![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
256 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Tissue |
Group of cells that work together to perform a specific function |
Define |
|
|
Epithelial tissue (e.t.) |
Covers, lines and forms glands |
Tissue are tightly packed |
|
|
Avascular |
Little or no blood supply |
Describes e.t. |
|
|
3 types of junctions associated with e.t. |
Tight junctions, anchoring, gap |
Describes e.t. |
|
|
Tight junctions |
Tightly fused together forming an impermeable barrier |
Skin |
|
|
Anchoring |
Seen where there is friction, which allows for stretching |
Under skin |
|
|
Anchoring |
Seen where there is friction, which allows for stretching |
Under skin |
|
|
Gap |
Only seen in an embryo cell connected by microscopic cylinders that allow impulses to pass |
Necessary because nervous system is not developed in embryo |
|
|
Simple squamous |
1 layer of flat cells |
Micro thin |
|
|
Simple squamous |
1 layer of flat cells |
Micro thin |
|
|
Simple squamous function |
Diffusion, osmosis, and filtration |
|
|
|
Simple squamous |
1 layer of flat cells |
Micro thin |
|
|
Simple squamous function |
Diffusion, osmosis, and filtration |
|
|
|
Simple squamous location |
Lungs, kidneys and blood capillaries |
Thin plastic wrap |
|
|
Endothelium |
Simple squamous tissue associated with circulatory system |
|
|
|
Endothelium |
Simple squamous tissue associated with circulatory system |
|
|
|
Simple cuboidal |
1layer cubed shape cells |
|
|
|
Endothelium |
Simple squamous tissue associated with circulatory system |
|
|
|
Simple cuboidal |
1layer cubed shape cells |
|
|
|
Simple cuboidal function |
Secretion and absorption |
|
|
|
Endothelium |
Simple squamous tissue associated with circulatory system |
|
|
|
Simple cuboidal |
1layer cubed shape cells |
|
|
|
Simple cuboidal function |
Secretion and absorption |
|
|
|
Simple columnar |
1 layer cylindrical cells |
|
|
|
Simple columnar location |
Digestive and respiratory systems |
|
|
|
Simple columnar respiratory |
Apical surface contains cilia and have goblet cells |
|
|
|
Simple columnar respiratory |
Apical surface contains cilia and have goblet cells |
|
|
|
Goblet cells |
Secrete mucus on surface of tissue |
|
|
|
Simple columnar respiratory |
Apical surface contains cilia and have goblet cells |
|
|
|
Goblet cells |
Secrete mucus on surface of tissue |
|
|
|
Simple columnar digestive |
Also have goblet cells, and villi |
|
|
|
Villi |
Microscopic finger like projections that increase surface area for absorption |
|
|
|
Stratified squamous |
Many layers where top layer is flat |
|
|
|
Stratified squamous keratinized |
Contains keratin which is a waterproofing protein |
Skin- resists friction |
|
|
Stratified squamous function |
Protection against mechanical injury |
|
|
|
Transitional ET |
Many layers that consistently change shape due to stretching |
Going back to original shape.ex: bladder |
|
|
Transitional ET |
Many layers that consistently change shape due to stretching |
Going back to original shape.ex: bladder |
|
|
Gland |
A group of cells that produce a product onto a surface into a duct or blood |
|
|
|
Transitional ET |
Many layers that consistently change shape due to stretching |
Going back to original shape.ex: bladder |
|
|
Gland |
A group of cells that produce a product onto a surface into a duct or blood |
|
|
|
Holocrine glands |
Produces a product in its cytoplasm then the cell dies and the product is released |
|
|
|
Merocrine glands |
Almost all exocrine glands are this type. They produce their product and release it to the outside |
Most exocrine glands are salivary glands |
