![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are bacteriophages? |
Viruses that infect bacteria |
|
|
What is the size of phages? |
20-200nm |
|
|
What are the advantages of phages as medicine? |
- only kill harmful pathogens - active against antibiotic-resistant bacteria - safe and cheap to produce - grown on bacteria |
|
|
What is T4? |
dsDNA phage complex structure - a head and contractile tail with attached tail fibres |
|
|
What is the structure of T4? |
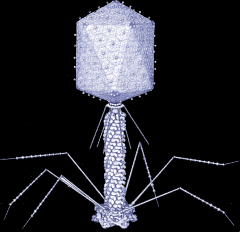
|
|
|
What is the length of time for T4 life cycle? |
30 minutes |
|
|
How does T4 adsorb to the cell? |
Binds to specific surface receptorsbacterial cell - cell wall LPS, teichoic acid, flagella, pili |
|
|
How does T4 penetrate the cell? |
transfer phage nucleic acid genome into the bacterial cell Requires lysozyme activity to break down peptidoglycan in the cell wall DNA/RNA from phage head into cell |
|
|
How does the tail enter the cell? |
T4 tail sheath contracts from cylinder of 24 to 12 rings and tail drawn through outer membrane Forces T4 tail tip composed of gp5 & gp27 is forced into the cell wall Cuts through peptidoglycan layer using lysozyme subunits around central barrel |
|
|
What is the structure of the T4 head? |
12 different proteinsincludes 120 hexamers of gp23 and 11 pentamers of gp24 |
|
|
How is the head structure composed? |
DNA is packed tightly in the phage head Packaging motor used until the head is ful 5 mins |
|
|
How is the cell lysed? |
Phage punctures holes in the membrane and uses enzymes to breakdown the cell wall Phage holins trigger to form non-specific lesions in membrane via assembly of rings |
|
|
What are the two options for phage lambda? |
CI - lysogeny Cro - lytic, stressed so Cro cleaved |
|
|
Give an example of a ssRNA phage? |
Leviviridae |
|
|
Give an example of a dsRNA phage? |
Cystoviridae phage envelope fuses with bacterial outer membrane to deliver phage into cell RNA replicase copies three dsRNA segments that comprise genome to make mRNA & dsRNA |

