![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
112 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Wavelengths:
UVA |
UVA 320-400nm
UVA2 320-340 UVA1 340-400
95% of suns UVR reaching earth |
|
|
Wavelengths:
UVB |
UVB: 280-320nm |
|
|
Wavelengths:
UVC |
UVC: 200-280nm |
|
|
Which UV is the most erythemogenic?
Germidical?
Delayed tanning? |
Erythemogenic- UVB
Germicidal- UVC
Delayed tanning- UVB |
|
|
Which UV is the most constant despite season/clouds/time of day?
Immediate tanning?
DNA damage? |
Most constant- UVA
Immediate tanning- UVA
DNA damage- UVB |
|
|
How does UVA light change skin color? |
UVA = ATE (tanning--> erythema)
Immediate pigment darkening (tan) that fades within minutes d/t photooxidation of preexisting melanin and redistribution of melanosomes from perinuclear position into dendrites
Followed by a different, distinct delayed erythema 6-24hours post exposure |
|
|
How does UVB light change skin color? |
UVB = BET (erythema--> tan)
UVB induced sunburn begins around 6 hours post exposure and peaks at 12-24 hours
Followed by delayed tanning after 72 hours d/t increase in tyrosinase activity and melanocyte number, and epidermal thickening |
|
|
Ultimately, what is the pathogenesis of photoaging? |
Photoaging or dermatoheliosis due to chronic sun exposure --> UVB and UVA induce reactive O2 species and hydrogen peroxide --> ultimately decreased collagen formation |
|
|
Suberythemogenic (anti-inflammatory) leads to (increase/decrease) adaptive immunity? |
Suberythemogenic decreased adaptive immunity |
|
|
Erythemogenic (proinflammatory) leads to increase/decrease innate immunity? |
Erythemogenic increased innate immunity |
|
|
UV light directly damages the DNA chromophore and creates what? |
cyclobutane-pyrimidine dimers, especially thymidine dimers, with signature mutations of C to T and CC to TT |
|
|
What is the difference in direct and indirect UV damage? |
Direct UV damage- damages the DNA chromophore and creates pyrimidines, most common mutation is C to T and CC to TT
Indirect UV damage- damages non-DNA chromophore and creates purines |
|
|
Indirect UV damage occurs when the energy is absorbed by chromophores other than DNA and you have a Type I or Type II reaction. What are these? |
Type I: energy absorbed by chromophores other than DNA and transferred to DNA
Type II: energy absorbed by molecular oxygen --> oxidative radicals --> DNA damage |
|
|
Melanomas and melanocytic nevi have T-A or A-T mutations in BRAF. Where is the mutation. Which drug targets this? |
V600E
Vemurafenib |
|
|
Just read this slide: |
Immune mediated: - PMLE - actinic prurigo - hydroa vacciniforme - chronic actinic dermatitis - solar urticaria - HIV photodermatitis
Inherited d/t DNA nucleotide excision repair: - XP - cockayne - trichothiodystrophy
Inherited d/t DNA helicase: - Bloom - Rothmund Thompson
Photoaggravated: - seborrheic dermatitis - rosacea - LE - Grovers - Psoriasis - Kindlers
Chemically induced sensitivity: - phototoxicity - photoallergy - porphyria
Photodamage: - Favre raucouchot - Erosive Pustular Dermatosis |
|
|
What is the most common photodermatosis? Clinical presentation? |
PMLE!!!
Idiopathic, non scarring, purirtic, grouped, erythematous papules, vesicles, plaques, bullae (polymorphic) that typically appears 1-4 days after exposure wtih itching and erythema, all lesions develop within 24 hours |
|
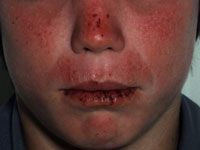
This immune mediated disease develops during childhood and fades in adolescence, more common in girls and Native Americans. Treatment? |
Actinic prurigo- erythematous pruritic papules or nodules, often hemorrhagic crusts, facial lesions may scar.
Tx with sun avoidance, phototherapy, thalidomide until remission, topical cyclosporine |
|
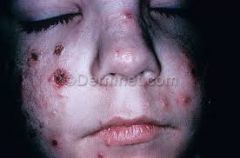
This is caused by what? |
UVA!!!
Hydroa vacciniforme (HV) is a rare, chronic photodermatosis of unknown origin occurring in childhood, remitting by 20. Recurrent vesicles on sun-exposed skin that heal with vacciniform or varioliform scarring. There's some talk that this is related to latent EBV.
