![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Protostomes determinate spiral cleavage blastopore forms mouth list 3 examples |
Mollusca Arthropoda |
|
|
Deuterostomes
indeterminate radial cleavage blastopore forms anus list 2 examples |
Echinodermata
Chordata |
|
|
Phylum Echinodermata
10,000 species deuterostomes have tube feet water vascular system open circulatory system dermal gills: absorb oxygen through skin |
Phylum Echiodermata
Classes: -Asteriodea (starfish/seastars) Asterias -Ophiuroidea (brittle stars) Gorgonocephalus -Echinoidea (sea urchins/sand dollars) Mellita -Holothuroidea (sea cucumbers/sea slugs) Cucumaria |
|
|
Class Asteriodea Genus Asterias starfish / sea stars thick arms, tube feet with suckers Pedicellaria remove algae from their skin |
Class Ophiuroidea Genus Gorgonocephalus brittle stars long thin arms no suckers on tube feet filter feeders mouth but no anus regeneration have mutualistic bacteria protects them from infection |
|
|
Class Echinoidea Genus Mellita (sand dollar) sea urchins and sand dollars no arms Aristotles lantern: sand dollar jaw area sea urchins: longest lived animals (200yrs) and share 7000genes w humans |
Class Holothuroidea Genus: Cucumaria (sea cucumber) no arms/spine tubular body (5 rows of tube ft) cuvier sticky feet protection eviscerate themselves respiratory tree near anus |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
50,000 species coelomate deuterostomes List 4 characteristics |
1. notochord: long flexible rod bw the digestive system and nerve cord (in vertebrates this is replaced by vertebrae)
2. dorsal nerve cord: spinal cord and brain 3. pharyngeal gill slits: in embryo 4. tail that extends beyond anus: at least in embryo |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Subphylums: -Cephalochordata (Brachiostoma) -Urochordata (Molgula / Trididemnin) -Vertebrata (classes: Agnatha, Chondrichthyes, Osteichthyes, Amphibia, Anura) |
Phylum Chordata
Subphylum Cephalochordata Genus Brachiostoma Evolved 500million yrs ago Invertebrates common name: lancelets no head or brain thin, fish like filter feeders cilia and gill slits to move water burrow tail first |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Subphylum Urochordata Genus Molgula / Trididemnin Invertebrates common name: Tunicate / sea squirt filter feeders outer layer (tunic) made from carbohydrate tunicin poisonous hermaphrodite simple heart pumps in both direction trididemnin is the source of anticancer drug Didemnin |
Phylum Chordata
Subphylum Vertebrata Classes: Agnatha, Chondrichthyes, Osteichthyes, Amphibia, Anura oldest fossil vertebrate (500 million yrs old) 50,000 species cephalization (strong head) cranium closed circulatory system dioecious |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Subphylum Vertebrata Class: Agnatha (jawless fish) cartilage skeleton no fins, long and eel like body, no jaw fill ouches empty through pores (instead of slits) Genus: Petromyzon (marine lamprey) Genus: Myxine (hagfish) feed on dead or decaying fish. located by smell, produces slime to deter predators. |
Phylum Chordata
Subphylum Vertebrata Class: Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) have jaw and skeleton of cartilage Sharks and rays -paired fins for swimming -oily liver gives them buoyancy -hard skin with placoid (backwards) scales -good sense organs: eyes, chemoreceptors, lateral line (detects water currents), can detect electrical field from buried prey -internal fertilization Genus: Torpedo (ray) |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Subphylum Vertebrata Class: Osteichthyes (bony fish) 30,000 species {largest class of vertebrates} hard bones can move gill so they can breath while stationary color vision swim bladder: buoyancy external fertilization used for biomonitoring (detect toxins in water) Genus: Bothus (flounder) |
Phylum Chordata
Subphylum Vertebrata Class: Osteichthyes (bony fish) 3 types of scales: Ganoid: thick, not overlapping Cycloid: thin, overlapping Ctenoid: thin, overlapping with teeth to reduce drag |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Subphylum Vertebrata Class: Amphibia "two lives" tadpole then adult external fertilization first land vertebrates: fossils date back 350million yrs tetrapod: 4 legs gas exchange through skin and lungs skin produces: magainins (antibiotics), fungicides, and toxins Order: Anura (Frogs and toads) |
Phylum Chordata
Subphylum Vertebrata Class: Amphibia Order: Anura (frogs and toads) 4 toes on front feet 5 on hind feet Poison arrow (Dendrobates) brightly colored warning of toxicity. Pipa: Pprotect eggs under skin of females back Rhinoderma: males protect young in their vocal sacs declining due to: habitat loss, predators, fungal infection |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Class Reptilia lay eggs on land internal fertiliztion dry skin hardened w keratin (protein) 3 chambered heart (crocodilians have 4) lungs use negative pressure good sense organs: eyes , ears (detect vibrations) smell (Jacobsons organs in snakes) pit vipers detect infrared (heat) |
Phylum Chordata
Class Reptilia skulls: Anapsid (no temporal openings) turtles Diapsid (two temporal openings) snakes |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Class Reptilia turtles are endangered due to over harvesting lizards due to increasing temperatures |
Phylum Chordata
