![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what do bacteria provide the host root system with?
|
NH3 to be used in Gln synthesis
|
|
|
what does the host provide the bacteria with?
|
provides anaerobic bacteria with protection from O2 which is toxic to the nitrogenase components
|
|
|
leghemoglobin
|
an O2 binding protein produced by legumes that traps O2 before it can interact with the nitrogenase complex
|
|
|
biologically, nitrogen fixing bacteria can reduce N2 to what?
|
NH3
|
|
|
Lightning fixes nitrogen by what?
|
oxidizing it to nitrogen oxides which dissolve in water and eventually form nitrates
|
|
|
nitrogen fixation is the process that coverts what?
|
N2 from the gas form to a form useable by plants
|
|
|
all nitrogen fixing species contain the nitroegnase complex which consists of what?
|
1)nitrogenase: Fe-Mo protein-2Mo,30Fe; 4 polypeptides - 2alpha and 2beta (heterotetramer)
2)nitrogenase reductase: Fe protein- 8Fe, 2 identical polypeptides (homodimer) |
|
|
nitrogenase complex is aerobic or anaerobic?
|
anaerobic
|
|
|
electrons for nitrogen fixation are supplied by what?
|
4NADH to form a reduced ferredoxin
|
|
|
what is the biproduct of nitrogen fixation?
|
H2
|
|
|
what is the overall reaction of nitrogen fixation?
|
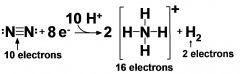
N2 + 8 e- + 16 ATP + 12 H2O + 10 H+ goes to 2 NH4+ + 16 ADP + 16 Pi + H2
|
|
|
what are the general essential AAs?What are the essential AAs for infants?
|
Essential = isoleucine
leucine lysine methionine phenylalanine threonine tryptophan valine Infants = arginine histidine |
|
|
nonessential AAs are synthesized how?
|
by incorporating ammonium ions into an alpha-keto acid
|
|
|
why must essential AAs be supplied in the diet?
|
b/c their precursors are not readily available - phenylpyruvate is not available to make phenyalanine
|
|
|
prolonged protein deficiency leads to what?
|
kwashiorkor which in children leads to growth failure and other problems
|
|
|
what combines to form glutamate?
|
alpha-ketoglutarate accepts ammonium ion (NADPH oxidized to NADP+)
|
|
|
glutamate becomes glutamine with the addition of what?
|
more ammonium ions and ATP
|
|
|
transamination requires what?
|
a specific aminotransferase enzyme and the coenzyme pyridoxal-5-phosphate (most useful form of vit. B6)
|
|
|
glutamate and glutamine are the primary nitrogen donor molecules transferring what?
|
the alpha-amino group of glutamate and the side chain amino group of glutamine to other molecules in a transamination reaction
|
|
|
schiff base
|
intermediate molecule that transamination occurs through, forms when a nitrogen atom adds to a carbonyl carbon
R-CH=N-R |
|
|
after the N of the AA adds to the C of the C=O and transfers an H to the O, a schiff base forms with what?
|
the loss of water - resulting in a double bond between the N and C
|
|
|
rearrangement of the double bond in the schiff base and addition of H2O forms what?
|
an alpha-keto acid and the coenzyme-amino form - water completely removes the double bond freeing the alpha-keto acid
|
|
|
how is alanine formed from the coenzyme-amino?
|
pyruvate is added to the coenzyme-amino and water is removed forming a double bond between the N and carbonyl C of pyruvate. the double bond is then moved to the N and C of the coenzyme. H3O+ is added freeing alanine and regenerating the aldehyde coenzyme
|
|
|
Serine AA Family
|
glycine and cystein
|
|
|
pyruvate AA family
|
valine, alanine, leucine
|
|
|
glutamate AA family
|
glutamine, proline, arginine
|
|
|
aspartate AA family
|
asparagine, methionine, lysine, threonine to isoleucine
|
|
|
aromatic AA family
|
phosphoenolypyruvate + erythrose-4-P goes to phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan
|
|
|
histidine AA family
|
ribose-5-P goes to histidine ; shares common pathways with synthesis of nucleotides
|
|
|
how is serine formed?
|
1. 3P-glycerate is converted into 3-phosphohydroxy-pyruvate by dehydrogenase (NADH is formed)
2. 3-phosphohydroxy-pyruvate is converted into 3-phosphoserine by transaminase (glutamate is added and a-ketoglutarate is removed) 4. 3-phosphoserine is converted into serine by phosphatase (H2O is added and Pi removed) |
|
|
glycine is synthesized from serine by what?
|
a one carbon transfer of the CH2OH carbon to THF
|
|
|
what is tetrahydrofolate (THF)?
|
a reduced form of folic acid and a frequently encountered one-carbon carrier
|
|
|
what are the reactive parts of THF?
|
nitrogens at positions 5 and 10
|
|
|
what is needed to convert homocysteine to methionine?
|
N5-methyl-THF and vit. B12 (cobalamin)
|
|
|
Vit. B12 deficiency results in what?
|
pernicious anemia; the disease can be caused by a missing stomach secretion needed to absorb the vitamin or by coeliac disease or tropical sprue; symptoms include low red blood cell count, neurological disorders
|
|
|
What are the steps in cysteine synthesis?
|
1. methionine is added to N5-methyl THF w/ addition of ATP
2. acceptor molecule removes methyl group leaving s-adenosyl homocysteine 3. H2O is added and adenosine is removed leaving homocysteine 4. serine is added and H2O is removed forming cystathionine by synthase 5. NH4+ and a-ketobutyrate are removed by gama-cystathionase forming CYSTEINE |
|
|
what is the structure of THF?
|
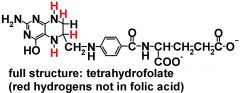
|
|
|
how is alanine formed from pyruvate?
|
by the addition of glutamate and the removal of a-ketoglutarate
|
|
|
proline is formed from what?
|
glutamate- by the addition of 1 ATP and 2NADPH
|
|
|
arginine forms from what?
|
The urea cycle but you can't just take it out of the cycle - you have to add something first. So glutamate is converted to ornithine by the addition of Ac-SCoA and the removal of CoASH. By adding ornithine to the urea cycle you can extract arginine
|
|
|
lysine forms from what?
|
aspartate -
*by the addition of 1 ATP, reduction by 1 NADPH, and addition of pyruvate it forms the intermediate dihydropicolinate; *forms the next intermediate diaminopimilate through NADPH reduction, addition of glutamate and removal of a-ketoglutarate,addition of succinyl CoA and removal of CoASH and succinate; *in the final step lysine is formed by the addition of H+ and removal of CO2 |
|
|
threonine is formed from what?
|
aspartate - by the addition of 2ATP, reduction by 2NADPH, it forms the intermediate phosphohomoserine; addition of H2O and removal of Pi forms threonine
|
|
|
methionine forms from what?
|
aspartate - it is reduced by NADPH, ATP and cysteine are added, and pyruvate and NH4+ are removed leaving homocysteine; N5 methyl-THF is added and THF is removed leaving methionine
|
|
|
the benzene ring is synthesized by what pathway?
|
shikimate pathway - produces aromatics
|
|
|
Phe or Trp are required for the synthesis of what?
|
dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine (part of the catecholamines);
Trp is required for synthesis of NAD(P) and the neurotransmitter serotonin |

