![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
sarcolemma |
plasma membrane of muscle cell |
|
|
transverse tubules (t-tubules) |
invaginations of the sarcolemma which form tunnels filled with interstitial fluid |
|
|
sarcoplasma |
cytoplasm of the muscle fiber |
|
|
myofibrils |
contractile organelles of skeletal muscle which extend the length of the muscle fiber |
|
|
sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) |
surrounds eahc myofibril: stores Ca+2 for eventual use in muscle contraction |
|
|
terminal cisterns |
part of SR next to T-tubules; 1 transverse tubule + 2 surrounding terminal cisterns = triad |
|
|
Actin |
thin filaments - contains binding sites for myosin |
|
|
myosin |
thick filaments - contains ATP binding site on head |
|
|
skeletal muscle |
striated, voluntary, all over |
|
|
cardiac muscle |
striated, involuntary, heart |
|
|
smooth muscle |
not striated. involuntary. blood vessels, airways, organs |
|
|
Isotonic |
(iso= equal, tonic=tone) contraction occurs when the tension in muscle remains nearly constant while the length of the muscle changes |
|
|
concentric |
contraction in which muscle shortens as it produces constant tension and overcomes the load it is moving. Ex: picking up a book |
|
|
eccentric |
contraction in which muscle lengthens as it produces constant tension and gives into the load it is moving. Ex: putting book back down on table |
|
|
isometric |
(iso= equal, metric= length) contraction occurs when the tension generated does not exceed resistance of object and muscle remains the same length. Ex: holding book steady with outstretched arm. Energy is expended, but no movement occurs. |
|
|
structural classification of joints |
fibrous joints, cartilaginous joints, synovial joints |
|
|
fibrous joints |
no synovial cavity, bones held together by dense irregular CT. Permit little/no movement due to dense irregular CT. 3 Types: Sutures, Syndesmoses, Interosseous membranes. |
|
|
sutures |
only occur between bones of the skull. Slightly moveable (AMPHIARTHOTIC) in infants and children, but immovable (SYNARTHOTIC) in adults. |
|
|
Interosseaus Membranes |
binds long bones and permits slight movement (AMPHIARTHOTIC). Found between radius and ulna as well as tibia and fibula. |
|
|
cartilaginous joints |
no synovial cavity, bones held together by cartilage. lacks synovial cavity like fibrous joints, but consists of cartilage instead of CT. 2 types: Synchondroses and symphyses |
|
|
symphyses |
Articulating ends covered w/hyaline cartilage, but it is fibrocartilage that actually connects the bones. Slightly movable. Ex: pubic symphysis, manubrium & body of sternum, intervertebral joints between vertebral bodies, annulus fibrosus of IVD |
|
|
synovial joints |
synovial cavity present, bones connected by dense irregular CT. Freely movable. Consists of: synovial cavity, articular capsule, synovial fluid, articulating bones (hyaline cartilage). |
|
|