Tx is UVB |
|
|
25 year old female comes in with CC of intermittent wheals lasting 3 hours max on her chest and upper outer arms after she goes on her mid day run. Whats up? |
Probably solar urticaria- onset 20s-30s, a/w AD in 21-48% of people, whealing within minutes of sun exposure and lasts less than 24 horus, limited to sun exposed areas, may decrease with hardening |
|
|
At what CD4 count do HIV positive patients begin to have issues with photodermatitis? What medications could be the culprit? |
CD4 < 200
maybe NSAIDS or Bactrim |
|
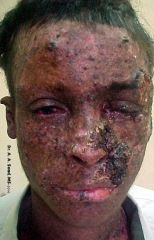
Most common defect in US? Inheritance? |
Xeroderma Pigmentosum
AR
DNA damage repair genes (XPC- endonuclease)... DNAP mutation-- prevents thymidine dimer to AA substitution
MC mutation in Japan in DDB1 |
|
|
What eye findings can be seen in xeroderma pigmentosum? Neuro findings? |
Eyes- ectropion, corneal vascularization, eyelid papillomas, photophobia, conjunctivitis
Neuro- MR, deafness, spasticity, ataxia, microcephaly, this is in 20% of cases, mostly cases of XPA (DDB1 gene in Japan) |
|
|
How often do you do a FBSE on a patient with xeroderma pigmentosum? |
q3mos
Marked increased risk of MM and NMSC |
|
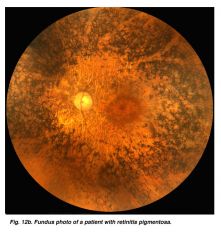
DX? |
Salt and pepper retina!!
Cockayne syndrome. |
|
|
More than 50% of the energy flux reaching the earth's surface is within which portion of the solar spectrum?
UVA UVB UBC Visible Infrared |
UVA= 5-6% UVB= <1% Visible= 40% Infrared = 54% |
|
|
Which of the following is true of UV light?
A. UVA radiation is 1000 times greater than UVB during midday hours B. UVB radiation is 1000 more erythrogenic than UVA C. Sunlight early in the morning and late in the day contain relatively more UVB D. UVA2 light is 340-400 E. Clouds absorb most UVA light |
B. UVB radiation is 1000 times more erythrogenic than UVA
UVA radiation is 100 times greater than UVB durring midday hours Sunlight early in the morning and late in the day contains relatively more UVA than UVB Cloud cover is a poor UV absorber |
|
|
All of the following are true about UVA radiation except:
A. 10 times more abundant than UVB B. penetrates to a greater depth in the dermis than UVB C. responsible for phototoxic drug reactions D. approximately 50% of exposure occurs in the shade E. Virtually all blocked by car window glass |
E. Virtually all blocked by car window glass
Window glass filters out UV wavelengths shorter than 320nm, so only UVB (290-320nm) and shorter are filtered |
|
|
Which of the following is not true about UVB radiation?
A. responsible for sunburn B. more intense in the summer than winter C. peaks at noon D. decreased with high wind velocity E. all blocked by car window glass |
D. decreased with high wind velocity
UVB is the primary cause of sunburn, skin cancer and other harmful effects UVB is more intense during summer and peaks during midday hours |
|
|
UV radiation from the sun causes which of the following acute effects in the skin?
A. redistribution of melanosomes from a perinuclear position into dendrites B. epidermal thickening C. mast cell degranulation D. photooxidation of preexisting melanin E. all of the above |
ALL |
|
|
Max erythema from UVA occurs at...
1hr 12hr 24hr 48hr |
Max erythema from UVA occurs at 24 hours |
|
|
When does a UVB induced sunburn reach its peak after exposure? |
6-24 hours |
|
|
What is the cause of delayed tanning? |
UVB |
|
|
When does delayed tanning peak? |
72 hours, then it lasts 10-14 days |
|
|
Which of the following statements is true?
