![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Eukaryotic Cell division occurs in what two steps? |
Nuclear division Cytoplasmic division |
|
|
What are the three stages of the cell cycle? |
Interphase mitosis cytoplasmic division |
|
|
The cell spends most of its life in what phase? |
Interphase (G1,S,G2) |
|
|
Describe G1 phase |
Growth before DNA replication Chromosomes are unduplicated |
|
|
What is S and what happens during S? |
Synthesis The cell makes copies of chromosomes by DNA replication |
|
|
What is G2 phase and what happens? |
After replication but before mitosis Cell prepares for division |
|
|
What happens during mitosis? |
The nucleus divides |
|
|
What happens to the cell during Interphase? |
Increases in size replicates DNA Doubles cytoplasm |
|
|
Where do most cell checks happen? |
G1 Phase |
|
|
Describe Homologous Chromosomes |
Have the same length, shape, and genes One pair is from mother other is from father Human Cells have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) |
|
|
Males have ____ Chromosomes Females have ____ Chromosomes |
Males: XY Females: XX |
|
|
What are the 4 phases of mitosis? |
Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase |
|
|
Cytoplasmic division results in what? |
Two diploid cells |
|
|
What is the point of cell checkpoints? |
If there is an issue in the cell it can be corrected before it moves on |
|
|
What happens to a cell's chromosomes during interphase? |
They are loosened to allow transcription & DNA replication |
|
|
What is a centrosome? |
A region near the nucleus that organizes spindle microtubules (includes two centrioles) |
|
|
What happens during Prophase? |
Chromosomes condense Nuclear envelope breaks up Microtubules attach to the chromosomes Microtubules for a bipolar spindle |
|
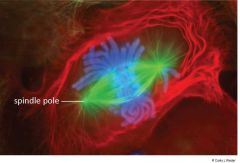
What is the spindle? |
A network of microtubules that form during nuclear division Grows from opposite poles and attach to duplicated chromosomes Attach to different sister chromatids and separate them |
|
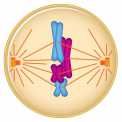
What happens during Metaphase? |
Duplicated chromosomes line up midway between spindle poles |
|
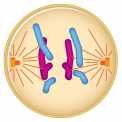
What happens during Anaphase |
Microtubules separate the sister chromatids and pull then to opposite spindle poles |
|

What happens during Telophase? |
Two new nuclei are formed |
|
|
What is cytokinesis and when does it normally happen? |
Cytoplasmic division Late Anaphase - End of Telophase |
|
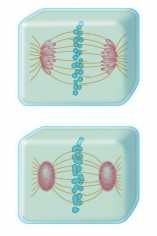
What's the difference between cytokinesis in plant cells and animal cells? |
Plant cells create a cell plate Animal cell creates cleavage & pinches |
|
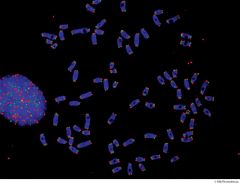
Describe Telomeres |
Noncoding sequences Protect chromosomes from losing genetic info |
|
|
How do tumors form? |
Checkpoint mechanisms fail and the cell loses control over its cycle, forms a neoplasm which forms a lump a.k.a a Tumor |
|
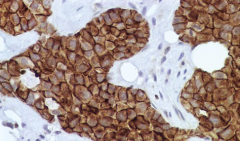
What is shown here? |
The white is the normal cells while the brown shows the active form of the EGF receptor (breast cancer) |
|
|
Characteristics of Cancer cells |
Grow and divide abnormally Cytoplasm is altered Malignant cell have abnormal chromosome numbers Cancer cells break lose and invade other parts of the body (metastasis) |

