![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Functions of Plasma Membrane (phospholipid bilayer)
|
Physical Isolation, Regulation of Exchange of Outside Environment, Sensitivity, Cell to cell communication.
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane Composition
|
Phospholipids, Proteins, glycolipids, sterols.
|
|
|
Phospholipid Bilayer composition
|
Heads at surface (hydrophilic), tails inward (hydrophobic),
|
|
|
What cant cross the pm?
|
Dissolved Ions, water soluble compounds. (tail portion wont associate)
|
|
|
two membrane proteins
|
Peripheral, Integral
|
|
|
Peripheral Protein in pm
|
attached to inner or outer membrane surface
|
|
|
integral protein in pm
|
embedded into pm
|
|
|
Integral proteins form?
|
Channels....some are gated |
|
|
Carbohydrate portion of glycolipid and glycoproteins that extend away from outer surface of pm make the???????
|
Glycocalyx
|
|
|
Function of sterols. what is an example?
|
help stabilize membrane structure and maintain its fluidity. ex. Cholesterol |
|
|
permeability. impermeable . freely permeable. Selectively permeable
|
Property determining the effectiveness of it as a barrier. nothing can cross = impermeable can cross without problem = freely impermeable selectively permeable = some can some cant |
|
|
3 passive passage processes 3 active passage process |
active- active transport, endocytosis, exocytosis |
|
|
Microvilli. where are they found?
|
found in cells actively engaged in absorbing materials from extracellular fluid. ex cells from kidneys and small intestines. |
|
|
Purpose of microvilli.
|
increase surface area for greater absorption, |
|
|
composition of Microvilli. Microfilaments and microvilli interaction.
|
network of microfilaments stiffens each microvillus and anchors it to terminal web ( dense supporting network within underlying cytoskeleton) |
|
|
microfilaments and cytoskeleton interaction.
|
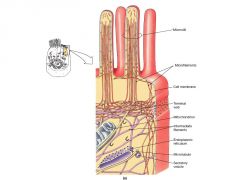
produce waving motions. help circulate fluid around microvilli, bringing dissolved nutrients into contact with receptors on membrane surface. |
|
|
|
|

