![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The extracellular matrix is the _____ in connective tissues between cells
|
ground substance
|
|
|
The main components of extracellular matrix are:
What do they do? |
-collagen - provides tensile strength
-elastic fibers - provides resilience -proteoglycans - provides resilience -hyaluronan - provides resilience -glycoproteins - mediate adhesive interactions between other matrix molecules or between cells and matrix molecules |
|
|
Collagen is the main _____ in connective tissue. It has a characteristic _____. It is heavily _____ and very ______
|
-fibrillar proteins
-triple helical structure -linked -stable |
|
|
What are the fibril forming collagen types? And where are they distributed
|
-Type I - skin, bone, tendon, blood vessels, cornea
-Type II - cartilage, intervertebral disk, vitreous body (fluid in eye) -Type III - blood vessels, fetal skin |
|
|
What are the network forming (forms meshes) collagen types? And where are they distributed
|
-Type IV - basement membrane
|
|
|
What is the precursor to collagen?
|
procollagen
|
|
|
Procollagen peptide chain has propeptides that are ______ after three procollagen chains assemble to form a ______
|
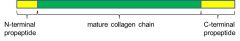
-removed extracellularly by proteolytic digestion
-triple helical structure |
|
|
Collagen are composed of _____
|
3 alpha chains (can be identical or different)
|
|
|
Name what types of alpha chains Type I - Type 4 collagen are composed of:
|

|
|
|
The long helical part of alpha chains of collagen are composed of _____ repeats. These repeats favor ____
|
Gly - X - Y
-X - proline -Y - hydroxyproline Triple helix formation |
|
|
Synthesis of the procollagen genes occur in the _____
|
RER
|
|
|
On procollagen, certain proline and and lysine residues are hydroxylated into _______. Then, certain _____ are _____
|
-hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine
-hydroxylysine -glycosylated |
|
|
When are prolines and lysines hydroxylated during the synthesis of collagen?
|
During synthesis of alpha chains in the RER
|
|
|
Triple helix formation of collagen forms in the ______
|
RER
|
|
|
Triple helix formation of collagen formation proceeds from the _____ end to the ____ end
|
C-terminal end to the N-terminal end
|
|
|
Triple helix formation of collagen is held together by ______. _____ also has a crucial role in stable triple helix formation
|
-hydrogen bonds
-hydroxylproline |
|
|
After the triple helix formation is made, the procollagen is sent to the ______ where ______ are cleaved by ______. Once they are cleaved, collagen monomers assemble into ____
|
-extracellular matrix
-N-terminal and C-terminal peptides -N and C procollagen peptidases -fibrils |
|
|
Collagen fibrils, which are formed by _____ associate in a _____ manner. These are stabilized ______ and it creates a ______ patterns when viewed under an electron microscope
|
-collagen monomers
-staggered -by covalent crosslinking between monomers -striated |
|
|
Triple helix of collagen is stabilized by ______. Hydroxyproline produced by ______ which requires _____ as cofactors
|
-Hydrogen bonds and hydroxyproline
-prolyl hydroxylase -Fe2+ and vitamin C (ascorbate) |
|
|
Covalent crosslinks within collagen fibers are created through formation of _______. Oxidation of these two is catalyzed by ______, which requires ____ as a cofactor
|
-oxidized lysine and hydroxylysine residues
-lysyl oxidase -Cu2+ |
|
|
Oxidation of lysine and hydroxylysine residues creates _______which react with _______ residues to create _______ between collagen
|
-allysine or hydroxyallysine
-lysine/hydroxylysine/allysine/hydroxyallysine -covalent crosslinks |
|
|
Collage IV is the main ______. Collagen IV alpha chains form triple helix ____
|
-basement membrane
-inside the cell |
|
|
Type IV monomers attach at their C-terminal to form a _____ in the _____. The dimers N terminals then attach to form _____ and eventually a large networking looking like ____
|
-dimer
-extracellular space -tetramer -chicken-wire |
|
|
What deficiency and disease is caused by the lack of fruits and vegetable in a diet?
This causes what enzymes to not work? This causes what kind of symptoms? |
-Scurvy and Vitamin C disease
-Prolyl hyroxylases (stabilizes triple helix formation) and lysyl hydroxylase (crosslinks collagen) -spots, bruises on skin (especially on leg); bleeding gums/loose teeth, delayed wound healing |
|
|
What are the three types of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) and what types of mutations do they cause?
|
Classic Type: type V collagen mutation (fibril associated collagen)
Vascular Type: type III collagen mutation Kyphoscoliotic Type: lysyl hydroxylase mutation |
|
|
Classic type EDS is caused a mutation in what and causes what kind of symptoms?
|
Type V collagen mutation
Symptoms: hypersensitive skin, delayed wound healing, atrophic scars, joint hypermobility |
|
|
Vascular type EDS is caused by a mutation in what and causes what kind of symptoms?
