![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Biology |
Bio: life or living Logy: the study of |
|
|
|
SMALLEST TO LARGEST Biosphere, biome, tissue, sub-atomic, individual, community, organelle, organ, ecosystem, population, organ-system, cell, molecule, atom |
sub-atomic, atom, molecule, organells, cells, tissue, organ, organ-systems, individuals, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biopsphere |
greatest to smallest : bbecpiootcomas |
|
|
6 Requirements to be "living" |
1: ability to repair, reproduce, and grow 2: ability to create waste/gases 3: posses cells 4: react to stimuli/environment 5: have a life cycle 6: require energy |
|
|
|
6 themes of biology |
1: Ecology 2: Evolution 3: Unity/Diversity 4: Continuity 5: Homeostasis (energy) 6: Interactions |
e e u/d c h i |
|
|
Define Scientific Method |
a tool used to answer complex questions in smaller steps |
|
|
|
Hypothesis and example |
An "if... then..." statement that is a testable prediction if you microwave the water for a plant then it won't grow properly |
|
|
|
What is a control? |
what you compare your experiment to |
|
|
|
Independent variable |
the variable that is changed/different |
|
|
|
What is DNA? |
a molecule that comprises chromosomes, a double helixed complex made up of nucleotides (sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous bases) |
|
|
|
Main Functions of DNA |
1: ability to mutate 2: cell division/replication - mitosis and meiosis 3: protein production controls genotypes and phenotypes |
|
|
|
Structure of DNA |
polymer of nucleotides (S, P, NBs) |
|
|
|
monomers and polymers of DNA |
m = nucleotides polymer is the dna |
|
|
|
how many NBs? |
4 ! ATCG |
|
|
|
how is DNA replicated? |
1) unzips - helicase breaks it 2) complimentary base pairs - new NBs from nucleus H bond w exposes bases on DNA strand 3) Joining of adjacent nucleotides - polymerase catalyses the Sugar-Phosphate backbone |
|
|
|
Draw a nucleotide |
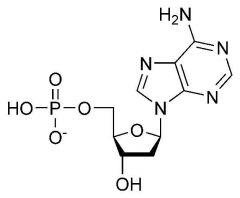
|
|
|
|
What are the complimentary base pairs for the DNA double helix? |
A = T and C ≡ G |
|
|
|
Why do cells duplicate? |
new cells are needed to grow, reproduce and repair |
|
|
|
Mutagen |
a physical/chemical agent tha can alter DNA (environmental factors) ex: XRAYS |
skeleton man |
|
|
Test to identify mutagens |
Ames Test |
|
|
|
Difference between germ and somatic cell mutations? |
Germ: affect the offspring Somatic: affect the individual, passed on via mitosis |
|
|
|
Chromosome Mutations |
Deletion - whole chromosome is lost Inversion - piece of chromosome is broken off and replaced in reverse orientation Translocation - two pieces swap places Nondisjunction - failure to separate during cell division |
|
|
|
Gene Mutations |
Point - a single nucleotide base change, insertion or deletion of the genetic material Frame shift - insertion of a number of nucleotides that is not divisible by 3 |
|
|
|
Species |
a group of individuals that look similar and can produce fertile offspring in their natural environment |
|
|
|
Hardy-Weinburg |
1) no natural selection 2) large population 3) no migration 4) random breeding 5) no mutation |
|
|
|
Darwin |
Natural selection, Galapagos island, finches, evolution |
|
|
|
MSC and BSC |
morphological species concept - if they look the same, they are the same biological species concept - classified by ability to breed in nature, if they can interbreed = same species |
|
|
|
Bell curve |
majority is average with a few exceptions on the extremes |
|
|
|
Genetic equilibrium |
Disrupted if any of the Hardy-Weinburg principles are not met |
|
|
|
Types of Natural Selection |
Directional, Stabilizing, Disruptive |
|
|
|
Genotype and Phenotype |
Genotype: the genetic makeup of an organism Phenotype: the outwards appearance of an individual |
|
|
|
How does speciation occur? |
Isolated populations - geographical or reproductive ex: earthquakes, lava, ponds, and when species stop interbreeding |
|
|
|
Divergent and Convergent evolution |
Divergent: 2 species diverging from the common ancestor becoming less and less like the original species Convergent: when organisms develop similar characteristics when adapting to the environment |
|
|
|
Adaptive radiation |
a process in which organisms diversify rapidly into a multitude of new forms, when a change in environment makes resources available, creates new challenges or opens new niches |
|
|
|
co-evolution |
the influence of closely associated species on each other in their evolution EX: bats w fuzzy faces, flowers that smell like fruit for pollen |
|
|
|
geographic isolation |
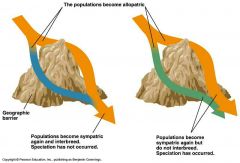
|
|
|
|
2 models that shows evolutionary rate of change for natural selection? |
Gradual change, rapid change |
|
|
|
morphology |
the study of the forms of things, in particular |
|
|
|
gene pool |
the stock of different genes in an interbreeding population |
|
|
|
allele frequency |
it is the fraction of all chromosomes in the population that carry that allele |
|
|
|
hybrid |
the offspring of two plants/animals of different species or varieties EX: mule (hybrid of donkey and horse) |
|
|
|
genetic drift |
variation in the relative frequency of different genotypes in a small population, owing to the chance disappearance of particular genes as individuals die/do not reproduce |
|
|
|
gene flow |
the transfer of alleles / genes from one population to another immigration/ emigration |
|
|
|
punctuated equilibrium model |
the hypothesis that evolutionary development is marked by isolated episodes of rapid speciation between long periods of little to no change |
|