Class Reptilia Orders: Squamata (snakes) Crocodilia (crocodiles and alligators) |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Class Reptilia Order: Squamata (snakes) less than 15% are venomous streamlined body sea snakes / boas are viviparous (give birth to live young) |
Phylum Chordata
Class Reptilia Order: Crocodilia (crocodiles and alligators) 4 chambered heart most acidic stomach of any animal Integumentary sense organs (ISO): detect pressure in water Palatal valve: keeps water out of lungs when submerged communicate using sound |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Class Aves (birds) Evolved from reptiles 150million years ago internal fertilization diapsid skull ( 2 temporal openings) feathers for flying and insulation light weight: hollow bones, no teeth, reduced # of organs (one ovary) 4 chambered heart endothermic (warm blooded) |
Phylum Chordata
Class Mammalia Subclasses: -Prototheria (monotremes) -Metatheria (marsupials) -Eutheria (placental mammals) {5 orders of placental mammals} |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Class Mammalia evolved 200 million yrs ago endothermic synapsid skull (one temporal opening) internal fertilization |
Phylum Chordata
Class Mammalia Subclass Prototheria (monotremes) lay eggs feed young milk but have no mammary gland or breast found in New Guinea and Australia ex: Platypus |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Class Mammalia Subclass Metatheria (marsupials) give birth to underdeveloped young and raise them in a pouch (marsupium) Genus Thylacine: evolved in southern hemisphere (Australia and S. America) but have spread to N. America (Genus: Didelphis [possum]) |
Phylum Chordata
Class Mammalia Subclass Eutheria (placental mammals) {5 orders of placental mammals} Orders: Carnivora Cetacea Chiroptera Sirenia Primates |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Class Mammalia Subclass Eutheria (placental mammals) Order Carnivora carnivores bears, cars, dogs, wolves Genus Canis |
Phylum Chordata
Class Mammalia Subclass Eutheria (placental mammals) Order Cetacea whales, dolphins Right Whales breed new Jacksonville whales are either toothed or baleen (filter feed) Genus Megaptera (humpback whale) |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Class Mammalia Subclass Eutheria (placental mammals) Order Chiroptera (bats) feed on insects and fruit echolocation Genus Lasiurus (seminole) |
Phylum Chordata
Class Mammalia Subclass Eutheria (placental mammals) Order Sirenia slow moving aquatic herbivores Genus Trichechus (manatee) |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
Class Mammalia Subclass Eutheria (placental mammals) Order Primates monkeys, apes, humans oldest fossils about 60 million yrs ago binocular vision: is vision in which creatures having two eyes use them together opposable thumb: A thumb that can be placed opposite the fingers of the same hand. large brain one birth at a time |
-Prosimians (oldest primates) (includes lemurs)
-American monkeys separated from African monkeys 40 million yrs ago -Humans, chimps and gorillas separated 6 million yrs ago |
|
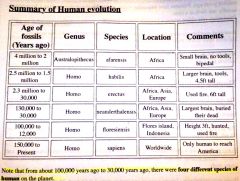
|
humans
|
|
|
cloaca
|
in vertebrates, common chamber and outlet into which the intestinal, urinary, and genital tracts open. It is present in amphibians, reptiles, birds, elasmobranch fishes (such as sharks), and monotremes. A cloaca is not present in placental mammals or in most bony fishes.
|
|
|
how do echinoderms get oxygen?
|
through dermal cells
|
|
|
how old are the oldest fossil primates?
|
60 million years
|
|
|
What sense organs do crocodilians have to detect the waves of pressure caused by swimming fish?
|
ISO
Integumentary sense organs |
|
|
Starfish have ___ symmetry, usually in ____parts
|
Starfish have radial symmetry, usually in 5 parts
|
|
|
give a genus name of cephalochordata
|
Brachiostoma (lancelets)
|
|
|
What is the name for the class of cartilaginous fish, such as sharks and rays?
|
Chrondrichtyes
|
|
|
The largest class of vertebrate is ___ with ____ species
|
The largest class of vertebrate is bony fish with 30,000 species
|
|
|
name 4 characteristics of chordates
|
1. notocord
2. dorsal nerve cord 3. pharyngeal gill slits 4. talk extends beyond anus |
|
|
Gill pouches that empty through pours, not slits, are typical of___.
|
Agnatha
|
|
|
Name a genus of a marsupial mammal.
|
Didelphis
|
|
|
pedicellaria are found in ___.
|
echinoderms
|
|
|
The genus Trichechus is in the order ____ and subclass _____
|
Order Sirenia
Subclass Eutheria |
|
|
What subclass of mammal lays eggs?
|
prototheria
|
|
|
What two areas of the world would you expect to find native marsupials?
|
S. America and Australia
|
|
|
Three types of scales
|
3 types of scales:
1. Ganoid: thick, not overlapping 2. Cycloid: thin, overlapping 3. Ctenoid: thin, overlapping with teeth to reduce drag |
|
|
Which human was the first to use fire?
|
Homo erectus
|
|
|
2 types of skulls
|
Anapsid: no temporal openings
Diapsid: 2 temporal openings |
|
|
birds and cartilaginous fish have what kind of fertilization?
|
internal
|
|
|
Whish anti cancer drug is extracted from tunicates?
|
Didemnin
|
|
|
The hagfish is in the class ___ and the genus ___.
|
class Agnatha
genus Myxine |
|
|
true or false:
Swim bladders of bony fish evolved from the lungs in early fish. |
true
|
|
|
The fishing in the Great Lakes was devastated by
|
lampreys
|
|
|
In what genus of frog, do the makes protect the young?
|
Rhinoderma
|