A. UVB erythema reaches a max in 24-36 hours B. the chromophores involved with UVB erythema are melanosomes C. immediate pigment darkening is brought on by UVA and visible light D. immediate pigment darkening fades within 12-24 hours after exposure E. delayed tanning, which becomes visible about 72 hours after exposure, is largely brough on by UVA |
C. immediate pigment darkening is brought on by UVA and visible light |
|
|
What UV is germicidal? |
UVC |
|
|
A patient that rarely burns and usually tans is which skin type? |
Type III |
|
|
The active spectrum for cutaneous vit D3 synthesis is:
A. 220-290nm B. 290-320nm C. 320-400nm D. 400-410nm E. 410-450nm |
290-320nm (UVB) |
|
|
UVB converts 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin to:
A. 25-hydroxyvitamin D B. 1, 25- dihydroxyvitamin D C. calcitriol D. previtamin D3 E. none of the above |
Previtamin D3 |
|
|
What is the inactive epidermal reservoir of Vit D called? |
lumisterol |
|
|
Long term PUVA is most commonly associated with which cancer? |
scc |
|
|
Which specific mutations are consideres 'signature mutations' in UV mutagenesis? |
C--> T CC -->TT
CUT |
|
|
How does skin fight back against UV damage? |
increased melanin production increased epidermal thickness antioxidative enzymes kick in cell cycle arrest so the repair proteins can work apoptosis immune surveillance |
|
|
What wavelength range most effectively induces cutaneous immunosuppression? |
290-320nm (UVB) |
|
|
Which is NOT affected in photoaged skin?
Col type I Col type II Col type IV Col type VII Fibrillin |
Type VI collagen
I, III, IV, VII and fibrillin are all affected by chronic UV |
|
|
A sunscreen containing which ingredient would afford the most photoprotection against UVA?
A. P-Aminobenzoic acid B. dioxybenzone C. methyl anthranilate D. red veterinary petrolatum E. zinc oxide |
ZINC! This is a physical blocker |
|
|
What is the most photolabile sunscreen? |
avobenzone |
|
|
Which is the most effective UVA sunscreen?
A. cinnamates B. dibenzolymethanes C. padeimate O D. para-aminobenzoic acid E. salicylates |
B. dibenzoylmethanes
aka avobenzone |
|
|
The active ingredient in sunfree tanners is?
A. diacylglycerol B. avobenzone C. anthranilate D. dihydroxyacetone E. para aminobenzoic acid |
D. dihydroxyacetone
turns orange-brown upon oxidateion
Maillard browning reaction |
|
|
Phototoxicity and photoallergy from exogenous agents typically involve absorption of:
A. UVA B. UVB C. UVA AND UVB D. UVA and visible light E. UVA, UVB, and visible light |
UVA
topical and systemic agents that produce phototoxicity and/or photoallergy usually have action spectra in the UVA range
**a noteable exception is photoallergic reaction to Benadryl --> in the UVB |
|
|
The potent photosensitizer, 5-methoxypsoralen, is contained in which of the following contact allergens?
A. oil of bergamot B. balsam of peru C. tuliposide A D. usnic acid E. eugenol |
A. oil of bergamot |
|
|
A common cause of medication in duced photoallergy is:
A. psoralens B. acitretin C. ibuprofen D. naproxen E. piroxicam |
Piroxicam-- all of the medications listed are causes of photosensitivity, but only prioxicam is a cause of photoallergy |
|
|
Which herbal is contradicted for starting light therapy?
A. ginko B. st johns wart C. ginseng D. ecchinacea E. black cohosh |
st johns wort-- may cause transient photosensitivity |
|
|
Kid on griseofulving x 1 week gets a mild itchy rash on face and ear. How do we treat him? |
sunscreen! griseofulving is associated with photosensitivity. They don't have to stop the med, just exercise better sun protection. |
|
|
Which drug produces a photosensitivity?
quinidine sulfonylureas griseofulvin |
ALL |
|
|
The most common cause of topical phototoxicity in the US is:
A. psoralens B. halogenated salicylanilides C. musk ambrette D. 6-methyl-coumarin E. PABA |
psoralens |
|
|
The most common cause of photoallergic contact dermatitis is:
halogenated salicylanilides musk ambrette 6-methyl-coumarin sunscreen mercaptobenzothiazole |
sunscreen!
sunscreen ingredients, especially oxybenzone, are the most common causes |
|
|
Medication photosensitivity is not induced by:
thiazides cephalosporins phenothiazenes quinolones doxycycline |
cephalosporins do not induce photosensitivity
neither does PCN
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most likely cause of photosensitivity?
A. quinolones B. sulfonamides C. doxycycline D. minocycline E. PCN |
doxycycline is the more likely tetracycline derivative to cause photosensivity
quinolones and sulfonamides will also cause this (not as often)
minocycline is the least photosensitizing of the tetracycline derivatives
|
|
|
Which of the following causes a photoinduced hyperpigmentation?