|
|
Merocrine glands |
Almost all exocrine glands are this type. They produce their product and release it to the outside |
Most exocrine glands are salivary glands |
|
|
Apocrine glands |
Produces a product that builds up on top of the cell then that region pinches off and the cell repairs itself |
Mammary glands |
|
|
Membrane |
Combination of epithelial and connective tissue |
|
|
|
Membrane |
Combination of epithelial and connective tissue |
|
|
|
Mucus membrane |
Lines every body cavity that opens to the outside |
|
|
|
Cutaneous membrane |
The skin |
|
|
|
Cutaneous membrane |
The skin |
|
|
|
Synovial membrane |
Lines the cavity of all freely movable joints |
|
|
|
Serous membrane |
A double layer membrane with fluid between the two layers |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane associated with the digestive system |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane associated with the digestive system |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, binds, store far and plays role in immunity |
Girdle |
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane associated with the digestive system |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, binds, store far and plays role in immunity |
Girdle |
|
|
Two major types of connective tissue |
Embryonic and adult |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane associated with the digestive system |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, binds, store far and plays role in immunity |
Girdle |
|
|
Two major types of connective tissue |
Embryonic and adult |
|
|
|
Precursor to every adult CT |
Embryonic |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane associated with the digestive system |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, binds, store far and plays role in immunity |
Girdle |
|
|
Two major types of connective tissue |
Embryonic and adult |
|
|
|
Precursor to every adult CT |
Embryonic |
|
|
|
Mucous ( whartons jelly) |
Found in a fetus supports the umbilical cord |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane associated with the digestive system |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, binds, store far and plays role in immunity |
Girdle |
|
|
Two major types of connective tissue |
Embryonic and adult |
|
|
|
Precursor to every adult CT |
Embryonic |
|
|
|
Mucous ( whartons jelly) |
Found in a fetus supports the umbilical cord |
|
|
|
Matrix |
Space that separates the cells in connective tissue |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane associated with the digestive system |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, binds, store far and plays role in immunity |
Girdle |
|
|
Two major types of connective tissue |
Embryonic and adult |
|
|
|
Precursor to every adult CT |
Embryonic |
|
|
|
Mucous ( whartons jelly) |
Found in a fetus supports the umbilical cord |
|
|
|
Matrix |
Space that separates the cells in connective tissue |
|
|
|
Macrophage |
Developed from a wbc called a monocyte |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane associated with the digestive system |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, binds, store far and plays role in immunity |
Girdle |
|
|
Two major types of connective tissue |
Embryonic and adult |
|
|
|
Precursor to every adult CT |
Embryonic |
|
|
|
Mucous ( whartons jelly) |
Found in a fetus supports the umbilical cord |
|
|
|
Matrix |
Space that separates the cells in connective tissue |
|
|
|
Macrophage |
Developed from a wbc called a monocyte |
|
|
|
Monocyte |
