![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
T or F. Hormones decide how we behave?
|
False hormones change the probability to react to an internal or external stimulus with a biologically meaningful behavior.
|
|
|
What are steroid hormones derived from?
|
Choleslterol
|
|
|
What are the 4 types of steroid hormones?
|
Mineralcorticoids (i.e. aldosterone from adrenal cortex); Stress hromones (i.e. cortisol from adrenal cortex); Male Hormones (i.e. testosterone); Female Hormones (i.e. estradiol)
|
|
|
Autonomic control requires what NTs?
|
ACH (parasympathetic), NE ( post ganglionic sympathetic)
|
|
|
___NT is involved in?
ACH DA NE SERA(5HT) |
ACH = Ef MALCAutoS
DA = Ef MALCEuM NE = RAEf AutoS 5HT = WREC Ef= executive function W or S = sleep wake L = learning M= memory uM = motor functions Auto = autonomic A = Attention R = reproduction C= consumatory behavior |
|
|
What are some major sites of NE release? DA? 5HT?
|
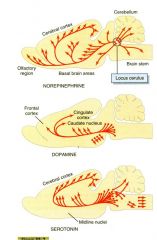
NE = Locus cerulus
Da = VTA, substantia Nigra PC 5HT = Raphe Nuclei |
|
|
What are the cholinergic nuclei atzori want us to know?
|
-Medial septum (major ACH to hypothalamus)
-Vertical & horizontal limbs of the diagnol band of Broca -Basal Forebrain -Substantia innominata -Lateral dorsal tegmentum -Pedunculopontine tegmentum |
|
|
True or false. Steroids use Ca and vesicles to have effects?
|
False, they cross the membrane becuase they are lipophilic like vesicels and have there effect on intracellular receptors.
|
|
|
What are the mechanisms of actions of hromones?
|
Membrane receptors (G proteins, TKR and others)and intracellular receptors (cytosolic and nuclear R)
|
|
|
How are G- proteins activated and what are they composed of?
|
a 7 transmembrane protein Receptor
A trimeric complex w/ alpha (Gs Gq Gi) beta gamma (B&G may undersome conditions activate L type Ca channels) subunits that are realesed from the receptor upon binding to start the 2nd msenger cascade. |
|
|
Gs
|
cAMP stimulatory g protien.
Actiaves adenylyl cyclase which increases production of cAMP. Increased cAMP activates PKA which phosphorylates proteins increasing their activity. |
|
|
Gi
|
Inhibits adenylyl cyclase. Opposing the effects of Gs
|
|
|
Gq
|
Activates phospholipase C which cleaves PIP2 into DAG(membrane) and IP3(diffusable)
DAG activates PKC which acts like PKA IP3 activates the ER Ca channels increasing intercellular Ca. |
|
|
What are the hypothalamic hormones, what cells do they come from, what cells do they act on, and what is their action?
|

They come from the parvocelluar cells of the hypothalamus and act on anterior pituitary. See figure.
|
|
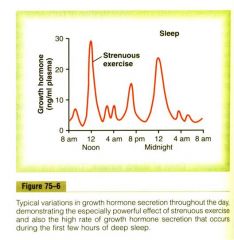
GH is released after?
|

Relased in the general hormone pulsitile pattern but also after strenuous exercise and in the first few hours of sleep. It accelerates cell growth, multiplication, metabollism, cell renewl and interestingly audlts with high GH turnover age more slowly.
|
|
|
General factors that effect hormone release?
|
Metabolic, psychologic, physiologic and environmental factors modify hormone release
The action of hormones on gene expression is the link that makes hormonal unbalances a major determinant of human personality |
|
|
Atzoris notes say hypothalamus has evolved for controlling?
|
Connection between
Body and External Environment through Behavior hypothalamus- communicates with the body via the pituitary (humoral) and autonomic & enteric NS (neural) Hypothalamus recieve info about the body state from organs and through emotional and motivational parts of the brain |
|
|
Elements of Feedback?
|
Set point, transducer (monitors and produces signal when change occurs), and control through autonomic or behavior
|
|
|
Examples of negative feedback?
|
Temperatrue Regulation through + & - error i.e. shivering or sweating. or even getting a blanket
|
|
|
Examples of Positive feedback?
|
Paturation, ovum removal, lactation
Snowball effect- once the variable departs it is propelled further untill a desired change occurs. |
|

