![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1)Domain Of Plant
2)Kingdom of Plant |
1) Eukarya
2) Plantae |
|
|
Five Characteristics of Kingdom Plantae
|
1)cell walls
2)cellulose 3)Chloroplasts with photosyn. pigments Ex. Chlorophyll A, Betacarotenoid 4)Food reserve(starch) 5)Autotrophic |
|
|
Chara
(Charophycean algae) |
-algal ancestors of land plants
-the closest relatives of land plants |
|
|
Similarities between Charophycean and green plants
|
1)composition of the cell walls
2)Ultrastructure of sperm is similar(flagellated) 3)Genitic similarities ( DNA&RNA) |
|
|
Problems on the land (1)
|
-loss of water thru leaves
(Gamete or Embryo drying out) Called " Dehydration " or " Dessication" -Solved by waxy cuticles on leaf's surface (to prevent dehydartion) |
|
|
Problems on the land (2)
|
-Gamete drying out
-Solve by developing "Gametangia" to keep gamete moist and protected |
|
|
Gametangia
|
-structures that contain gametes and keep them moist
-There are two types of Gmaetangia: 1)Antheridia(produce sperms) *Flagellated sperms 2)Archegonia (produce eggs) |
|
|
Problems on land(3)
|
-Embryo drying out
-Solve by Plant embryos developed from zygote that are retained within tissues of parent plants to keep embryo from drying out and protect embryos(*Embryo develop within maternal tissue of plants) |
|
|
Another name for land plants
|
" Embryophytes"
|
|
|
Sporophyte
|
-Multicellular Diploid (2n)
then meiosis to become haploid spores |
|
|
Gametophyte
|
-Multicellular Haploid (n)
Then mitosis to become gamete(n) |
|
|
Motility of Gametes
|
Bryophytes(nonvascular plant)
- all sperms are flagellated Cycadophyta -primitive gymnosperms -*primitive flagellated sperm |
|
|
Bryophytes
(nonvascular plants) |
-Gametophyte is dominant
|
|
|
Vascular plants
|
-Sporophyte is dominant
|
|
|
NonVascular plants
|
Known as "Bryophytes"
-gametophyte(n) is dominant -No xylem or Phloem -Ex.liverworts(Phylum Hepatophyta,Genus Marchantia) -Ex.Hornworts (Phylum Anthocerophyta) -Ex.Mosses(Phylum Bryophyta ,genus Polytrichum) Other phylums are vascular |
|
|
vascular plants
|
Plant that have two types of tube:Xylem and Phloem
-Sporophyte(n) is dominant -Seedless Vascular plant ->Use spores because it has no seed |
|
|
Xylem
|
conduct water and minerals
-down the plants |
|
|
Phloem
|
conduct food or sugar
-in Up direction |
|
|
Gametes
|
are cell that requires other gametes to fuse and form individuals
|
|
|
Spores
|
are *unicellular reproductive cell that doesn't have to fuse with other cells to form individuals
|
|
|
Bryophyta
|
mosses
**Genus Polytrichum -nonvascular plant -Gametophyte is dominant |
|
|
Protonema***
|
-immature gametophyte(n)
of mosses, look alike algae |
|
|
Peristome teeth
|
This structure is in Mosses and genus " Polytrichum "***
|
|
|
Operculum*
|
-Look like a lid
-locate on top of sporangium or capsule -pop off to let spores come out |
|
|
Phylum Hepatophyta
|
-Liverwort
Genus-> Marchantia*** -remember Antheridiophore* Archegoniophore* |
|
|
Antheridiophore*
|
*(look like mushroom) has Antheridia that make sperms(flaggellated)
- in life cycle of liverwort(Marchantia*) Phylum Hepatophyta |
|
|
Archegoniophore*
|
*(look like palm tree) has Archegonia that make eggs
- in life cycle of liverwort(Marchantia*) Phylum Hepatophyta |
|
|
Gemmae cups
|
containing Gemmae. It can mitosis to become liverworts
(Asexual reproduction) it's haploid because it becomes liverworts(n) by mitosis |
|
|
Elater(2n)
|
Cork screw shape cells that are responsible for dispersing spores in the liverworts (Marchantia*)
Phylum Hepatophyta* |
|
|
Hornwort
|
-Phylum Anthocerophyta
-nonvascular plant -Gametophyte is dominant |
|
|
Pteridophyte
|
-seedless vascular plant
-Sporophyte is dominant |
|
|
Phylum Lycophyta
(seedless vascular plant) |
-" Isoetes flaccida*"
(Florida quillwort) -Seleginella Rrausianna(spike moss) -Lycopodium(club moss) |
|
|
most seedless plants are Homosporous
*** fern are Homosporous |
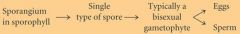
Homosporous=same spores
|
|
|
ALL seed plants and a few seedless vascular plant are heterosporous
|

Heterosporous
|
|
|
megaspore
|
female gametophyte or megagametophyte
|
|
|
microspore
|
male gametophyte or microgametophyte
|
|
|
Phylum Psilophyta
(seedless plants) |
"**Psilotum nudum"
(whisk fern) -most primitive vascular plants coz it has no true leave and root -has dichotonously branching limbs, no root but have leaf like outgrowths in their stems |
|
|
Phylum Sphenophyta
|
"*Equisetum hyemale" (horsetails or *scouring rushed;use to scrub pots and pans)
- Have SiO2(Silica)in stem -*stem is used for photosyn. -nonphotosyn.leave called leave sheath -Strobillus ahs its spores -Living fossils = 400 million years ago |
|
|
Phylum Pterophyta
(seedless plants) |
-Holly fern
-responsible for life cycle of fern - Sporophyte is dominant - Remember Sorus, Annulus,*Prothallus |
|
|
Sorus
(plu. = sori) |
One sorus have so many sporangium(contains spores)
" cluster of sporangia" |
|
|
Annulus
|
when it is dried out,it causes the sporangium to break open exposing the spores to air currents
|
|
|
*Prothallus or Prothallium
(heart-shape stucture) in fern |
- a bisexual gametophyte
because it has both Archegonium and Antheridium on there |
|
|
**Circinate Vernation
|
Cicular growth pattern of the fiddle head associated with immature sporophyte** of fern
|