A. bleomycin B. rifampin C. dapsone D. chlorpromazine E. quinacrine |
Chlorpromazine produces a blue-gray hyperpigmentation on sun exposed skin
dapsone causes a photodistributed bullous reaction
bleomycin produces a flagellate pattern
rifampin turns fluids orange
quinacrine turns skin yellow |
|
|
The most common presentation of a patient with medication photosensitivity is:
A. photoonycholysis B. lichenoid eruptions C. diffuse erythema in sun exposed areas D. pseudoporphyria E. fixed erythematous patch |
diffuse erythema in sun exposed areas
|
|

Which drug is this bro on for his arrythmia? |
Amiodarone
bluish gray hyperpigmentation on face/arms, low grade photosensitivity seen in over 75% of patients over 40g cumulative dose |
|
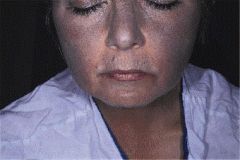
This chick is a schizophrenic. What is she on? |
Chlorpromazine (typical antipsychotic)
Amiodarone, chlorpromazine and TCAs can all cause blue-gray pigmentation on sun exposed areas |
|
|
An MED phototest should be read when? What type of UV do we use? |
Read 24 hours after delivery of the doses, we use UVA |
|
|
An MPD should be read when? |
Minimal phototoxic dose- read at 48-72 hours |
|
|
The best place for phototesting patients suspected of photosensitivity is:
A. affected skin of the buttock B. unaffected skin of the lower back C. affected skin of the ventral forearm D. unaffected skin of the upper back E. unaffected skin of the outer thighs |
B. unaffected skin of the lower back
Patients with photosensitivity can be tested on unaffected skin of the buttocks, lower back or ventral foreamr |
|
|
NBUVB bulbs emit light at: |
311nm |
|
|
Most PUVA bulbs emit predominanty at:
A. 290-320nm B. 320-340nm C. 340-400nm D. 350-360nm E. 390-410nm |
350-360nm
the UVA emitted by the bulbs is absorbed by psoralens, causing covalent bonding of psoralens to DNA |
|
|
Oxsoralen plus UVA results in all of the following except:
A. forms monofunctional adducts B. binds to purine bases C. can form DNA crosslinks D. suppresses DNA synthesis E. has immunomodulating effects |
B. binds to purine bases
oxsoralen, in the presence of UVA, forms covalent bonds to pyrimidine bases |
|
|
Common side effects of PUVA include all of the following except:
A. nausea B. hair loss C. painful erythema D. prolonged pruritis E. SCC |
Hairloss |
|
|
Advantages of NBUVB over PUVA are the following except:
A. no need for protective eyewear after treatment B. no nausea C. safe in childhood D. safe in pregnancy E. more effective in treating thick plaques of CTCL |
More effective in treating thick plaques of CTCL
UVB is less penetrating into the skin than UVA. The UVB does not reach to the bottome of the plaques
therefore, PUVA is more effective for thick CTCL |
|
|
What is the wavelength of a woods lamp? UV? |
365 UVA |
|
|
What is the woods lamp filter made out of? |
NICKEL OXIDE!!!
a nickel for your thoughts 365 days a year |
|
|
What is the most common idiopathic photodermatosis? |
PMLE-- the papular variant is the most common morphology |
|
|
Which of the following is not true regarding PMLE?
A. usually appears in the first three decades B. may be a manifestation of a type IV hypersensitivity reaction C. vesicles and an eczematous dermatitis are a common presentation D. not all exposed areas show lesions E. it may occur through windowglass, which filters out UVB |
Vesicles and eczematous dermatitis are a common presentation-- FALSE
most lesions are erythematous, pruritic papules. The plaque forme is less common, and vesicles and an eczematous dermatitis are rare.
Not all exposed areas show lesions, but the same areas are affected year after year.
It may improve as the summer progresses.
