![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does turbid mean?
|
cloudiness
|
|
|
How much organism must be present to detect turbity?
|
10⁷ organism/mL
|
|
|
Convert 10⁻¹ mm to µm
|
10² µm
|
|
|
Convert 10³ mm to meter(s)
|
1 meter
|
|
|
Convert 10³ µm to millimeters
|
1 mm
|
|
|
Convert 10³ nanometers to micrometers (µm)
|
1 micrometer
|
|
|
Convert 10⁶ micrometers to meter(s)
|
1 meter
|
|
|
What does TNTC mean?
|
too numerous to count
|
|
|
define: pathogenesis
|
origin or birth of disease
|
|
|
define: labile
|
heat it and it will break down
|
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus
|
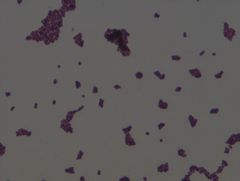
• gram negative organism
• heat labile toxin Example of a Gram Stain |
|
|
Salmonella spp.
|
• gram negative organism
• live organism growth |
|
|
Shigella spp.
|
• gram negative organism
• live organism growth |
|
|
Campylobacter jejuni
|
• gram negative organism
• live organism growth |
|
|
Escherichia coli
|
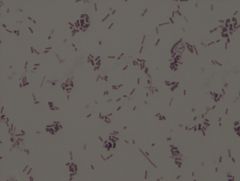
• gram negative organism
• rod, coccobacillary form, singles, pairs, short chains • live organism growth • grown at 37° C • grown on nutrient agar Example of a Gram Stain |
|
|
Clostridium botulism
|
• gram negative organism
• heat labile toxin • causes botulism |
|
|
What are some characteristics of the Clostridium species?
|
• can form spores
• anaerobic (likes O₂) • produces a deadly neurotoxin |
|
|
Bacillus megaterium
|
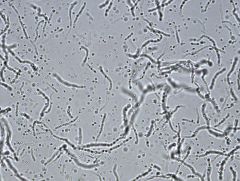
• creamy texture
|
|
|
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
|
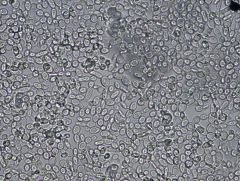
• creamy textures
• oval cells, round cells - almost football shaped |
|
|
Aspergillus niger
|
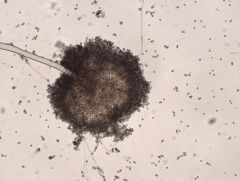
• black stuff = spores
|
|
|
Chlorella vulgaris
|
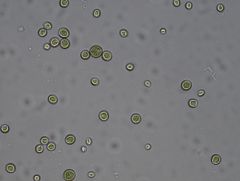
• photosynthetic cell
• greenish tint, round cells |
|
|
Bacillus subtilis
|
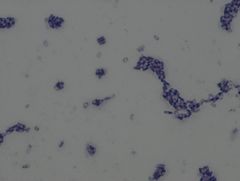
• gram positive organism
• rod arrangement: singles, chains (palisades patter) • spores - capable of making spores (may or may not be present) Example of a Simple Stain TCV |
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus
|
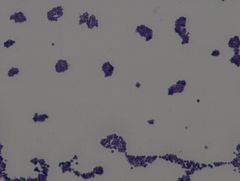
• gram positive organism
• coccus, irregular clusters • fastidious organism Example of a Simple Stain TCV |
|
|
Streptococcus faecalis
|
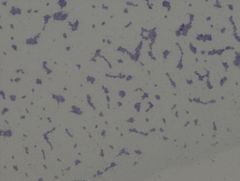
Enterococcus faecalis (newer name)
• gram negative organism • coccus, pairs, short chains Example of a Simple Stain TCV |
|
|
Sarcina lutea
|
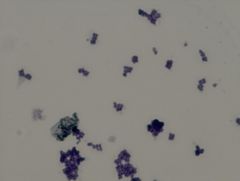
• gram positive organism
• coccus, box cars (pairs of 8) • lutea means yellow Example of a Simple Stain TCV |
|
|
Neisseria sicca
|
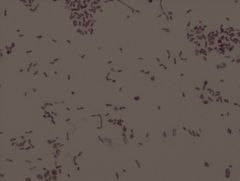
• gram negative
• diplococci, filaments Example of a Gram Stain |
|
|
Sarcina lutea
|
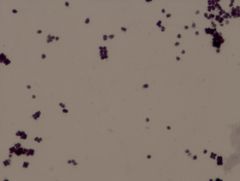
• gram positive
• box cars (8s) Example of a Gram Stain |
|
|
Proteus vulgaris
|
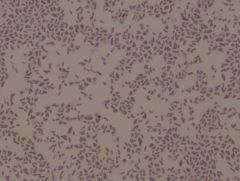
• gram negative
• light pinkish color • small cells • rod - coccibacilliary • grown at 37° C Example of a Gram Stain |
|
|
Micrococcus luteus
|
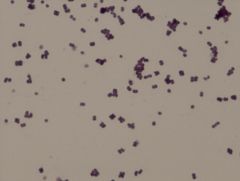
• gram positive
• tetrads Example of a Gram Stain |
|
|
What occurred during the motility test with Proteus vulgaris?
