![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What makes up the superficial cervical plexus and how is it blocked? |
anterior branches of the first four cervical nerves, |
|
|
What are signs of a successful superficial cervical plexus block and what are complications? |
- horners syndrome and horseness (RLN block) |
|
|
where do intercostal nerves arise and what is their relationship to the rib artery and vein? |
-anterior rami of first 11 thoracic nerves; |
|
|
What are the branches of the intercostal nerves and what do they supply? |
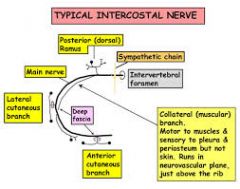
1. first branch passes to sympathetic ganglia |
|
|
Which intercostal nerves supply sensory innervation of the thorax and which supply abdomen? |
1. upper 6 thoracic nerves supply thorax |
|
|
How could you do intercostal nerve block for extensive intraabdominal surgery |
intercostal nerve blocks from T4-T12 and the celiac plexus is blocked |
|
|
what makes up the celiac plexus? |
thoracic sympathetic ganglion and the greater and lesser splanchnic nerves |
|
|
What does the celiac plexus innervate? when do you use it? |
intraabdominal organs; |
|
|
where is the celiac plexus and what is the positioning of the patient for a celiac plexus block? |
-L1 along the aorta in the retroperitoneal space; |
|
|
What are complications of the celiac plexus block? |
1. hypotension, |
|
|
what is the most effective of all maneuvers for pancreatic cancer pain? |
alcohol celiac plexus block |
|
|
How can the brachial plexus be injured by positioning? |
1. stretch by the head of the humerus, |
|
|
How can the median nerve be injured? |
needles due to superficial location in antecubital fossa |
|
|
What are signs of radial nerve injury? |
-wrist drop (cannot extend MCP joints), |
|
|
What are signs of median nerve injury? How can it be injured? |
1. inability to oppose the thumb and little finger, |
|
|
How is the ulnar nerve injured? |
compression against post aspect of medial epicondyle of the humerus |
|
|
What are signs of ulnar nerve injury? |
1. inability to abduct the little finger, and |
|
|
How is the sciatic nerve injured? |
stretching (lithotomy position), needle injection, |
|
|
How is the common peroneal nerve injured? |
compression of the nerve between the head of the fibula and the metal brace used in the lithotomy position |
|
|
What are the signs of common peroneal nerve injury? |
1. foot drop, |
|
|
How is the anterior tibial nerve injured? |
feet are dorsiflexed for long periods of time; feet and ankles should be in neutral or slightly extended position |
|
|
How is the femoral nerve injured? |
at the pelvic brim by a self retaining retractor or by excessive thigh angulation in the lithotomy position |
|
|
What are signs of femoral nerve injury? |
loss of hip flexion and knee extension, |
|
|
How can the saphenous nerve injured? |
foot is suspended lateral to a vertical brace |
|
|
How is the obturator nerve injured? |
difficult forceps delivery, |
|
|
What are the signs of obturator nerve injury? |
inability to adduct the leg, |
|
|
What nerve innervates the larynx? |
Vagus nerve (CN X) |
|
|
What are the 5 major cartilages of the larynx? |
1. Hyoid |
|
|
What are the 2 branches of the vagus nerve that innervate the larynx and trachea? |
1. Superior laryngeal nerve |
|
|
What forms the brachial plexus? |
The union of the anterior primary divisions of C5-T1 with frequent contributions from C4 and T2 |
|
|
How is the brachial plexus divided? |
"Randy Travis Drinks Cold Beer" |
|
|
What does each trunk form? |
An anterior and posterior division |
|
|
What do the lateral and medial cord of the brachial plexus give off? |
-The lateral and medial cord give off the lateral and medial heads of median nerve |
|
|
What does the posterior cord of the brachial plexus give off? |
The axillary nerve and continues as the radial nerve |
|
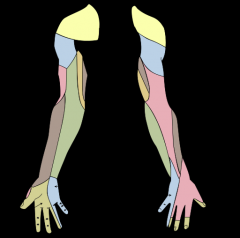
What is the innervation of the following colors? |
Yellow - Cervical plexus |
|
|
Where is the axillary vein found in relation to the axillary artery when performing a block? |
Anterior to the artery |
|
|
Describe the cutaneous innervation of the hand. |
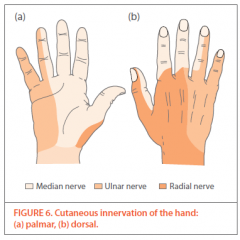
-Median nerve innervates the index and middle fingers beyond the PIP as well as the radial half of the ring finger |
|
|
What does the median nerve supply in the hand? |
The thenar eminence and the 1st and 2nd lumbricals |
|
|
Where is the median nerve found in the wrist? |
Between the flexor carpi radialis and the palmaris longus |
|
|
What nerve covers the posterior portion of the tongue? |
Glossopharyngeal nerve |
|
|
What is the significance of the lateral cutaneous branch of the 2nd intercostal nerve? |
This is the intercostobrachial nerve which supples the skin of the medial arm |
|
|
Which block has the highest blood levels of local anesthetic than any other regional anesthetic? |
Intercostal nerve block |
|
|
How is sciatic nerve injury manifested? |
1. Weakness below the knee |