It may occur through window glass. |
|
|
Most patients with PMLE require treatment with:
A. sunscreen and sun avoidance between 11-3 B. UVB hardening C. chloroquine D. prednisone E. cyclophosphamide |
sunscreen and avoidance between 11-3
in very severe cases, UV hardening, antimalarials or prednisone can be used. cyclophosphamide is NOT used in PMLE. |
|
|
All of the following are true regarding PMLE except:
A. pruritic B. abnormal metabolism of arachidonic acid C. hardening occurs with subsequent episodes D. lesions heal without scarring E. anti-Ro positive |
Anti ro positive
if it is, should raise suspicion for subacute cutaneous lupus |
|
|
What is a variant of PMLE that only affects the helices? |
juvenile spring eruption of the ears |
|
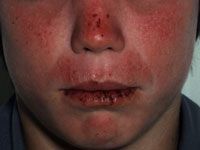
Genetic association? |
Actinic prurigo-- HLA DR4 |
|
|
What is the most common specific eye finding associated with actinic prurigo? |
conjunctivitis: limbal type vernal catarrh (itching, increased tearing, photophobia)
this spelling is actually right, WTF. |
|
|
Hydroa Vacciniforme
Boys or girls? Black or white? Kids or adults? Scarring or nonscarring? UV responsible? |
BOYS WHITE KIDS SCARRING UVA (330-360) |
|
|
Viral association with hydroa vaccinforme? |
EBV!!
the diagnosis of HV may precede a lymphoma by a decade |
|
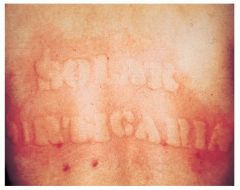
What tests should be considered?
A. ANA B. ANCA C. urinalysis D. CXR E. ESR |
ANA
Solar urticaria is an idiopathic, type I photosensitivity disorder
Rare cases have been a/w erythropoietic protoporphyria and lupus
screen urine porphyrins |
|
|
Solar urticaria:
A. is an idiopathic, type IV photosensitivity B. can present with HA, N, syncope C. rarely lasts for more than 6 mos-1yr D. usually occurs to only UVB radiation E. is not benefitted by antihistamines |
Can present with HA, N, syncope
solar urticaria is a type I photosensitivity mediator release during whealing may results in HA, n, syncope, wheezing this lasts for years tx includes sun avoidance, protection, antihistamines |
|
|
In solar urticaria, when do the wheals begin? How long do they last? |
Begin 10-15 minutes after exposure, last for about 1 hour |
|
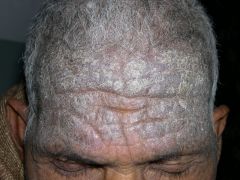
All of the following are true except:
A. affects elderly men B. CD8+ t cells in lesions C. is a premalignant condition D. atypical dermal mononuclear cell infiltrate E. generalized lymphadenopathy is common |
this is NOT a premalignant condition!
chronic actinic dermatitis affects old men, lymphadenopathy is very common, trend towards lower CD4+/CD8+ |
|
|
A 64 year old outdoor worker presented with a chronic lichenified eczematous dermatitis of 25 years. Duration affecting predominantly sun exposed areas. ML cause is exposure to:
A. compositae B. fiberglass C. rhus antigen D. thiuram E. vinyl chloride |
Compositae |
|
|
Photoexacerbated genodermatoses include all except:
A. tuberous sclerosis B. cocayne's syndrome C. hailey-hailey disease D. hartnup disease E. darier's disease |
tuberous sclerosis is not associated with photosensitivity |
|
|
What is pellagra? |
triad of: diarrhea, dermatitis and dementia
dermatitis begins as a burning erythema in sun exposed areas, there may be bullae and erosions, this is followed by a dry, brittle, scaling phase
deficiency of niacin or tryptophan |
|
|
Which medication is classically associated with inducing pellagra like dermatosis? |
isoniazid |
|
|
Which of the following genodermatoses is NOT worsened by sunlight?
A. Darier's disease B. Kindler syndrome C. Hartnup disease D. Rothmund-Thompson syndrome E. Job syndrome |
Job syndrome is not worsened by sunlight |
|
|
Which of the following conditions would be least likely to be photo-exacerbated?
A. Herpes simplex B. Pellagra C. Transient acantholytic dermatosis D. Psoriasis E. Pyrodoxine deficiency |
Psoriasis is improved by phototherapy, especially, NBUVB |
|
|
Which statement is true regarding pseudoporphyria?
A. porphyrins may be normal B. it has been associated with furosemide C. clinically it may be indistinguishable from porphyria cutanea tarda |
All of these are true!
pseudoporphyria is a phototoxic reaciton that clinically and histologically resembles PCT
there is NO porphyrin abnormality
has been associated with numerous medications including NSAIDS (classically naproxen), TCN, furosemide |
|
|
Which medication reactivates UVB and PUVA induced erythema?
