substrate - prods |
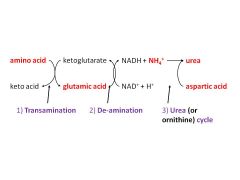
in LIVER
amino group of GLUTAMATE → converted to NH4+ |
|
|
in step 3) UREA CYCLE of urea synthesis;
- where do the 2 nitrogens come from - where is the carbon derived from |
1 from NH4+ [from step 2) de-amination]
1 from aspartic acid C from CO2 |
|
|
after step 1) transamination of urea synthesis, removal of amino group leaves what?
- what are these used for - via which 2 methods |
CARBON SKELETONS
used for energy generation: - converted to GLUCOSE - oxidised in TCA |
|
|
depending on the type of carbon skeleton remaining after transamination (removal of amino group);
- which type can give rise to ketone bodies or FAs - which type converted to TCA intermediates→ glucose |
KETOGENIC= ketone bodies/ FAs
GLUCOGENIC= glucose via TCA |
|
|
3 inherited disorders of amino acid degradation (step 1 transamination)
|
PKU
Maple-syrup urine disease Alcaptonuria |
|
|
what's the danger of urea cycle disorders
how to treat |
free NH4+ accumulation = TOXIC
low-protein diet & nitrogen-removing drugs |

