![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The molecule that functions as the reducing agent (electron donor) in a redox or oxidation-reduction reaction:
|
loses electrons and loses energy.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements describes the results of this reaction?
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy |
C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced
|
|
|
When a glucose molecule loses a hydrogen atom as the result of an oxidation-reduction reaction, the molecule becomes
|
oxidized
|
|
|
When a molecule of NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) gains a hydrogen atom (not a hydrogen ion) the molecule becomes
|
reduced
|
|
|
Which of the following statements describes NAD+
|
NAD+ is reduced to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
|
|
|
Where does glycolysis takes place?
|
cytosol
|
|
|
The ATP made during glycolysis is generated by
|
substrate-level phosphorylation
|
|
|
The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event?
|
accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
|
|
|
An electron loses potential energy when it
|
shifts to a more electronegative atom
|
|
|
Why are carbohydrates and fats considered high energy foods?
|
They have a lot of electrons associated with hydrogen.
|
|
|
Which step shows a split of one molecule into two smaller molecules?
|
B
|
|
|
Which step shows a split of one molecule into two smaller molecules?
|
B
|
|
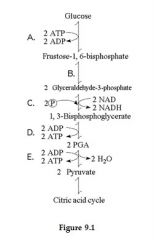
Which step shows a split of one molecule into two smaller molecules?
|
B
|
|
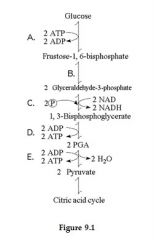
which step is an inorganic phosphate added to the reactant?
|
C
|
|
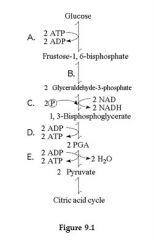
In which reaction does an intermediate pathway become oxidized?
|
C
|
|
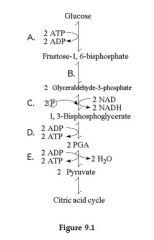
Which step consists of a phosphorylation reaction in which ATP is the phosphate source?
|
A
|
|
|
During glycolysis, when glucose is catabolized to pyruvate, most of the energy of glucose is
|
retained in the pyruvate
|
|
|
In addition to ATP, what are the end products of glycolysis?
|
NADH and pyruvate
|
|
|
Starting with one molecule of glucose, the "net" products of glycolysis are
|
2 NADH, 2 H+, 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, and 2 H2O
|
|
|
In glycolysis, for each molecule of glucose oxidized to pyruvate
|
2 molecules of ATP are used and 4 molecules of ATP are produced.
|
|
|
How does pyruvate enter the mitochondrion?
|
active transport
|
|
|
Which of the following intermediary metabolites enters the citric acid cycle and is formed, in part, by the removal of a carbon (CO2) from one molecule of pyruvate?
|
acetyl CoA
|
|
|
Which of the following are products of the light reactions of photosynthesis that are utilized in the Calvin cycle?
|
ATP and NADPH
|
|
|
any ecosystem, terrestrial or aquatic, what group(s) is (are) always necessary?
|
autotrophs
|
|
|
When oxygen is released as a result of photosynthesis, it is a by-product of which of the following?
|
splitting the water molecules
|
|
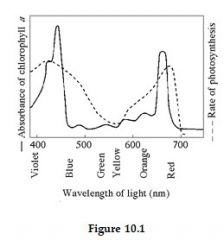
Figure 10.1 shows the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll a and the action spectrum for photosynthesis. Why are they different?
|
Other pigments absorb light in addition to chlorophyll a.
|
|
|
In the thylakoid membranes, what is the main role of the antenna pigment molecules?
|
harvest photons and transfer light energy to the reaction-center chlorophyll
|
|
|
The reaction-center chlorophyll of photosystem I is known as P700 because
|
this pigment is best at absorbing light with a wavelength of 700 nm.
|
|
|
Which of the events listed below occur in the light reactions of photosynthesis?
|
light is absorbed and funneled to reaction-center chlorophyll a.
|
|
|
Which of the following are directly associated with photosystem I?
|
receiving electrons from plastocyanin
|
|
|
Some photosynthetic organisms contain chloroplasts that lack photosystem II, yet are able to survive. The best way to detect the lack of photosystem II in these organisms would be
|
to test for liberation of O2 in the light.
