![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Atomic number
|
# of p+ (left subscript); atomic weight = # of p+ + n (left superscript)
|
|
|
Isotopes
|
have different #s of neutrons, but same # of protons
|
|
|
Electrons
|
orbit around a nucleus like planets around a star. There are different shells, or energy levels,in which electrons move.
|
|
|
Outermost shell (aka valence shell)
|
prefers to be full → more stable atom
|
|
|
An atom is composed of
|
nucleus w/ protons and neutrons; electrons that move around the nucleus
|
|
|
Covalent bonds
|
Are usually polar.
Relatively weak bond formed between atoms,made by sharing electrons. |
|
|
Ionic bonds
|
Strong molecular bond, formed beteen atoms with opposite charges
|
|
|
Hydrogen bonds
|
Weak bond formed by electrical attraction between molecules
|
|
|
Water has six ‘life‐sustaining’ properties
|
1. liquid at RT
2. great solvent 3. cohesive and adhesive (‘sticky’) 4. high specific heat 5. high heat of vaporization 6. solid water (ice) floats |
|
|
what is the pH in your stomach? in your blood?
|
7,3
|
|
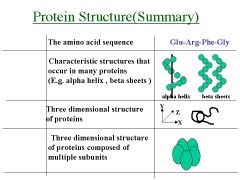
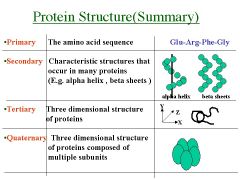
Name the structure
|
|

