![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the main points of the cell theory |
all living things are made of one or more cells all life functions take place in cells all cells are made from pre existing cells |
|
|
what are the five needs of all living things |
need energy reproduce grow produce wastes respond and adapt to their environment |
|
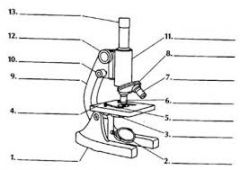
label the microscope |

|
|
|
define ocular lens or eyepiece |
the part of microscope that you look through
|
|
|
define coarse adjustment knob |
moves tube up and down to focus the specimen |
|
|
define fine adjustment knob |
focuses specimen and produces clear image |
|
|
define revolving nosepiece |
holds objective lens |
|
|
define objective lenses |
low medium high, allows the magnification of the specimen |
|
|
define stage |
slide is placed on for examination
|
|
|
define stage or slide clips |
holds slide in place |
|
|
define diaphragm |
controls the amount of light reaching the specimen |
|
|
define lamp or mirror |
light source |
|
|
define condenser lens |
directs the light to the specimen |
|
|
define arm |
holds eyepiece and objective lens the correct distance apart |
|
|
define base |
supports the microscope |
|
|
define total magnification |
eyepiece 10X magnification and objective lens 4X low, 10X medium, 40X high |
|
|
define field of view |
how much you can see through the microscope |
|
|
what is a micro meter |
1mm = 1000Mm |
|
|
how do you calculate FOV on low power
|
measure with a ruler in mm how large the micro space is then multiply the mm of the ruler by 1000 |
|
|
what is the FOV formula for medium and high |
FOV = magnification low --------------------------- × FOV low magnification med/high |
|
|
ex. Find the FOVmed if FOVlow = 4000Mm and eyepiece = 10X and low=4X, medium =10X high=100X |
FOVmed= 4X -------- × 4000 = 1600Mm 10X |
|
|
how do estimate the size of a specimen |
estimate how many would fit in the FOV and then divide that number by the FOV |
|
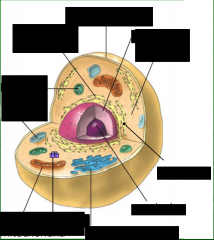
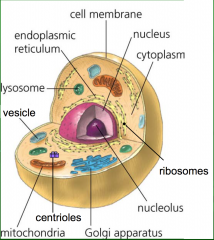
label the animal cell |
|
|
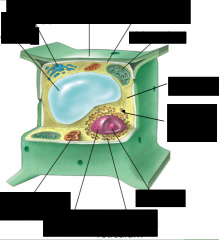
label the plant cell |
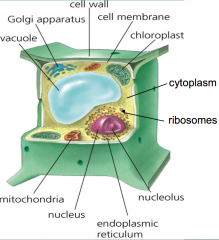
|
|
|
define the cell membrane |
protective barrier, control what enter and leaves the cell |
|
|
define cytoplasm
|
jelly like substance hat fills the cell and helps transport things in the cell |
|
|
define nucleus |
contains DNA and genetic material like the brain of the cell and controls everything |
|
|
define chloroplasts |
only in plants, where photosynthesis take place, contains chlorophyll producing a green color |
|
|
define vesicles and vacuoles |
stores things for the cell |
|
|
define lysosomes |
place where digestion takes place |
|
|
define ribosomes |
may be attached to the endoplasmic reticulum and it is where proteins are produced |
|
|
define endoplasmic reticulum smooth and rough |
interconnected tubes that branch from the nuclear envelope rough- protein synthesis smooth- fat and oil production |
|
|
define golgi apparatus |
composed of flat disc snapped sacs involved with secretion |
|
|
define mitochondria |
rod like structures where reactions occur to produce sugar |
|
|
define centrioles |
animal cells, involved in cell division |
|
|
define cell wall
|
rigid outer shell in plant cell that protects the cell |
|
|
what are differences between plant and animal cells |
plants have - cell wall, chloroplasts, larger vacuoles animals have- lysosomes, centrioles |
|
|
what are the benefits of multicellular organisms |
cell specialization grow larger survive i wider rang of environments |
|
|
whats the organization of multicellular organisms |
organelles,cells, tissues, organs, systems |
|
|
define stem cells |
unspecialized cells |
|
|
what is the chemical formula for photosynthesis |
CO2 + H2O + light energy -> C6H12O6 + O2 |
|
|
define epidermal cells |
protective skin prevents the evaporation of water |
|
|
define palisade tissue cells |
photosynthetic cells - most photosynthesis happens here |
|
|
define spongy tissue cells |
contain chloroplasts |
|
|
define stomata |
small openings in the epidermal layer that allow the exchange of gas |
|
|
define guard cells |
guard cells open and close the stomata |
|
|
what are the two types of vascular tissue |
phloem and xylem |
|
|
define phloem |
transports sugar from the leaves to the rest of plant |
|
|
define xylem |
transports water from the roots to the rest of the plant |
|
|
what are xylem and phloem arranged in |
vascular bundels |
|
|
what is the difference between photosynthesis and respiration |
respiration is the process of the release of carbon dioxide and can happen normally in the dark |
|
|
what is the most important gas exchange organ in the plant |
leaves |
|
|
define turgor pressure |
water pressure inside the plant cells that allow them to stay rigid
|
|
|
what happens to turgor pressure during osmosis |
increase |
|
|
what happens to turgor pressure during transpiration |
decrease |
|
|
define lenticels |
woody plants containing openings in bark for gas exchange |
|
|
define xylem |
composed of dead cells, that form a tube from the roots to the rest of the plant |
|
|
define root hairs |
small hairs on roots to increase absorption
|
|
|
define phloem |
live cells , walls contain pores to allow exchange of materials with near by cells transports sugars |
|
|
define cohesive force |
attractive force between water pulling it up |
|
|
define adhesive force |
attractive forces between water and surfaces |
|
|
define tropisms |
a plants response to the environment |
|
|
define phototropism |
growth of a plant towards its light source |
|
|
define auxins |
plants growth chemical |
|
|
define gravitropism |
growth of a plant in response to gravity |
|
|
what gravitropism do roots and stem show |
stem is negative and roots is positive |
|
|
define nastic responce |
plants that respond to touch |
|
|
define sleep movements |
plants responding to the time of day |
|
|
what is 6267 in scientific notation |
6.267 x 103 |
|
|
whats 0.0000072 in scientific notation |
7.2 x 10 -6 |
|
|
define significant digits |
meaningful digits in a measured or calculated quantity |
|
|
how many sig dig are in 34576 |
5 sig digs |
|
|
how many sig digs are in 0.000045 |
2 sig digs |
|
|
how are sig digs counted in multiplication |
least amount of sig digs is your answer
|
|
|
how are sig digs in addition or subtraction |
least number of decimal places |
|
|
whats 6.38 x 10 -2 in real number |
0.0638 |
|
|
solve for x 3x=bm ---- ---- 3 3 |
x=bm ----- 3 |
|
|
whats the formula for slope |
m = y2 - y1 -------------- x2 - x1
|
|
|
what are the formulas for the area of a triangle and a rectangle |
triangle = bh ------ 2 rectangle= bh |