articular capsule |
encloses synovial cavity. Outer fibrous membrane (dense CT, mostly collagen). Inner synovial membrane (areolar CT w/elastic fibers |
|
|
ligaments |
dense regular CT holding bones together |
|
|
functional classification of joints |
synarthrosis, amphiarthrosis, diarthrosis |
|
|
synarthrosis |
immovable joint |
|
|
amphiarthrosis |
slightly moveable |
|
|
diarthrosis |
freely movable |
|
|
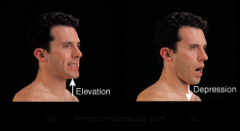
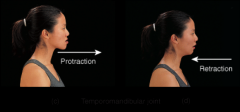
Temporomandibular joint |
Combined hinge & planar joint. Formed by condylar process of mandible and mandibular fossa of temporal bone. Meniscus present (fibrocartilaginous). |
|
|
TMJ disorder |
pain and inflammation of the temporomandibular joint. Potential causes- injury, arthritis, bruxism (grinding teeth). |
|
|
Shoulder Joint |
Ball & socket joint. Formed by head of humerus and glenoid cavity of scapula. Glenoid labrum- fibrocartilage around edge of glenoid cavity. 4 bursae present. |
|
|
Shoulder injuries |
rotator cuff injury, dislocation, Torn glenoid labrum |
|
|
Rotator cuff injury |
strain or tear in rotator cuff muscles (shoulder) |
|
|
Dislocation |
most common is inferior displacement of humeral head |
|
|
Torn glenoid labrum |
can lead to dislocation, common in pitchers and weight lifters |
|
|
Elbow Joint |
Hinge joint. Formed by trochlea & capitulum of humerus, trochlear notch of ulna, and head of radius. |
|
|
Elbow injury |
Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis). Golfers elbow (medial epicondylitis. |
|
|
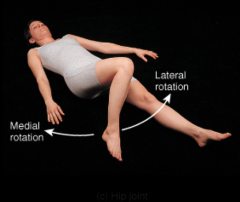
Hip Joint |
ball-and-socket joint. Formed by head of femur and acetabulum of coxal (hip) bone. |
|
|
Knee Joint |
Hinge joint. Consists of 3 joints: Tibiofemoral (laterally). Tibiofemoral (medially). Patellofemoral. 2 menisci (medial & lateral). 3 bursae |
|
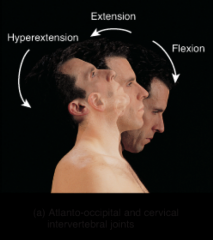
|
atlanto-occipital and cervical intervertebral joints |
|
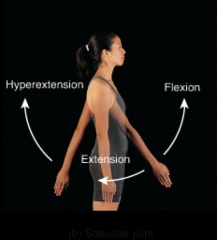
|
shoulder joint |
|
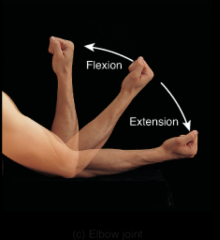
|
elbow joint |
|
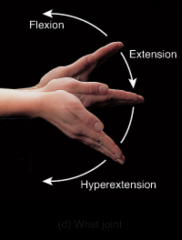
|
wrist joint |
|
|
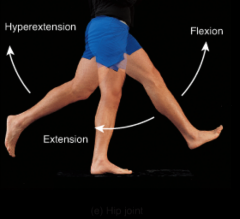
hip joint |
|
|
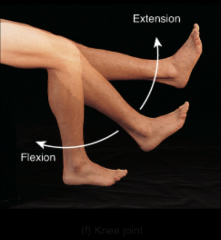
knee joint |
|
|
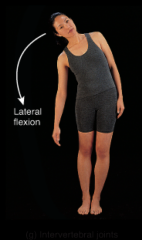
intervertebral joint |
|
|
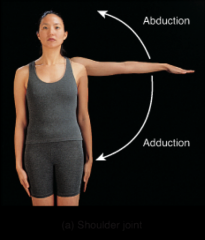
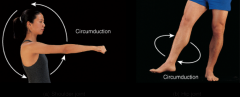
shoulder joint |
|
|
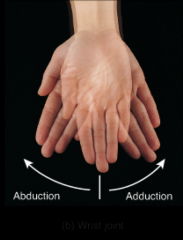
wrist joint |
|
|
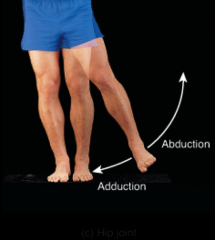
hip joint |
|
|
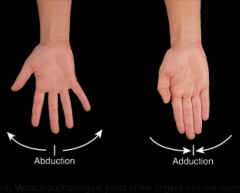
metacarpophalangeal joints of the fingers (not the thumb) |
|
|
shoulder joint. hip joint. |
|

|
atlanto-axial joint. shoulder joint. |
|
|
hip joint |
|
|
temporomandibular joint |
|
|
temporomandibular joint |
|
|
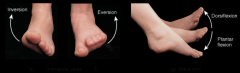
intertarsal joint. ankle joint. |
|
|
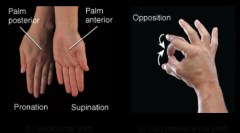
radioulnar joint. carpometacarpal joint |