|
|
|
What are the products of linear photophosphorylation?
|
ATP and NADPH
|
|
|
Produces NADH
|
neither the light reactions nor the Calvin cycle
|
|
|
Produces NADPH
|
light reactions alone
|
|
|
Requires CO2
|
the Calvin cycle alone
|
|
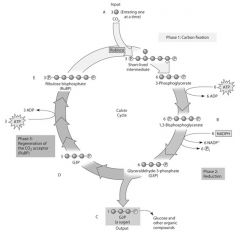
If the carbon atom of the incoming CO2 molecule is labeled with a radioactive isotope of carbon, where will the radioactivity be measurable after one cycle?
|
in E only
|
|
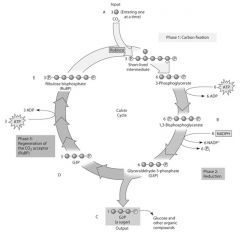
Why are C4 plants able to photosynthesize with no apparent photorespiration?
|
They use PEP carboxylase to initially fix CO2.
|
|
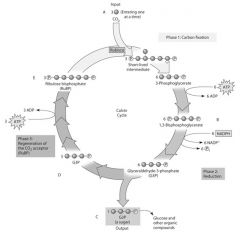
CAM plants keep stomata closed in daytime, thus reducing loss of water. They can do this because they
|
fix CO2 into organic acids during the night.
|
|
|
Photorespiration lowers the efficiency of photosynthesis by preventing the formation of
|
carbon dioxide molecules.
|
|
|
What is a chromatid?
|
a replicate chromosome
|
|
|
The centromere is a region in which
|
chromatids remain attached to one another until anaphase.
|
|
|
If there are 20 chromatids in a cell, how many centromeres are there?
|
10
|
|
|
How do the daughter cells at the end of mitosis and cytokinesis compare with their parent cell when it was in G1 of the cell cycle?
|
The daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes and the same amount of DNA.
|
|
|
A cell containing 92 chromatids at metaphase of mitosis would, at its completion, produce two nuclei each containing how many chromosomes?
|
46
|
|
|
If there are 20 centromeres in a cell at anaphase, how many chromosomes are there in each daughter cell following cytokinesis?
|
20
|
|
|
If there are 20 chromatids in a cell at metaphase, how many chromosomes are there in each daughter cell following cytokinesis?
|
10
|
|
|
In order for anaphase to begin, which of the following must occur?
|
Cohesin must be cleaved enzymatically
|
|
|
Nucleotides can be radiolabeled before they are incorporated into newly forming DNA and can therefore be assayed to track their incorporation. In a set of experiments, a student-faculty research team used labeled T nucleotides and introduced these into the culture of dividing human cells at specific times.
If mammalian cells receive a go-ahead signal at the G1 checkpoint, they will |
complete the cycle and divide.
|
|
|
Nucleotides can be radiolabeled before they are incorporated into newly forming DNA and can therefore be assayed to track their incorporation. In a set of experiments, a student-faculty research team used labeled T nucleotides and introduced these into the culture of dividing human cells at specific times.
Which of the following is released by platelets in the vicinity of an injury? |
PDGF
|
|
|
Which is a general term for enzymes that activate or inactivate other proteins by phosphorylating them?
|
protein kinase
|
|
|
Which of the following is a protein maintained at constant levels throughout the cell cycle that requires cyclin to become catalytically active?
|
Cdk
|
|
|
Which of the following triggers the cell's passage past the G2 checkpoint into mitosis?
|
MPF
|
|
|
What is a karyotype?
|
A display of every pair of homologous chromosomes within a cell, organized according to size and shape
|
|
|
The human X and Y chromosomes
|
include genes that determine an individual's sex.
|
|
|
Which of the following is true of a species that has a chromosome number of 2n = 16?
|
Each cell has 8 homologous pairs.
|
|
|
A given organism has 46 chromosomes in its karyotype. We can therefore conclude which of the following?
|
Its gametes must have 23 chromosomes.
|
|
|
Which of the following happens at the conclusion of meiosis I?
|
Homologous chromosomes are separated.
|

