![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In the amylase experiment, what was the substrate?
|
Starch
|
|
|
In the amylase experiment, what was the Benedict's test used for? Describe a positive result
|
To test for the presence of Glucose, indicating the starch had been digested/broken down into glucose. A color change to yellow/orange = positive for glucose.
|
|
|
In the amylase experiment, what was Lugol's solution (iodine) used for? Describe a positive result.
|
To test for the presence of starch. A blue/black color change indicated starch was still present, thus no digestion occurred.
|
|
|
What conditions reacted the most and fastest in the amylase experiment.
|
amylase at 37 degrees C
|
|
|
In the Pepsinogen experiment, what was the substrate?
|
egg white (protein)
|
|
|
In the pepsinogen/pepsin experiment, what indicated a positive test for protein digestion?
|
complete - egg white gone
partial - cloudy water, frayed edges of egg. |
|
|
What is necessary for pepsinogen to activate and digest the egg white
|
hydrochloric acid.
|
|
|
In the lipase experiment, what was the substrate?
|
butter fats/lipids
|
|
|
In the lipase experiment, what was the reagent?
|
litmus powder
|
|
|
Litmus powder turns ________ in acidic conditions and ____________ in basic conditions
|
red
blue/purple |
|
|
In the lipase experiment, what was necessary for the lipase to digest fully?
|
Bile salts
|
|
|
In the pig dissection, where would you find the thymus?
What does it do? |
extends down from the neck to the heart
important for a healthy immune system |
|
|
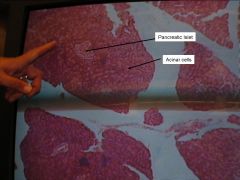
In the pig dissection, where would you find the pancreas?
What does it do? |
under the stomach
endocrine fxn - secretes insulin exocrine fxn - secretes lipase into small intestine. |
|
|
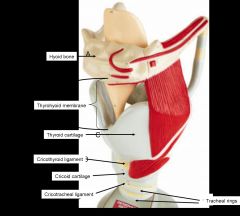
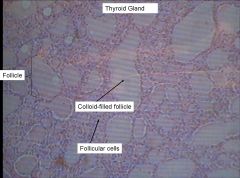
In the pig dissection, where would you find the thyroid?
what does it do? |
in the throat medially
Secretes thyroid hormone, which regulates metabolism |
|
|
what is inspiratory reserve volume? IRV
|
the amount of air you can forcibly inhale after normal inspiration
|
|
|
what is expiratory reserve volume? (ERV)
|
the amount of air you can forcibly exhale after normal expiration
|
|
|
what is tidal volume
|
the amount of air you normally inhale and exhale while resting
|
|
|
what is inspiratory capacity? IC
|
it is inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) + tidal volume
IRV + TV = IC |
|
|
what is residual volume? RV
|
the amount of air left in the lungs after forcibly exhaling as much air as possible
|
|
|
What is vital capacity?
|
Vital Capacity = inspiratory reserve volume + tidal volume + expiratory reserve volume.
|
|
|
What is total lung capacity?
|
Total lung capacity = inspiratory reserve volume + tidal volume + expiratory reserve volume + residual volume.
|
|
|
what is the formula for inspiratory reserve volume using vital capacity (VC), Tidal volume (TV) and Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
|
IRV = (VC-TV) - ERV
|
|
|
How to determine a person's minute respiratory volume?
|
TV x breaths/minute
|
|
|
what is the typical residual volume amount for
women? men? |
women = 900 mL
men = 1200 mL |
|
|
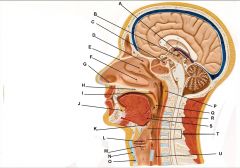
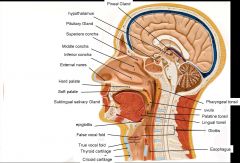
What does the hypothalamus synthesize?
|
oxytocin and ADH
|
|
|
on a lab slide what color is the posterior pituitary gland?
|
pink
|
|
|
on a lab slide, what color is the anterior pituitary gland?
|
purple (or darker pink)
|
|
|
what does the posterior pituitary gland do?
|
stores oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from the hypothalamus
|
|
|
what does the anterior pituitary gland do?
|
Called the "Master Endocrine Gland" - secretes growth hormone and Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
|
|
|
pineal gland function
|
secretes melatonin - regulates sleep cycles
|
|
|
general adrenal gland function
|
secretes over 2 dozen steroid hormones called corticosteroids which help deal with stress
|
|
|
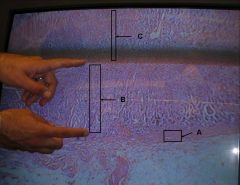
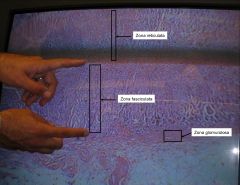
What does the zona glomerulosa secrete
|
mineralcorticoids
|
|
|
what does the zona fasciculata secrete
|
glucocorticoids
|
|
|
what does the zona reticularis secrete?
|
sex steroids
|
|
|
what does the thyroid gland do?
|
secretes thyroid hormone (TH) which regulates metabolism
|
|
|
what does the parathyroid gland do?
|
secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH), which regulates calcium balance in the blood
|
|
|
what does the thymus do?
|
instrumental in immune response) - secretes peptide hormones which are necessary for the normal development of T lymphocytes
|
|
|
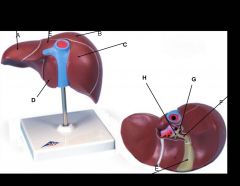
what is the most important function of the spleen?
|
Cleanses the blood - extracts aged and defective blood cells and platelets from the blood, and it macrophages remove debris and foreign matter from blood.
|
|
|
what is the lymphatic function of the thymus?
