![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the 4 layers of the gastrointestinal tract?
|
Tunica Mucosa
Tunica Submucosa Tunica Muscularis Tunica Adventitia |
|
|
|
Structure and Function of Tunica Mucosa?
|
Epithelial Layer
|
Produces Digestive glands
Mucous membrane protects from digestive juices |
|
|
Structure and Function of Tunica submucosa?
|
Dense irregular connective tissue
|
Location of blood, lymphatic, and nervous system vessels.
Blood vessels for absorption. Parasympathetic and sympathetic connections here |
|
|
Function of the parasympathetic vs sympathetic branch of autonomic nervous system?
|
Parasympathetic:
Everyday functions like digestion. Promotion of release of digestive juices Increase motility in GI tract |
Sympathetic:
Decrease digestive functions Decrease motility in GI tract |
|
|
Structure and function of tunica muscularis?
|
Smooth muscle layer with 2 regions:
Inner circular and outer longitudinal layer |
Promotes movement of GI tract through peristalsis
|
|
|
Structure and Function of tunica adventitia?
What is in the center? |
At beginning and end of GI tube
Connective tissue anchors tube to body wall, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves to tube |
In center is serosa or serous membrane
|
|
|
Structure and Function of serous membranes?
|
Membrane that lines cavity and organs within cavity that don't open to exterior.
|
|
|
|
What are the 3 serous membranes and what 2 components do they all share?
|
Pleural
Pericardial Peritoneal |
All have perietal peritoneum
All have visceral peritoneum |
|
|
Function of the perietal peritoneum?
|
Lines the body wall
|
|
|
|
Function of the visceral peritoneum?
What is space in between called (fluid)? |
Covers organs within cavity (stomach, small intestines, large intestines)
|
Paritoneal space contains fluid
|
|
|
3 things exit the cloaca?
|
Liquid & solid waste, & gametes
|
|
|
|
What is diphyodont? What are the organisms that have it?
|
Have 2 sets of teeth.
|
Mammals have
|
|
|
What is polyphyodant? What are the organisms that have it?
|
Has many replacement sets of teeth.
|
All vertebrates w/ teeth except mammals.
|
|
|
What is homodont vs heterodont?
|
Homodont- teeth are same within same organism
|
Heterodont- teeth vary within organism
|
|
|
These 3 organism species have Homodont & polyphyodont?
|
Fish, Amphibians, & Reptiles
|
|
|
|
These 4 organism species have oral glands?
|
Terrestrial amphibians
reptiles, birds, & Mammals |
|
|
|
Birds have which kind of teeth?
|
Edentate- No teeth
|
|
|
|
Mammals have glands?
Mammals have the 3 types of teeth? |
Mammals have oral glands
|
Have heterodont, diphyodont, and monophyodont
|
|
|
What is function of small intestines?
What are 2 parts of small intestines in all vertebrates? In mammals? |
All digestion completed here in vertebrates.
Most absorption occurs here. 2 parts are duodenum and ileum |
In mammals, parts are
Duodenum Jejunum Ileum |
|
|
Large intestines AKA?
Function? |
Colon
Prepares excretory product for excretion |
Absorbs majority of water here.
|
|
|
What is shape and 3 parts of stomach of Man?
|
J-shaped
|
Top= cardiac region
Middle = Fundus Bottom= pyloris region |
|
|
Characteristics of tunica mucosa in stomach of man?
|
Is irregularly folded (like crumbled paper)= Rugae
|
Function of Rugae is for distention
|
|
|
Characteristics of tunica muscularis in man?
Function of middle layer? |
Most of tract is skeletal.
2 Layers= inner circular, middle oblique, and outer longitudinal |
Middle Oblique facilitates churning
|
|
|
Near pyloris at base of stomach is?
|
Pyloric Sphincter
|
|
|
|
What is duodenum?
|
C-shaped and most fixed part of small intestine
|
|
|
|
What is Jejunum?
|
Highly coiled
|
|
|
|
What is ileum?
|
Circular smooth muscle
End of ileum is ileosecal valve which controls passage of waste producte from small intestine. |
|
|
|
Characteristics of tunica mucosa in small intestines of man?
|
Fingerlike projections called villi stick out into lumen
|
|
|
|
What are the crypts of lieberkuhn?
|
Portion of villi that extends down into submucosa
|
|
|
|
What does it mean that intestines are plicae?
|
They are pleated or folded to increase surface area
|
|
|
|
Breaking of cecum is?
|
Appendix
|
|
|
|
3 ways to increase surface area in man's intestines?
|
Villi
Each cell at luminar surface has brushed border/ microvilli Mucosa is pleated |
|
|
|
3 Salivary glands of man?
|
Parotid, sublingual, and submandibular
|
|
|

LEFT COLUMN?
|
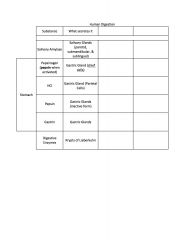
|
|
|

RIGHT COLUMNS?
|
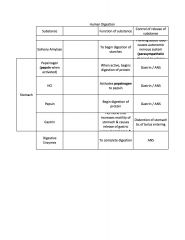
|
|

