![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Epic of Gilgamesh
|
epic poem from Ancient Mesopotamia and is among the earliest known works of literary fiction
|
|
|
irrigation
|
artificial application of water to the soil usually for assisting in growing crops; systems first developed in Mesopotamia allowing them to develop the arid areas
|
|
|
Sargon of Akkad
|

Akkadian king famous for conquest of the Sumerian city-states
|
|
|
Hammurabi's Codes/Laws
|
law codes from ancient Babylon, created ca. 1760 BC
|
|
|
stele
|
stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected for funerary or commemorative purposes, most usually decorated with the names and titles of the deceased or living
|
|
|
Assyrians
|
ethnic group whose origins lie in what is today Iraq, Iran, Turkey and Syria
|
|
|
economic specialization
|
labor specialization began with the combination of tin and copper into bronze individuals began to focus on specific areas of craftsmanship
|
|
|
stratified patriarchal society
|
social, economic, and political power lay in the hands of the males thus forming a patriarchal society
|
|
|
commoner, dependant, slave
|
lower classes were commoners and slaves with an intermediary class ie. the dependent clients who owned no property but were slaves
|
|
|
cuneiform
|
Sumerian-made first form of written expression
|
|
|
Moses
|
13th century BCE[1] Biblical Hebrew religious leader, lawgiver, prophet, and military leader, to whom the authorship of the Torah is traditionally attributed
|
|
|
polytheism
|
multiple gods
|
|
|
Semitic
|
first used to refer to a language family of largely Middle Eastern origin
|
|
|
city-state
|
region controlled exclusively by a city, usually having sovereignty
|
|
|
empire
|
state that extends dominion over populations distinct culturally and ethnically from the culture/ethnicity at the center of power
|
|
|
Hammurabi
|
sixth king of Babylon
|
|
|
Indo-Europeans
|
original people that historically spoke Indo-European languages
|
|
|
Hittites
|
ancient people in Anatolia who spoke an Indo-European language, and established a kingdom centered at Hattusha
|
|
|
Hanging Gardens of Babylon
|
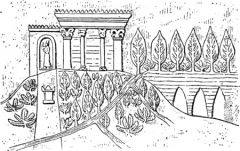
built by Nebuchadnezzar II around 600 BC. He is reported to have constructed the gardens to please his wife, Amytis of Media. They were destroyed by earthquakes.
|
|
|
bronze and iron metallurgy
|
the working of bronze and iron into tools and weapons
|
|
|
pastoral nomads
|
communities of people that move from one place to another, rather than settling down in one location
|
|
|
Hebrews, Israelites, Jews
|
the Ibri people, known in the Middle East for their place of origin relative to the major culture of the time;English name for the nation of Israel who were the dominant cultural and ethnic group living in the southern Levant;member of the Jewish people, an ethnoreligious group originating in the Israelites or Hebrews of the ancient Middle East
|
|
|
Abraham
|
Jewish, Christian, and Muslim beliefs dictate him as the founding patriarch of the Israelites, Ishmaelites and Edomite peoples
|
|
|
monotheism
|
meaning a single god
|
|
|
Phoenicians
|
civilization with an enterprising maritime trading culture that spread across the Mediterranean between the period of 1200 BC to 900 BC
|

