![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are angiosperms?
What are sexual and asexual reproductive parts? |
They are highest level of plants (flowering plants)
They reproduce sexually and asexually |
Sexual- flowers, formation of fruits and seeds
Asexual- leaves, stems, roots |
|
|
What are the 2 types of angiosperms and there general differences?
|
Monocot has:
Parallel veins 3 Sepals, 3 Petals. Fibrous roots One embryonic seedling (i.e. Lillies, orchids, grass) |
Dicot has:
Reticular veins 4-5 Sepals, 4-5 Petals Tap roots 2 embryonic seedlings (i.e. trees, shrubs) |
|
|
What is another name for the asexual parts of plants?
|
Vegetative parts
|
|
|
|
What are the 3 main vegetative parts of plants?
How do they reproduce and which of 3 has most variety in asexual reproduction? |
Leaves, stems, & roots
|
They reproduce mitotically.
Some leaves capable of reproduction. Variety of stems capable of asexual reproduction. |
|
|
What are the 4 variety of stems capable of asexual reproduction and examples of each?
|
Rhizome- horizontal underground stem.
Tubers- enlarged for storage Bulbs- shortened underground stem with fleshy leaves Stolons- runners, horizontal, above ground stems |
Rhizomes- Iris & grass
Tubers- potato Bulbs- tullips, lilies, onions, daffodils Stolons- strawberries |
|
|
What is the example of asexual reproduction from roots given in class? Example of this type?
|
Suckers- above ground stems that develop from adventitious buds on the roots.
|
Example: raspberries, and blackberries
|
|
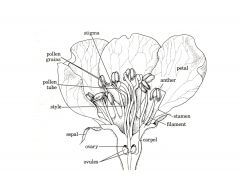
What are the 4 layers to sexually reproducing flowers? (From outermost layer to innermost) Their function?
|
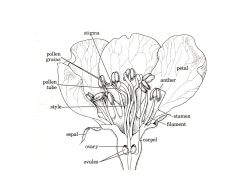
Sepals
Petals Stamens (3 parts)(male organ) Carpel (3 parts)(female organ) |
Sepal- protect bud when closed
Petals- lure bugs into flower for fertilization (colorful part of flower) |
|
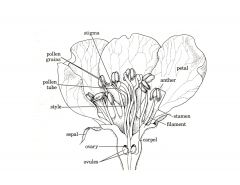
What are the 3 parts of stamens? Their function?
|
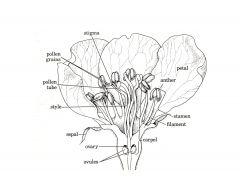
Male reproductive organs
Anther Filament Pollen |
Anther - produces pollen
Filament- holds anther in place Pollen- male gamete (haploid) |
|
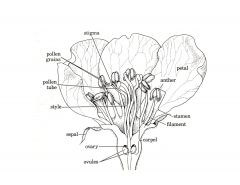
What are the 3 parts of carpels or pistels? Their function?
|
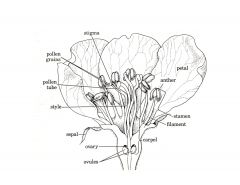
Stigma
Style Ovary |
Stigma- sticky pad where pollen adheres
Style- Stalk with inner tube carrying pollen into ovary Ovary- contains ovules (female gametes) |
|
|
What are complete and incomplete flowers?
|
Complete- contain all 4 whirls
|
Incomplete- missing one or more whirls
|
|
|
What are perfect and imperfect flowers?
|
Perfect- contains both stamens and carpels
|
Imperfect- contains either stamens or carpels
|
|
|
Ovaries ripen into what?
|
Fruit
|
|
|
|
Fertilized egg are seeds of what?
|
Seeds of fruit
|
|
|
|
What are the 4 types of fruits? Their main characteristic? Example of each?
|
Simple -develops from single ovary of single flower
Aggregate- develops from single flower containing many carpels Multiple- develops from many ovaries of many flowers Accessory- ovary and other plant tissues are used in forming fruit |
Examples:
Simple - peach, plum, avocado Aggregate- Raspberry Multiple - pineapple Accessory - strawberry |