The most active phagocyte in the body because it eats and destroys bacteria |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Fibroblast |
Most numerous CT cell that is formed in the matrix |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane associated with the digestive system |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, binds, store far and plays role in immunity |
Girdle |
|
|
Two major types of connective tissue |
Embryonic and adult |
|
|
|
Precursor to every adult CT |
Embryonic |
|
|
|
Mucous ( whartons jelly) |
Found in a fetus supports the umbilical cord |
|
|
|
Matrix |
Space that separates the cells in connective tissue |
|
|
|
Macrophage |
Developed from a wbc called a monocyte |
|
|
|
Monocyte |
The most active phagocyte in the body because it eats and destroys bacteria |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Fibroblast |
Most numerous CT cell that is formed in the matrix |
|
|
|
Plasma cells |
Makes antibodies that fight infection |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane associated with the digestive system |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, binds, store far and plays role in immunity |
Girdle |
|
|
Two major types of connective tissue |
Embryonic and adult |
|
|
|
Precursor to every adult CT |
Embryonic |
|
|
|
Mucous ( whartons jelly) |
Found in a fetus supports the umbilical cord |
|
|
|
Matrix |
Space that separates the cells in connective tissue |
|
|
|
Macrophage |
Developed from a wbc called a monocyte |
|
|
|
Monocyte |
The most active phagocyte in the body because it eats and destroys bacteria |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Fibroblast |
Most numerous CT cell that is formed in the matrix |
|
|
|
Plasma cells |
Makes antibodies that fight infection |
|
|
|
Adipocytes |
Produce and stores fat |
Fat cells |
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane associated with the digestive system |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, binds, store far and plays role in immunity |
Girdle |
|
|
Two major types of connective tissue |
Embryonic and adult |
|
|
|
Precursor to every adult CT |
Embryonic |
|
|
|
Mucous ( whartons jelly) |
Found in a fetus supports the umbilical cord |
|
|
|
Matrix |
Space that separates the cells in connective tissue |
|
|
|
Macrophage |
Developed from a wbc called a monocyte |
|
|
|
Monocyte |
The most active phagocyte in the body because it eats and destroys bacteria |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Fibroblast |
Most numerous CT cell that is formed in the matrix |
|
|
|
Plasma cells |
Makes antibodies that fight infection |
|
|
|
Adipocytes |
Produce and stores fat |
Fat cells |
|
|
Osteoblasts |
Build bone |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane associated with the digestive system |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, binds, store far and plays role in immunity |
Girdle |
|
|
Two major types of connective tissue |
Embryonic and adult |
|
|
|
Precursor to every adult CT |
Embryonic |
|
|
|
Mucous ( whartons jelly) |
Found in a fetus supports the umbilical cord |
|
|
|
Matrix |
Space that separates the cells in connective tissue |
|
|
|
Macrophage |
Developed from a wbc called a monocyte |
|
|
|
Monocyte |
The most active phagocyte in the body because it eats and destroys bacteria |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Fibroblast |
Most numerous CT cell that is formed in the matrix |
|
|
|
Plasma cells |
Makes antibodies that fight infection |
|
|
|
Adipocytes |
Produce and stores fat |
Fat cells |
|
|
Osteoblasts |
Build bone |
|
|
|
Osteoclasts |