Hormone action summary
|

|
|
|
Which hormone have inhibitory factors instead of a typical feedback loop?
|

Both prolactin and GH have many more functions beyond these
They do not have the three-level production control, but they are just controlled by the “short loop” because they act more in a distributed manner These two pituitary hormones have the important property that the hypothalamus can - Increase their release with a Prolactin releasing factor and a growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH), respectively, or (here is the novelty) - Decrease their release with Dopamine, or Somatostatin, respectively Eating disorders may have to do with a bad feedback loop. |
|
|
Atzori said know the example
|
|
|

Atzori said knop the example
|

|
|
|
What happens if you lesion or have hyper activity of the organ?
|
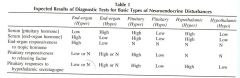
|
|
|
Neuroendocrine reflex example
|
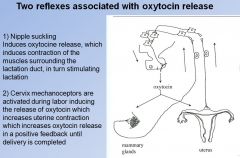
|
|
|
Graded Reflex example
|
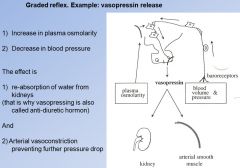
|
|
|
Difference b/t reflex and homeostatic mechanism?
|
Reflex-Controlled and feedback variable is a hormone
Homeostatic-Controlled and feedback variable is a systemic variable A reflex is usually triggered by a large displacement of a system variable outside the normal variation range (life-threatening situation) Homeostasis is part of the physiological control of a variable within the physiological range Reflex after a car accident limit loss of blood |
|
|
What is pulsitility? What is the biological effect
|
The propensity of endocrine cells to synchonize when firing. Ca plays a role in at least some instances
The biological Corollary of this fact is that the presentation of continuous stimuli of hypothalamic hormones is less effective, or even inhibitory, in releasing pituitary hormones. |
|
|
How can neurosecreation be effected?
|
1) Neuroendocrine pulse generating mechanisms
(cell-cell connectivity and local signaling) 2) Membrane and Voltage-dependence modulation 3) Modulation in hormone or receptor transcription or translation (mRNA production or protein synthesis) 4) post-translational processing 5) Stimulus secretion coupling (presynaptic terminal) |
|
|
T or F. Hormone create neural ciruits?
|
False, they simply activate them.
|
|
|
induction of sexual behavior in the female by estrogen and progesterone
|
Estrogen ↑ the production of oxytocin receptors in the VMN of the hypothalamus
Progesterone facilitates their cellular distribution An increased oxytocin response ↑ the sensibility to oxitocin of this nucleus and produces the lordotic behavior |
|
|
T or F. Hormones can have permanant effects?
|
True. can have permanent or long-lasting consequences
Example: growth hormone during development -genes create the structure the hormone make it grow |
|
|
General info on crosstalk and effect on intracellular cascades.
|
Basically One hormone can facilitate or inhibit another
Cross-talk between different hormones: Effect of Intracellular cascades Although many chemical cascades are sometimes compartimentalized (they happen in different anatomical regions, cell types, or at least different part of the same cell), in most cases metabolic cascades are NOT compartimentalized Example: steroid hormones receptors can be activated, or their sensitivity to their activators can be increased (or decreased) by cAMP and growth factors This cross-talk greatly complicates the interpretation of neuroendocrine experiments |
|
|
Can other cells and areas make hypthalamic hormones?
|
hypothyalamus is not exclusive in synthezising and releasing its hormones, but also several other classes of cells in the brain can produce the same hormones
|
|
|
What hypothalamic hormones are relased in the posterior pituitary? What is the cell type?
|
oxytocin and vassopressin
magnocellular |
|
|
CRH
|
Peptide, parvocellular, corticotropes, Gs maybe Gq, ACTH, glucocoricoid cortisol, suppresses GHRH & LHRH, involved in psychiatric disorders, and
CRH-MEC Auto M=memory; E=emotion; C=Consumatory behavior; Auto= autonomic |
|
|
GnRH or LHRH
|
