![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Light |
- type of electromagnetic radiation - occurs in energy packs called photons |
|
|
|
Visible light has wavelengths of |
380 nm - 750 nm |
Violet to red |
|
|
Photosynthesis |
The process by which green plants and some other organisms use solar energy, carbon dioxide, and water to produce carbohydrates |
|
|
|
Chlorophyll |
The light absorbing green coloured pigment that begins the process of photosynthesis |
|
|
|
Which pigment is the primary light absorbing pigment? |
Chlorophyll a |
|
|
|
Which colours of light do chlorophyll a and b absorb? |
Blue-violet and red |
|
|
|
Which pigment transfers energy from sunlight to the reactions of photosynthesis? |
Chlorophyll a |
|
|
|
What do chlorophyll b and the carotenoids do? |
They absorb the photons the chlorophyll absorbs poorly or not at all. |
|
|
|
Chloroplast |
A membrane bound organelle in green plant and algal cells that carries out photosynthesis. |
|
|
|
Stroma |
The protein rich semiliquid material in the interior of a chloroplast. |
|
|
|
Thylakoid |
A system of interconnected flattened membrane sacs forming a separate compartment within the stroma of a chloroplast. |
|
|
|
Grana |
Stacks of thylakoids |
Singular: granum |
|
|
Lamellae |
Groups of unstacked thylakoids between grana |
Singular: lamella |
|
|
Thylakoid membrane |
The photosynthetic membrane within a chloroplast that contains light-gathering pigment molecules and electron transport chains |
|
|
|
Thylakoid lumen |
The fluid filled space inside a thylakoid |
|
|
|
What must a plant cell have/have access to in order to undergo photosynthesis? |
Chlorophyll, carbon dioxide, oxygen, and solar energy |
|
|
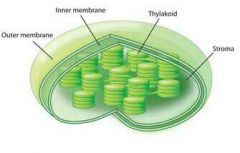
What am I? |
Chloroplast |
|
|
|
ATP |
A molecule containing three high-energy phosphate bonds that acts as the primary energy-transferring molecule in living organisms |
|
|
|
ADP |
A molecule containing two high-energy phosphate bonds that may be formed by breaking one of the bonds in ATP |
|
|
|
NADP+ |
A compound that accepts one hydrogen atom and two electrons, forming NADPH; is an electron acceptor |
|
|
|
NADPH |
A compound that donates one hydrogen atom and two electrons to another molecule, to reform NADP+; is an electron donor |
|
|
|
Oxidation |
Loses electron |
LEO |
|
|
Reduction |
Gains electron |
GER |
|
|
Glucose |
- transport molecule - medium term energy storage in most cells |
|
|
|
ATP (function) |
Provides immediate energy for cellular functions |
|
|
|
Light dependant reactions |
The first set of reactions of photosynthesis in which light energy excites electrons in chlorophyll molecules, powers chemiosmotic ATP synthesis, and results in the reduction of NADP+ to NADPH |
|
|
|
Carbon fixation |
The process of incorporating CO2 into carbon molecules |
|
|
|
Calvin cycle |
A cyclic set of reactions occurring in the stroma of chloroplasts that fixes the carbon of CO2 into carbohydrate molecules and recycles coenzymes |
|
|
|
Light-dependant reactions |
The second set of reactions in photosynthesis (the Calvin cycle); these reactions do not require solar energy. |
|
|
|
Photosynthesis - stage 1 |
Capturing solar energy and transferring it to electrons |
Light dependant |
|
|
Photosynthesis - stage 2 |
Using captured solar energy to make ATP and to transfer high-energy electrons to NADP+; yields NADPH, which is then used as a high energy electron carrier molecule |
Light dependant |
|
|
Photosynthesis - stage 3 |
Using energy stored in ATP and high-energy electrons carried by NADPH to form energy-rich organic molecules, such as glucose, from CO2 |
Light independant |
|
|
Photosystem |
A cluster of photosynthetic pigments embedded in a thylakoid membrane of a chloroplast that absorbs light energy |
|
|
|
Electron transport chain |
A series of progressively stronger electron acceptors; each time an electron is transferred, energy is released |
|
|
|
Photolysis |
A chemical reaction in which a compound is broken down by light; in photosynthesis, water molecules are split by photolysis |
|
|
|
ATP synthase complex |
A specialized protein complex embedded in the thylakoid membrane that allows H+ ions to escape from the lumen and uses the resulting energy to generate ATP |
|
|
|
Chemiosmosis |
A process for synthesizing ATP using the energy of an electrochemical gradient and the ATP synthase enzyme |
|
|
|
NADH |
An electron carrier, donates electrons in cellular processes |
|
|
|
NAD+ |
An electron carrier, accepts electrons in cellular processes |
|
|
|
FADH2 |
An electron carrier, donates electrons in cellular processes |
F |
|
|
FAD+ |
An electron carrier, accepts electrons in cellular processes |
F |
|
|
Equation for photosynthesis |
CO2 + H2O + energy = C6H12O6 + O2 |
|
|
|
Equation for cellular respiration |
C6H12O6 + O2 = CO2 + H2O + energy |
|
|
|
Active transport |
The movement of substances through a membrane against a concentration gradient using membrane-bound carrier proteins and energy from ATP |
|
|
|
Sodioum-potassium pymp |
An active-transport mechanism that pumps sodium and potassium ions into and it of a cell |
|
|
|
Aerobic cellular respiration |
The set of reactions that takes place in the cell in the presence of oxygen and releases energy stored in glucose |
|
|
|
Anaerobic cellular respiration |
The set of reactions that takes place in the cell in the absence of oxygen and releases energy stored in glucose |
|
|
|
Stages of aerobic respiration |
Stage 1: glycolysis Stage 2: pyruvate oxidation Stage 3: the Krebs cycle Stage 4: the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis |
|
|
|
Stages of anaerobic respiration |
Stage 1: glycolysis Stage 2: fermentation |
|
|
|
Glycolysis |
A process for harnessing energy in which a molecule is broken into two pyruvate molecules in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
|
|
|
Mitochondrion |
A eukaryotic cell organelle in which aerobic cellular respiration occurs |
|
|
|
Mitochondrial matrix |
The fluid that fills the interior space of the mitochondrion |
|
|
|
Intermembrane space |
The fluid filled space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes |
|
|
|
Krebs cycle |
A cyclic series of reactions that transfers energy from organic molecules to ATP, NADH, and FADH2, and removes carbon atoms as C02 |
|
|
|
Alcohol fermentation |
A form of fermentation occurring in yeast in which NADH passes its hydrogen atoms to acetaldehyde, generating carbon dioxide, ethonal, and NAD+ |
|
|
|
Lactic acid fermentation |
A form of fermentation occurring in animal cells in which NADH transfers its hydrogen atoms to pyruvate, regenerating NAD+ and lactic acid |
|