|
It's where T lymphocytes mature.
|
|
|
what do tonsils do?
|
gather and remove many pathogens entering the pharynx in food or in inhaled air.
|
|
|
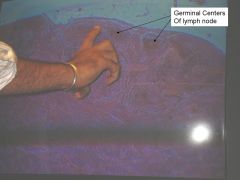
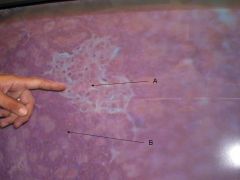
what do lymph nodes do?
|
Help activate the immune system - contain lymphocytes.
filter the lymph - macrophases in the nodes remove and destroy mircroorganisms and debris that enter the lymph from the loose connective tissues, preventing them from being deliever to the blood |
|
|
what does the appendix do?
|
contains lymphoid follicles which destroy bacteria and also generates memory lymphocytes for long-term immunity
|
|
|
what blood type is the universal donor? Why?
|
O negative
B/C O blood contains neither type A nor type B surface antigens, nor does it contain Rh surface antigens |
|
|
what blood type is the universal recipient?
|
AB positive blood does not contain any antibodies to A, B, or Rh negative.
|
|
|
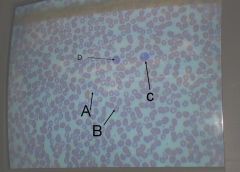
what is hematocrit?
what's normal |
The percent of RBC's in whole blood (not the number of RBC's)
45 - 50 % |
|
|
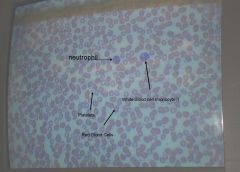
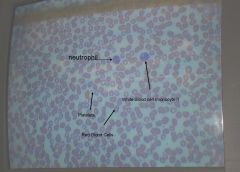
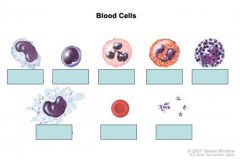
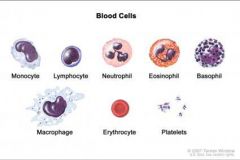
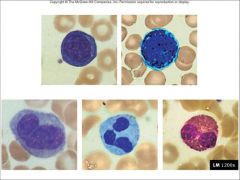
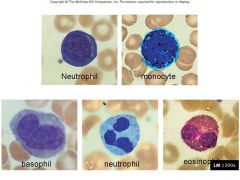
in what order of commonality are the different white blood cells (leukocytes) found?
|
neutrophils
lymphocytes monocytes eosinophils basophils |
|
|
what is the general fxn of
neutrophils? |
phagocytic - eat foreign pathogens
|
|
|
what is the general fxn of lymphocytes?
|
immunity - recognizes and then attacks and destroys foreign bodies
|
|
|
what is the general fxn of monocytes?
|
become macrophages which are large phagocytic cells that eat foreign pathogens
|
|
|
what is the general fxn of eosinophils?
|
reduce inflammation
|
|
|
what is the general fxn of basophils?
|
increase inflammation - release histamine.
|
|
|
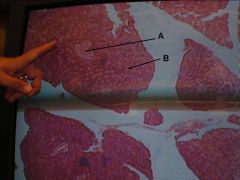
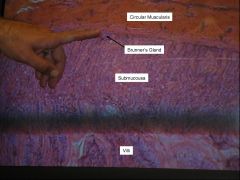
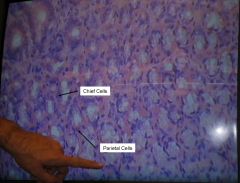
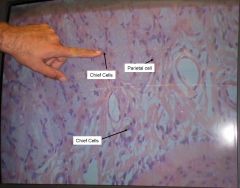
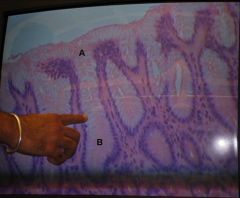
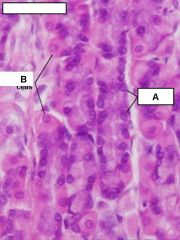
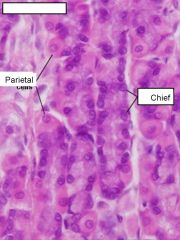
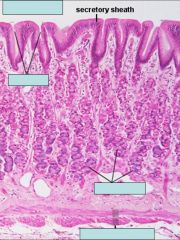
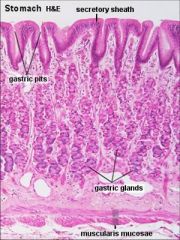
what do chief cells secrete?
|
Pepsinogen
|
|
|
what do parietal cells secrete?
|
hydrochloric acid
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
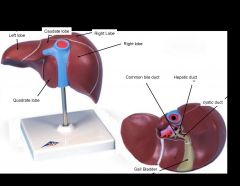
|
|
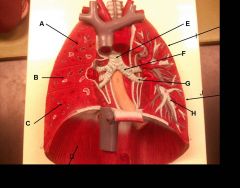
|
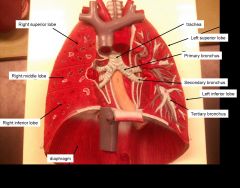
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
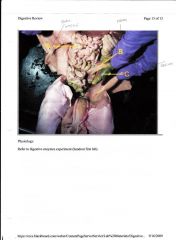
|
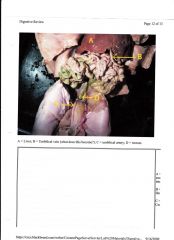
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
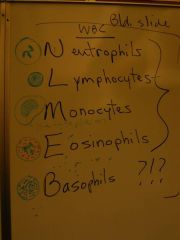
|
|
|
|