LHRH/GnRH is a peptide released from the parvocellular cells (primarilly Mid. & Preop hypo) affected by light and steroid hormones but atzori says not sex steroids it acts on ganadotropes through Gq/11 to releases LH & FSH which act on the sex organs to produce sex hormones facilitating sexual behavior.
The ventromedial n. of the hypothalamus is necessary for development of lordotic behavior No receptors for sex steroids, no negative feedback closing the loop acts to close the loop through different cells |
|
|
GHRH or Samatotropin
|
Produced in MEDIAL ( arcuate, medial perifonical region of lateral) hypothalamus and other low density
Co released w/ DA or galanin modulated by TRH, Substance P, enkephalins, monamines |
|
|
SRIH
|
Peptide produced by somatotropes (primarly anteriorr hypo) which activates Gi and many act by block of Ca by V depdent Ca channels
extrahypothalamic areas pancreas, gut Neocortex, amygdala, hippocampus, septumm, brainstem Autosynapses -branch that goes back to cells that produce somatostatin found in a lot of gabaergic interneurons Modulated by CRH,NPY, GABA |
|
|
TRH
|
produced by ANTERIOR(PVN), PREOPTIC, MEDIAL
& uses Gq/11 to simulate TSH release [ paraventricular (anterior), preoptic, dorsomedial (medial), laterobasal,] Outside hypo: Raphe, Olfacotry bulb, diagnal band of broca, septum Modulated by NPY, Proopiomelanocortin, NE, 5HT, autosynapses |
|
|
PIF
|
A Major PIF is DA
produced in the anterior and middle (tuberoinfundibular of arcuate N (middle), Anterior Periventricular (Anterior)) Modulated by CRH and 5HT |
|
|
What are the hypothalmic outputs?
|
Humoral via portal system and Neural output to brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
What are the hypothalamic inputs?
|
Humorla form body glands
Neural from amygdala Hippocampus septum thalamus basal ganglia cortex lower brainstem (modulatory NT nuclei especially) spinal cord |
|
|
How does the immune system effect the endocrine and vice versa?
|
The immune system effects by cytokines but can also produce peptide hromones.
Hormones and neurohormones regulate immune function Thymus activates antibodie producing cells and is involved in the stress response. |
|
|
What are the Nuclei of Anterior hypothalamus Atzori wants us to know?
|
Periventricular (somatostatin, DA)
Suprachiasmatic (biological clock, peptidergic neruons) Anterior Hypothalamic N Supraoptic (Oxytocin[dorsal]; Vasopressin [ventral]) Paraventricular ( peptides like CRF, TRH. |
|
|
What are the Nuclei of Middle hypothalamus Atzori wants us to know?
|
Arcuate N (peptides, DA, GRH, POMC)
VM N (connected to limbic system hippocampus and amygdala) DM N Perifornical N (angiotensin II, projects to other hypo N) |
|
|
What are the Nuclei of posterior hypothalamus Atzori wants us to know?
|
Tuberomammillary N (HA)
Ventral premammillary (POMC) Dorsal Premammillary Posterior Premammillary (DA cells to spinal cord) Supramammillary to dentate gyrus ( hippocampus) medial septum + diagonal band of Broca |
|
|
T or F. The median eminance has both fibers from hypothalamus and extrahypothalamic areas.
|
True, Extrahypothalamic are monaminergic fibers.
The hypo are POMC, NT, SubP, galanin, GABA, pituitary hormones, CCK, enkephalins, VIP, AII, ANP |
|
|
Glucocorticoid system regulates?
|
Such as cortisol effect HPA axis and stress
|
|
|
Mineralcoricoid regulate?
|
such as aldosterone effect body fluid and electrolyte balance through angiotensin-renin via kidney and smooth muscle of vessels
|
|
|
Vitamin D is?
|
a derivative of cholesterol with many functions.
|
|
|
Name the Estradiol R?
|
ERbeta, ER alpha
|
|
|
Testsoterone plays a role in?
|
not just sexual behavior but regulating and coordinating neuroendocrine and NT behavior
|
|
|
Progesterone role is?
|
alot like testosterone but can inhibit sexual receptivity and facilitate lordotic behavior.
|
|
|
Steroid hormones are produced and bind to?
|
are produced both inside and outside the brain; They bind to n uclear R, GABAaR and GluR
|
|
|
Nuclear R
|
are steroid R activated transcription factors influenciung gene expression in many areas. Affecting Neuronal morphology, Cell survival, Neurochemical phenotype, connectivity
|
|
|
Oxytocin an Vassopressin structure are?
|
Similar and vary by 2 AA 1 being in the ring portion
|
|
|
Name the early genes that are used as activyt markers?
|
cFos, cJun, Elav, Homer, Arc
|