Destroys bone |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane associated with the digestive system |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, binds, store far and plays role in immunity |
Girdle |
|
|
Two major types of connective tissue |
Embryonic and adult |
|
|
|
Precursor to every adult CT |
Embryonic |
|
|
|
Mucous ( whartons jelly) |
Found in a fetus supports the umbilical cord |
|
|
|
Matrix |
Space that separates the cells in connective tissue |
|
|
|
Macrophage |
Developed from a wbc called a monocyte |
|
|
|
Monocyte |
The most active phagocyte in the body because it eats and destroys bacteria |
|
|
|
Pleural |
Serous membrane associated with the lungs |
|
|
|
Fibroblast |
Most numerous CT cell that is formed in the matrix |
|
|
|
Plasma cells |
Makes antibodies that fight infection |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, binds, stores fat and plays role in immunity |
Girdle |
|
|
Osteoblasts |
Build bone |
|
|
|
Osteoclasts |
Destroys bone |
|
|
|
Osteocytes |
Mature bone cells |
|
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane associated with the heart |
|
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane associated with the digestive system |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports, binds, store far and plays role in immunity |
Girdle |
|
|
Two major types of connective tissue |
Embryonic and adult |
|
|
|
Precursor to every adult CT |
Embryonic |
|
|
|
Mucous ( whartons jelly) |
Found in a fetus supports the umbilical cord |
|
|
|
Matrix |
Space that separates the cells in connective tissue |
|
|
|
Macrophage |
Developed from a wbc called a monocyte |
|
|
|
Monocyte |
The most active phagocyte in the body because it eats and destroys bacteria |
|
|
|
Adipose function |
Stores energy |
|
|
|
Adipose function |
Stores energy |
|
|
|
Areolar |
Gives strength, support and elasticity |
|
|
|
Adipose function |
Stores energy |
|
|
|
Areolar |
Gives strength, support and elasticity |
|
|
|
Fibrocartilage composition, location, function |
Comp:Chondrocytes, elastic fibers and collagen fiber
Location: where pelvic bones join, knee joints, disks between vertebrae
Function: joins bones- fusion of bones |
Can degenerate |
|
|
Adipose function |
Stores energy |
|
|
|
Areolar |
Gives strength, support and elasticity |
|
|
|
Fibrocartilage composition, location, function |
Comp:Chondrocytes, elastic fibers and collagen fiber
Location: where pelvic bones join, knee joints, disks between vertebrae
Function: joins bones- fusion of bones |
Can degenerate |
|
|
Hyaline cartilage |
Attaches to the sternum, external nose, rings of the trachea, growth plates |
|
|
|
Adipose function |
Stores energy |
|
|
|
Areolar |
Gives strength, support and elasticity |
|
|
|
Fibrocartilage composition, location, function |
Comp:Chondrocytes, elastic fibers and collagen fiber
Location: where pelvic bones join, knee joints, disks between vertebrae
Function: joins bones- fusion of bones |
Can degenerate |
|
|
Hyaline cartilage |
Attaches to the sternum, external nose, rings of the trachea, growth plates |
|
|
|
Osseous ( bone) |
Gives support and shape |
|
|
|
Muscle tissue |
Contracts when stimulated |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle tissue |
Voluntary and striated |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle tissue |
Voluntary and striated |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle tissue |
Involuntary and striated also has intercalated disks (join cells) |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle tissue |
Voluntary and striated |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle tissue |