|
Type III mutation
Symptoms: arterial, intestinal, and uterine (during pregnancy) ruptures |
|
|
Kyphoscoliotic type EDS is caused by a mutation in what and causes what kind of symptoms?
|
lysyl hydroxylase mutation
Symptoms: hypersensitive skin, delayed wound healing, easy bruising, thin scars; joint hypermobility; progressive scoliosis |
|
|
Osteogenesis imperfecta has has at least _____ different types
Types I, II, III, IV are associated with what type of mutation? |
-seven
-Type I collagen mutation |
|
|
What are they symptoms of osteogenesis imperfecta?
|
-can range from perinatal lethal to mild predisposition to fractures including:
-increased incidence of fractures -short stature -grey/brown teeth that wear down easily (dentinogenesis imperfecta) -blue sclera -loose ligaments |
|
|
Alport syndrome is a mutation of ______ genes and is related to ____
|
-type IV collagen
-neuropathy |
|
|
Alports syndrome mainly effects ______ and can lead to ____ failure. The main symptoms of this disease are:
|
-glomerular basement membranes
-renal failure Symptoms: -Hematuria -Proteinuria -Hepertension -Renal insufficiency -Hearing loss |
|
|
_____ is the major component of elastic fibers. It is mainly found in the _______. It is synthesized in the ____
|
-elastin
-blood vessels and lungs -ER |
|
|
Elastin is secreted from the cell as what?
When it is secreted, what happens? |
-monomers
-lysine residues are oxidized by lysyl oxidase, then they form crosslinks between elastin molecules |
|
|
The correct assembly of elastic fibers require what?
And what forms these? |
-microfibrils formed by fibrillins
|
|
|
What is responsible for excessive degradation of elastin in the lungs?
How does it stop excessive degradation of elastin? |
-alpha1 - antitrypsin is a natural inhibitor of neutophil elastase (a proteolytic enzyme)
-neurtophil elastase degrades elastin in the lungs |
|
|
What does deficiency in alpha 1-antitrypsin leads to what?
Who may have an increase in this deficiency? |
-lower elastin content in lungs, can lead to collapse of alveoli when patient exhales, and leads to emphysema (shortness of breath)
-smokers are prone to deficiency |
|
|
Marfan syndrome is caused by deficiency in what?
|
fibrillin-1 (microfibrils are deficient, which leads to a deficiency in elastic fibers)
|
|
|
Marfan syndrome can occur in three places, where and what are its symptoms in those locations?
|
Skeletal
-very tall stature, kyphoscoliosis -disproportionally long limbs, finger and toes -hyperflexible joints Ocular: -dislocation of lens of eyes (ectopia lentis) Cardiovascular -dilation of aorta -heart valve problems |
|
|
Cells have dynamic interactions with the extracellular matrix. Resident cells ____ the extracellular matrix, while the extracellular matrix provides _____ for the cells. Cells bind to matrix through_____, which allow cells to sense ____ in the extracellular matrix and respond
|
-synthesize
-optimal environment -cell surface receptors -changes (ex. if tissue is damages, primary response is to restore integrity of tissue by resynthesizing tissue) |
|
|
What are the main receptors that anchor the cells to the extracellular matrix?
These can bind to what? |
-integrins (alpha-beta dimer)
-collagens and glycoproteins (ex. fibronectin and laminin) |
|
|
What interaction between cells and extracellular matrix is essential for correct formation of basement membranes?
|
Integrin-laminin interactions
|
|
|
______ are basement membrane proteins. These interact with _____
|
-Laminins
-other basement proteins and integrins on the cell surface |
|
|
Laminins form ____ (which are built from ____ chains) that are stabilized by _____ bonds. Synthesis of these chains occur in the _____ and the assembly occurs in the _____
|
-heterotrimers
-alpha, beta, gamma -disulfide bonds -ER -golgi apparatus |
|
|
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa is cause by a mutation in _____. This can effect ____, can can cause symptoms such as ____
|
-certain laminins and integrins
-the basement membrane below epidermis and mucosal membranes -fragile skin that shows extreme blistering |
|
|
Tissue remodeling takes place during:
|
-tissue differentiation (matrix composition changes) and cell migration (cells "cut through" the matrix)
|
|
|
In order to remodel the matrix, what do cells secrete? And what does this do? What inhibits this?
|
-they secrete matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) that degrade the matrix proteins
-TIMPs (tissue inhibitors of metalloprteinases) inhibit MMPs |
|
|
What does the extent of tissue remodeling depend on?
|
The ratio of MMPs (metalloproteinases) and TIMPs (Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases)
-both are secreted by cells |
|
|
Tumors frequently secrete large amounts of what to invade surrounding tissues?
|
matrix metalloproteinases
|