|
diffused cloudiness
|
|
|
What occurred during the motility test with Escherichia coli?
|
cloudy on top & everywhere
|
|
|
What occurred during the motility test with Staphylococcus aureus?
|
non-motile form
|
|
|
Flavobacterium capsulatum
|
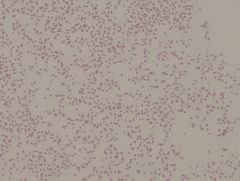
• gram negative rod
• tiny cells, yellow organism Example of a Gram Stain |
|
|
Streptomyces albus
|
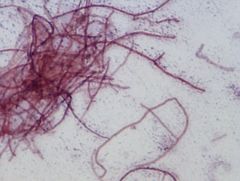
• Streptomyces genus is associated with antibiotics
• gram variable depending on age of bacteria, you may/may not see features appearance: nice, white chalky growth, stubborn to get out, smells like a musty basement • grown at 37° C • filamentous • coccoid structures, prokaryotic cell • uniqus |
|
|
Bacillus cereus varieties mycoides
|

• spreading like a mold
• given in broth culture • has longer chains that Bacillus cereus Example of a Gram Stain |
|
|
Enterobacter aerogenes
|
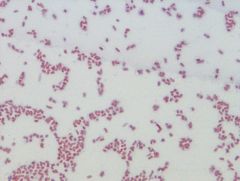
• gram negative rods
• coliform: grows in the intestines • grown at 37° C Example of a Gram Stain |
|
|
The Zones of Inhibition depend on:
|
1. concentration of antibiotic on disc
2. temperature 3. thickness of media used |
|
|
What is the Cold Acid Fast Stain Technique used to highlight?
|
This stain is designed to reveal the members of the genus Mycobacterium. They are acid fast positive due to a waxy substance in their cell walls known as mycolic acid which hods on to the carbolfuchsin. All other bacteria will stain acid fast negative
Acid fast positive cells are stained the pink/red color of carbolfuchsin. Acid Fast negative cells are stained the light blue color of methylene blue. |
|
|
What is the Cell Wall Staining Procedure used to highlight?
|
This procedure is used to highlight the cell wall and therefore provide an improved look at cell morphology. Although there is swelling of the cells, this enlargement occurs proportionally so that the shape of the cell is maintained. This technique is useful in determining morphology of smaller cocci and coccobacillary forms.
Most bacterial cell walls have a net anionin (negative charge). Cetypridinum choloride is a cationic solution that places a positive charge on the cell wall exterior by sticking to the negative charge on the cell wall. The Congo Red is negatively charged and when introduced can not stick to the positive charge of the added cetylpyridinium chloride. |
|
|
What is the Capsule Stain used to distinguish?
|
Leaving the structures a violet/purple color. However, the Copper Sulfate will remove the Tyler's Crystal Violet from the capsule, leaving them almost colorless
|
|
|
The plague is caused by ___.
|
Yersinia pestis
|
|
|
Tuberculosis is caused by ___.
|
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
|
|
|
Necrotizing fascitis caused by
|
Streptococcus pyogenes
also called "flesh eating" bacteria |
|
|
Lassa fever is caused by
|
Lassa fever
|
|
|
West Nile encephalitis is caused by
|
West Nile virus
|
|
|
Ebola hemorrhagic fever is caused by
|
Ebola virus
|
|
|
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is caused by
|
SARS virus
|
|
|
What does liquefaction mean?
|
that the organism was capable of protein (gelatin) hydrolysis
A positive result means that the tube showed some form of liquid when placed in an ice bath. |
|
|
define: ubiquitous
|
omnipresent or everywhere
|
|
|
define: colony
|
a macroscopic visible growth of microorganisms on a solid culture medium, which may be derived from one or more cells. To visualize a colon, there must be at least 10⁶ cells. A pinpoint colony is referred to as a punctiform colony
|
|
|
define: nonsocomial infection
|
an infection derived from a clinical/hospital setting
|
|
|
define: fastidious organisms
|
organisms that have complex nutritional requirements
|
|
|
define: resolution
|
the ability to distinguish fine detail; also called resolving power
|
|
|
define: fomites
|
inanimate objects capable of absorbing, retaining and transmitting infectious agents
|
|
|
What is the resolution of a microscope?
|
0.2 micrometers
|
|
|
define: bacteriostatic
|
inhibits growth and reproduction of bacteria
|
|
|
define: bactericidal
|
kills microorganisms
|

