![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Net Present Value |
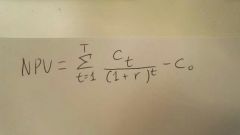
The difference between the present value of cash inflows and the present value of cash outflows. Used in Capital Budgeting to analyze profitability of projected investment. |
|
|
|
Equivalent Annual Cost |
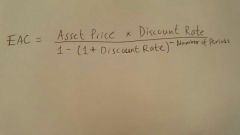
The Annual Cost of owning , operating and maintaining an asset over its entire life. Used by firms for capital budgeting decisions. Allows a company to compare the cost effectiveness of various assets with unequal lifespan. |
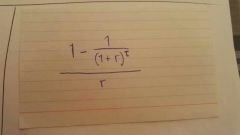
|
|
|
Present Value |
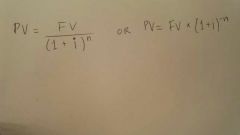
The current worth of a future sum of money or stream of cash flow given a specified rate of return. |
|
|
|
Tax Shield |
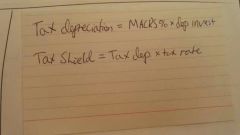
A reduction in taxable income for a individual or corporation achieved through claiming allowable deductions such as mortgage interest, medical expenses, charitable donations, amortization and depreciation. These deductions reduce a taxpayers taxable income for a given year or defer income taxes into future years. |
|
|
|
Rate of Return |
The gain or loss on an investment over a specified time period, expressed as a percentage of the investment's cost. A rate of return can be applied to any Investment Vehicle, from real estate to bonds, stocks and fine art, provided the asset is purchased at one point in time and produces cash flow at some point in the future. |
|
|
|
Real Rate of Return |
The annual percentage return realized on a investment, which is adjusted for changes in prices due to inflation or other external effects. During periods of high inflation, expressing rates of return in real values rather than nominal values offer a clearer picture of an investment's value. |
|
|
|
Standard Deviation |
A measure of the dispersion of a set of data from its mean. In finance, Std.Dev. is applied to the annual rate of return of an investment to measure the investment's volatility. For example, a volatile stock has a high Std.Dev. , while the deviation of a stable blue-chip stock is lower! |
|
|
|
Risk Premium |
A form of compensation for investors who tolerate the extra risk, compared to that of a risk free asset. A form of Hazard pay for your investments |
|
|
|
Variance |
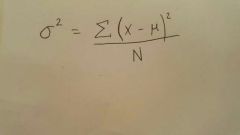
A measurement of the spread between numbers in a data set. The variance statistics can help determine the risk an investor might take on when purchasing a specific security. |
|
|
|
Beta |
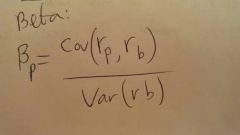
The standard risk measure for individual securities. The beta of an indiv. sec. measures its sensitivity to market movements. Notice that many of the stocks that have a high Standard deviation also have high betas(Not always the case) |
|
|
|
Expected rate of return |

|
|
|
|
Stock price |

|
|
|
|
Real interest rate |

|
|
|
|
Duration |
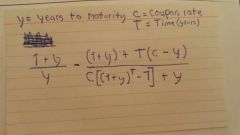
It should say Yield to maturity on Y= |
|
|
|
Internal Rate of Return(IRR) |
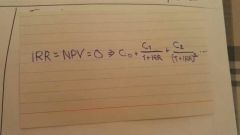
|
|
|
|
Present value of an annuity (NPV) |

|
|
|
|
Sample Variance (Standard deviation) |

|
|
|
|
Forward Interest rate |

|
|
|
|
Future value |
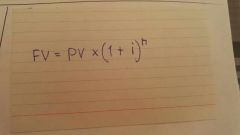
|
|
|
|
Covariance |

|
|
|
|
Expected return on portfolio |
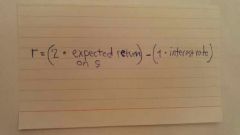
|
|
|
|
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) |
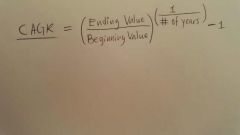
The mean annual growth rate of an investment over a specified period of time longer than one year. |
|

