![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
width of corridors in residential occupancies with an occupant load of 50 or less |
36" min |
|
|
Offices corridors with occupant load of 50 or less |
44" min |
|
|
wainscotting |

|
|
|
What's the difference between "regular" and "Type X" gypsum board? |
ASTM C 36 designates two types of gypsum board, regular and Type X. Type X gypsum board, which is typically required to achieve fire resistance ratings, is formulated by adding noncombustible fibers to the gypsum. These fibers help maintain the integrity of the core as shrinkage occurs, providing greater resistance to heat transfer during fire exposure.To receive the "Type X" designation under ASTM C 36, a gypsum board product must be shown to achieve not less than a one-hour fire resistance rating for 5/8" board or a 3/4-hour fire resistance rating for 1/2" board applied in a single layer |
|
|
non-combustible means |
It will not ignite and burn when subject to fire |
|
|
construction type refers to |
fire resistance ratings of various building compenents |
|
|
waterproofing uses these applications |
watertight membranes, waterstops, or bentonite panels
typically built below the water table |
|
|
dampproofing |
control of water and moisture when hydrostatic pressure is not present
applications include admixtures for concrete, bituminous coatings, cementious coatings, membranes, and plastics for dampproofing
typically at grade |
|
|
surcharging |
the preloading of the ground with fill material to cause consolidation and settlement of the underlying soil. It is used to increase the bearing capacity of the soil |
|
|
waterproofing |
the control of water and moisture that is subject to hyrdostatic pressure.
applications include watertight membranes (elastomeric membrances, liquid applied membranes), waterstops, bentonite panels
typically below the water table |
|
|
bentonite |
a type of expansive clay that can push foundations and floor slabs upward when it gets wet. To prevent this you may use a combination of drilled piers, grade beams, and voids left below grade
bentonite panels are also used for waterproofing below grade |
|
|
electrical resistances test |
determines the moisture in concrete by measuring the electrical conductivity with meter probes |
|
|
cylinder test |
requires a sample to be taken at the time of the concrete pour before it is hardened |
|
|
core cylinder test |
gives the strength of the hardened concrete |
|
|
Kelly ball test |
requires a sample to be taken at the time of the concrete pour before it is hardened |
|
|
Type I |
General purpose
Fairly high C3S content for good early strength development
General construction (most buildings, bridges, pavements, precast units, etc)
|
|
|
Type II |
Moderate sulfate resistance
Low C3A content (<8%)
Structures exposed to soil or water containing sulfate ions
|
|
|
Type III |
High early strength
Ground more finely, may have slightly more C3S
Rapid construction, cold weather concreting |
|
|
Type IV |
Low heat of hydration (slow reacting)
Low content of C3S (<50%) and C3A
Massive structures such as dams. Now rare. |
|
|
Type V |
High sulfate resistance, gains strength slower
Very low C3A content (<5%)
Structures exposed to high levels of sulfate ions |
|
|
Type M |
High strength mortar
masonry below grade
subjected to hight lateral or compressive loads or severe frost action |
|
|
Type S |
Medium-high strength mortar
Generally above grade (exterior)
high flexural bond strength but subjected only to normal compressive loads |
|
|
Type N |
Medium strength mortar
Generally above grade (parapet or interior) |
|
|
Type O |
Medium low strength mortar
Non-loadbearing interior walls and partitions |
|
|
According to code horizontal masonry reinforcement is required every... |
16" (approx. 4 bricks) |
|
|
SW brick |
severe weathering
northeast in the US |
|
|
NW brick |
normal weathering |
|
|
MW brick |
Moderate weather |
|
|
FBX brick |
finish appearance
Brick for general use in exterior and interior walls where a high degree of mechanical perfection, narrow color range, and minimal variation in size is permitted |
|
|
what are the most weather resistant types of brick joints? |
concave and V joint |
|
|
common bond running bond english bond flemish bond |
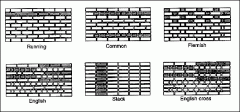
|
|
|
Which additives are added to steel to improve corrosion resistance? |
Chromium, copper, molybdenum, nickel |
|
|
Tungsten |
added to steel to improve the material's ability to retain it's strength when exposed to high temperatures |
|
|
oil canning |
gives a metal siding panel a wavy appearance |
|
|
astragal |
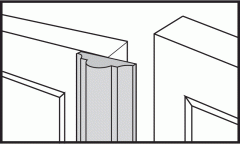
|
|
|
shoe molding |

|
|
|
check and shake |
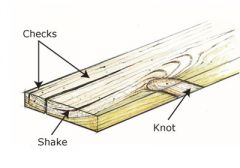
the separation of wood fibers occurring across or though the growth rings |
|
|
wane |
the presence of bark in a piece of lumber |
|
|
wale |
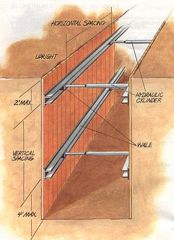
horizontal member that holds individual pieces of shoring in place |
|
|
raker |
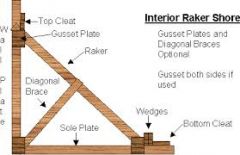
|
|
|
firestop |
A firestop is a fire protection system made of various components used to seal openings and joints in fire-resistance rated wall and/or floor assemblies. |
|
|
minimum suggested pitch for a normal-slope asphalt or composition shingle roof |
4:12 |
|
|
minimum suggested pitch for a low-slope asphalt or composition shingle roof |
2:12 |
|
|
EIFS |
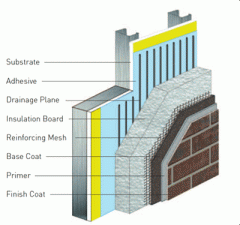
exterior insulating finish system |
|
|
Tar paper |
a heavy duty paper impregnated with asphalt. Typically used on roofs. |
|
|
cant strip |
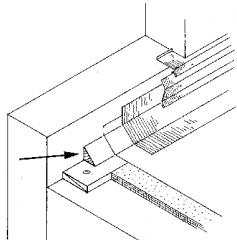
A three-sided piece of wood, one angle of which is square, used under the roofing on a flat roof where the horizontal surface abuts a vertical wall or parapet. The sloped transition facilitates roofing and waterproofing. |
|
|
annealed glass |
standard glass used in most noncritical glazing situations |
|
|
stile |
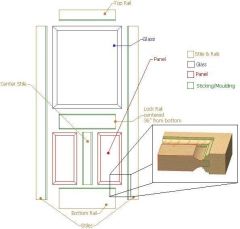
The lockset of a panel door is mounted in the stile |
|
|
parquet flooring |

|
|
|
urethane |
Urethane is a high-performance coating that has superior resistances to abrasion, grease, alcohol, water, and fuels. It resists the adhesion of graffiti to surfaces and allows relatively easy removal of graffititi |
|
|
alkyd |
Alkyds are used in paints and in moulds for casting. They are the dominant resin or "binder" in most commercial "oil-based" coatings. (exterior) |
|
|
terrazo |

|
|
|
Access floor systems |

|
|
|
EPDM |

EPDM is an extremely durable synthetic rubber roofing membrane (ethylene propylene diene terpolymer) widely used in low-slope buildings in the United States and worldwide. Its two primary ingredients, ethylene and propylene, are derived from oil and natural gas. |
|
|
how do I know how large my aggregate should be? |
Aggregate should be no larger than 1/3 the slab thickness |

