![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
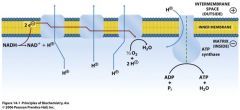
Proton gradient serves as an energy reservoir for the synthesis of ATP
|
|
|
Oxidative phosphorylation
|
the process by which NADH and QH2 are oxidized and ATP is formed
|
|
|
Respiratory electron-transport chain (ETC)
|
Series of enzyme complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane, which oxidize NADH and QH2. Oxidation energy is used to transport protons creating a proton gradient
|
|
|
ATP synthase
|
uses the proton gradient energy to produce ATP
|
|
|
Chemiosmotic theory
|
A proton concentration gradient serves as the energy reservoir for driving ATP formation
|
|
|
Respiration by mitochondria
|
Oxidation of substrates is coupled to the phosphorylation of ADP – don’t get oxidation when ADP is absent
Respiration (consumption of oxygen) proceeds only when ADP is present The amount of O2 consumed depends upon the amount of ADP added |
|
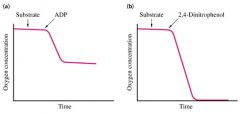
Coupled nature of respiration in mitochondria
|
(a) O2 consumed only with ADP, excess Pi - normal oxidative phosphorylation
(b) (+) Uncoupler DNP (O2 consumed without ADP) – oxidation reactions without conservation of energy into ATP |
|
|
Uncouplers
|
stimulate the oxidation of substrates in the absence of ADP
|

