![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the TRAP signs for parkinsonism?
|
-Tremor at rest
-Rigidity -Akinesia (or bradykinesia) -Postural instability |
|
|
T or F:
Parkinsonism affects proximal muscles early and spreads to face and extremities? |
TRUE
|
|
|
_______________ is a jerky, ratchetlike resistance to passive movement as muscles alternately tense and relax.
|
COGWHEEL
|
|
|
____________ is a slowed or difficulty maintaining movement?
|
-Bradykinesia
|
|
|
What is the inability to initiate movement?
|
-Akinesia
|
|
|
__________________ is one of the most common signs present at initial diagnosis
|
Resting tremors
"pill-rolling" |
|
|
Which type of falls are very common with parkinsonism and why?
|
-Forward Falls
-Rapid, festinating gait in combination with a stooped posture leads to forward falls. |
|
|
What are a few other common motor signs with parkinsonism?
|
-Masked face
-Micrographia -Slowing of ADLs -Stooped, shuffling gait -Decreased arm swing when walking -Hypophonia -Swallowing and chewing difficulty |
|
|
Parkinsonism from strokes, toxins, trauma (boxing), infections (encephalitis, HIV), metabolic abnormalities (hypo- or hyper- thyroidism or parathyroidism, liver failure), drug-induced is known as?
|
Secondary parkinsonism
|
|
|
What is the most common parkinson-plus syndrome?
|
-Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Symptoms include: postural instability leading to falls within first year of disease onset; supranuclear ophthalmoplegia: vertical gaze paresis, especially in the downward direction. |
|
|
What is the key sign you see with Progressive Supranuclear Palsy?
|
-VERTICAL GAZE PALSY
|
|
|
Which part of the brain is the Substantia Nigra Pars Compacta located?
|
-MIDBRAIN
|
|
|
Symptoms of Parkinson begin with Lewy Bodies reach/affect _______?
|
Midbrain, specifically the substantia nigra pars compacta
|
|
|
NORMAL ACTIVITY
|
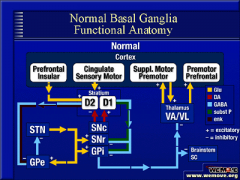
-Normally the D1 and D2 are balanced as shown, and we are able to both initiate wanted movements (D1) and inhibit unwanted movements (D2)
|
|
|
PARKINSON ACTIVITY
|
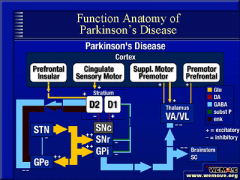
1a) Direct path gets less excitation:
1b) Inderect gets less inhibition 2) Causing increase unwanted movements (cant inhibit) 3) Causing increase difficulty with wanted movements (due to less excitation) 4) |
|
|
The causes direct excitation:
|
D1
-This allows us to choose and perform motion |
|
|
This causes direct inhibition:
|
D2
-This allows us to inhibit unwanted movements |
|
|
How is a clinical diagnosis of Parkinson disease made?
|
-Must have 2 of 4 cardinal signs (TRAP)
-Tremor -rigidity -akinisea -postural instability |
|
|
A definitive diagnosis of Parkinson disease can be made how?
|
-Autopsy
|
|
|
The following are associated with getting Parkinson disease:
|
-Olfactory deficits
-Obesity -Constipation -Slow reaction time |
|
|
What are three symptoms that will give a worse prognosis for PD?
|
-Older age at onset (> 57 years)
-Rigidity/hypokinesia as a presenting symptom -PIGD |
|
|
What is PIGD?
|
Postural Instability
Gait Disturbances |
|
|
T or F:
Deep brain stimulation is another option for treating parkinson disease? |
TRUE
-Indicated when person has symptoms not adequately controlled with medications. -Person still has to have a good response to levodopa. |
|
|
What drug will a younger patient commonly begin with?
|
-May start with Dopamine agonist then advance when needed to a levadopa/sinemet
|
|
|
T or F:
Deep brain stimulation has great effects on Gait and balance in Parkinson disease? |
FALSE
-Non-motor symptoms (gait and balance) of PD not affected by DBS |
|
|
Describe "BIG therapy"?
|
-Treatment effective in treating speech and voice disorders of patients with PD
-Very large exaggerated movements and speech to break motor patterns and reteach "norms" |

