![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define membrane potential |
The difference in electrical potential between the interior and exterior of the cell. (Interior is usually more negative at resting potential) |
|
|
Secondary Active Transport |
These transporters move two molecules, one against a gradient, one with a gradient. |
|
|
Types of Secondary active transporters |
Antiporter: Molecules move in opposite directions. |
|
|
ATP Pump |
Uses energy from hydrolysis of ATP to move molecules against a gradient. important for maintaining medium levels of particular ions in cell (eg Calcium and Sodium). |
|
|
Transport Proteins |
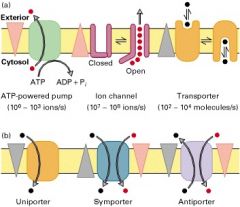
|
|
|
Nernst Potential/Reversal Potential |
Membrane potential at which there is no net flow of that particular ion across membrane. |

