![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Exercise 5: The Organization of Cells
-Lab Study C: Multicellular Organism (Purpose) |
-Characterize the organization of plants cells in a wet mount Elodea
-Characterize animal cell organization in human cells |
|
|
Exercise 5: The Organization of Cells
-Lab Study D: Unknowns (Purpose) |
-Characterize morphological and behavioral traits of unknown microbes in a sample pond water
|
|
|
Tissues
|
Group of specialized cells
|
|
|
Organ
|
Group of Tissue
|
|
|
Organ System
|
Group of Organ
|
|
|
Cell Wall
|
Rigid outer framework surrounding the cell. Gives cell a definite shape and support. (not found in animal cells)
|
|
|
Protoplasm
|
Organized contents of the cell, exclusive of the cell wall
|
|
|
Cytoplasm
|
The protoplasm of cell, exclusive of the cell wall
|
|
|
Central Vacuole
|
Membrane bound sac within the cytoplasm that is filled with water and dissolved substances.
-Structure serves to store metabolic wastes -Gives the cell support by means of turgor pressures -Plant and animal cells have them, but animal vacuoles are smaller |
|
|
Chloroplast
|
Green, spherical organelles often seen moving within cytoplasm.
-carry pigment chlorophyll -involved in photosythesis |
|
|
Elodea Canadensis
(Plant Cell) |
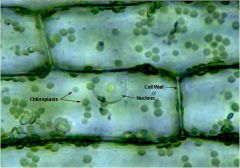
Other structures: cytoplasmic strands
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Streaming (Cyclosis)
|
As the microscope heats up the cells, cytoplasm and chloroplasts may begin to move around the central vacuole.
|
|
|
Nucleus
|
Usually spherical, transparent organelle within the cytoplasm
-Controls cell metabolism and division |
|
|
Epithelial Cells
|
Occur on the outside of animals and serve to protect the animals from
-water loss -mechanical injury -foreign invaders -line interior cavities and ducts in animals (similar to plant epidermal cells) |
|
|
Cell Membrane
|
Boundary that separates the cell from its surroundings (in animals cells they have cell membrane not cell wall)
|
|
|
Cheek Cells
|
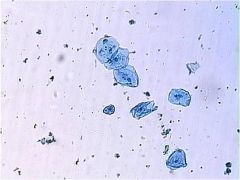
|
|
|
Prokaryotic Organization
|
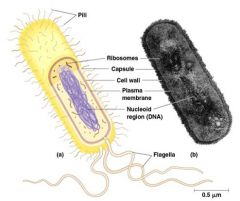
|
|
|
Eukaryotic Cell
|
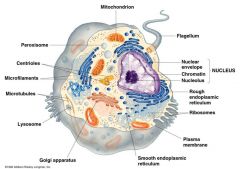
|
|
|
Aggregates
|
Clusters of cells
|
|
|
Colonies
|
Cluster composed of a consistent and predictable number of colonies
|
|
|
Autotrophic
|
photosynthetic
|
|
|
Hetereotrophic
|
Deriving food from other organism or their by-products
|
|
|
Ectoplasm
|
the thin, transparent layer of cytoplasm directly beneath the cell membrane
|
|
|
Endoplasm
|
the granular cytoplasm containing the cell organelles
|
|
|
Contractile vacuoles
|
clear, spherical vesicles of varying sizes that gradually enlarge as they fill with excess water. Once you've located a vacuole, watch it fill and then empty its contents into surrounding environment. These vacuoles serve an excretory function for the amoeba.[amoeba]
|
|
|
Food vacuoles
|
Small, dark, irregularly shaped vesicles within the endoplasm. They contain undigested food particles [amoeba]
|
|
|
Vacuoles
|
transparent spheres. In the Scenedesmus alga, it tends to occur at either end of the cell.
|
|
|
Spines
|
In the Scenedesmus alga, they are the transparent projections that occur on the two end cells
|
|
|
Scenedesmus
|
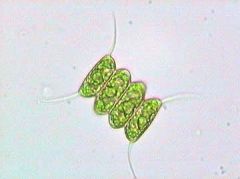
terrestrial green alga that grows on the north sides of trees
|
|
|
Volvox
|
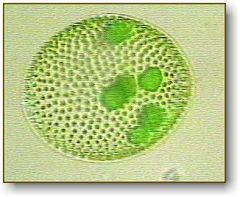
an aquatic green alga is common in aquaria, ponds and lakes
* form a large complex colony * cytoplasmic connections between cells |
|
|
Complex Colony
|
Approx. 500-50,000 cells that are permanently united, there are cytoplasmic connections between cells and some cells are specialized for reproduction.
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Strands
|
Connections between adjacent cells
|
|
|
Daughter colonies
|
Smaller spheres within the larger colony.
-Produced asexually -When large enough they will be discharged into surrounding environment. |