Involuntary and striated also has intercalated disks (join cells) |
|
|
|
Smooth muscle tissue |
Involuntary non-striated and found in blood vesicles and the gi tract |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle tissue |
Voluntary and striated |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle tissue |
Involuntary and striated also has intercalated disks (join cells) |
|
|
|
Smooth muscle tissue |
Involuntary non-striated and found in blood vesicles and the gi tract |
|
|
|
Nerve tissue |
Conducts impulses throughout the body |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle tissue |
Voluntary and striated |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle tissue |
Involuntary and striated also has intercalated disks (join cells) |
|
|
|
Smooth muscle tissue |
Involuntary non-striated and found in blood vesicles and the gi tract |
|
|
|
Nerve tissue |
Conducts impulses throughout the body |
|
|
|
Cell body |
Location of organelles |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle tissue |
Voluntary and striated |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle tissue |
Involuntary and striated also has intercalated disks (join cells) |
|
|
|
Smooth muscle tissue |
Involuntary non-striated and found in blood vesicles and the gi tract |
|
|
|
Nerve tissue |
Conducts impulses throughout the body |
|
|
|
Cell body |
Location of organelles |
|
|
|
Dendrite |
Carries pluses into the cell body |
|
|
|
Axon |
Carries impulses away from the cell body |
|
|
|
Osteons |
Structures found inside of bone |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Blood cells |
|
|
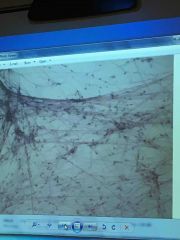
Front (Term) |
Areolar |
|
|
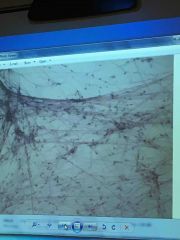
Front (Term) |
Areolar |
|
|
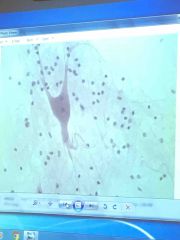
Front (Term) |
Nerve cell |
|
|
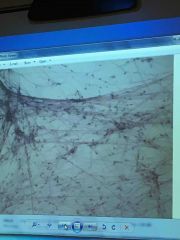
Front (Term) |
Areolar |
|
|
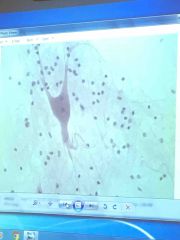
|
Nerve cell |
|
|
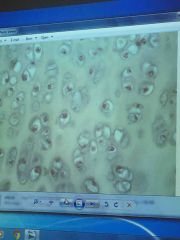
Front (Term) |
Hyaline cartilage |
|
|
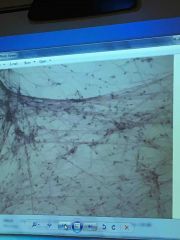
Front (Term) |
Areolar |
|
|
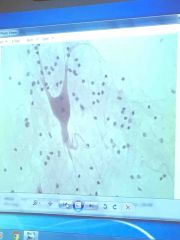
|
Nerve cell |
|
|
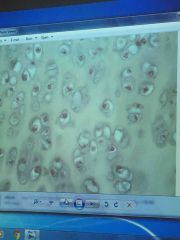
Front (Term) |
Hyaline cartilage |
|
|
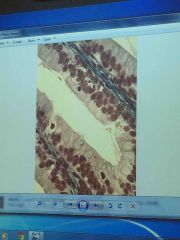
Front (Term) |
Goblet cell |
|
|
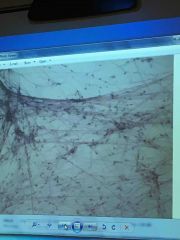
Front (Term) |
Areolar |
|
|
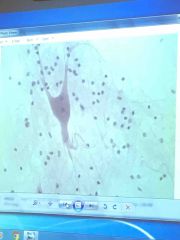
|
Nerve cell |
|
|
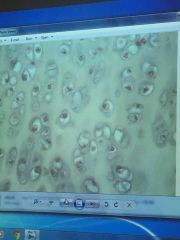
Front (Term) |
Hyaline cartilage |
|
|
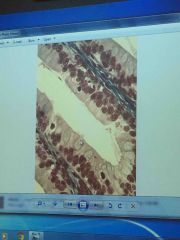
Front (Term) |
Goblet cell |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Adipose |
|
|
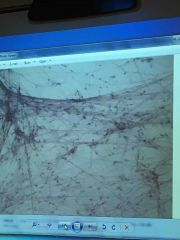
Front (Term) |
Areolar |
|
|
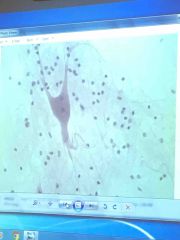
|
Nerve cell |
|
|
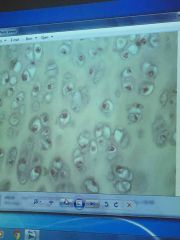
Front (Term) |
Hyaline cartilage |
|
|
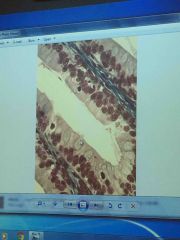
Front (Term) |
Goblet cell |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Adipose |
|
|
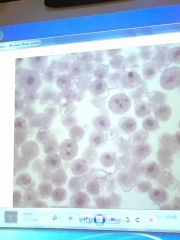
Front (Term) |
Mitosis |
|
|
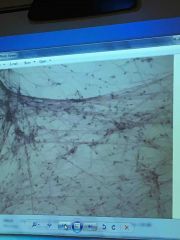
Front (Term) |
Areolar |
|
|
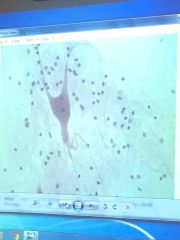
|
Nerve cell |
|
|
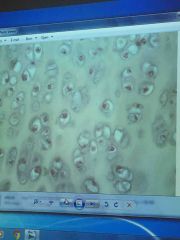
Front (Term) |
Hyaline cartilage |
|
|
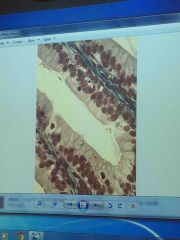
Front (Term) |
Goblet cell |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Adipose |
|
|
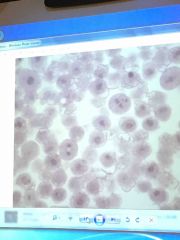
Front (Term) |
Mitosis |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Connective tissue |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Cilia |
Look at the mouse |