A. dacarbazine B. 5-FU C. vinblastine D. methotrexate |
Methotrexate reactivates UVB and PUVA induced erythema
ultraviolet recall |
|
|
Neurologic findings in 20% of XP cases. Which variant? Gene mutation? |
MR, deafness, spacsticity, ataxia MC in XPA
XPA defect in DDB1, MC in Japan
also can be in XPD (ercc2) |
|
|
Most common variant of XP in the US? Gene defect? |
XPC (endonuclease) |
|
|
Cachetic dwarf with sunken eyes, Mickey Mouse ears, what do you need to be aware of? |
Cockayne Syndrome
be aware of progressive neuro degeneration (CNS demyelination, sensorineural hearing loss) and salt and pepper retinal pigmentation cataracts |
|
|
Photosensitivity, hair disorder, infertility, short stature, intellectual impairment
Problem? Gene defect? |
Trichothiodystrophy = P(IBIDS)
photosensitivity, intellectual impairment, brittle hair, icthyosis, decreased fertility, short stature
ERCC2 **wait what?! this is the same as the XPD gene?! NEAT!
Dont forget to check fo ra sulfer deficiency |
|
|
Tiger tail hair? |
decreased cysteine --> decreased sulfer bonds
trichoschisis |
|
|
Early infantile photosensitivity, FTT, short stature, early cancer (avg age 25), high pitched voice |
BLOOM Syndrome |
|
|
Inherited photosensitivities d/t helicase defects? |
Werner syndrome --> RECQL2 Bloom syndrome --> RECQL3 Rothmund Thompson syndrome --> RECQL4
We Bloom and Rot in Hel(icase) |
|
|
Features of Bloom syndrome? Mutation? |
photodistributed butterfly erythema, telangiectasias, CALMs, high pitched voice, short stature
Mutation in RECQL3 helicase |
|
|
How do we diagnose Bloom syndrome? |
photodistributed butterfly erythema, telangiectasias, CALMs, high pitched voice, short stature
Mutation in RECQL3 helicase
amniocentesis, low IgA, low IgM --> recurent respiratory/GI infections
|
|
|
If you dx someone with Bloom syndrome, what consults do you want to put in? |
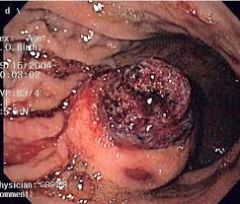
a/w ALL, GI adenocarcinoma
looks like a carcinoma blooming in the colon |
|
|
What is Rothmund Thompson syndrome? |
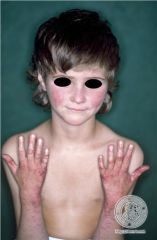
AR mutation in RECQL4 (We Bloom and Rot in hell(icase))
early poikiloderma and reticulated patches (esp on butt) in not just SES, alopecia, juvenile cataracts, osteosarcoma, absent radium, absent thumbs, short stature |
|
|
DX patient with Rothmund Thompson, what consults do you want to put in? |
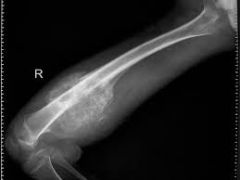
Ophtho (juvenile cataracts in 50%) Ortho (osteosarcoma, absend radium, absend thumbs) |
|
|
Time difference between phototoxicity and photoallergy? |
Phototoxicity- erythema in 2-6 hours
Photoallergy- erythema in 7-10 days |
|
|
What is the most common type of porphyria? Mutation? |
Porphyria cutanea tarda- deficiency of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase
look at hep C, hemochromatosis, homeless, alcoholic, hypertrichosis, hyperpigmentation (hands), milia (hands) |
|
|
How do we diagnose porphyria cutanea tarda? |
port wine urine, brignt pink flurescence under woods lamp
elevated uroporphyrin in urine |
|
|
Most common cause of pseudoporphyria? |
Pseudoporphyria AKA drug induced porphyria
NAPROSYN |
|
|
Deficiency of ferrochelatase? |
Erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP)
EPP starts with E, lacks ferrochEEEEEElatase |
|
|
Erythropoietic protoporphyria begins in childhood with burning and redness in the sun, abnormal LFTs, cirrhosis, gallstones. Treatment? |
Treat with beta- carotene
remember this is d/t deficiency of ferrochelatase |
|
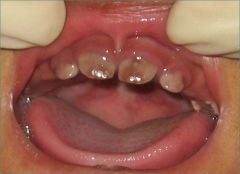
Defect? |
EW.
defect in uroporphyrinogen 3 cosynthetase
'UR t33th are colored' |

