![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the parts of an animal cell moraines
|
Nucleus
Cytoplasm Cell membrane Mitochondria |
|
|
What does the nucleus do?
|
Contains DNA which contains instructions for making proteins
|
|
|
What is the cytoplasm?
|
A gel like substance where proteins like enzymes are made and some enzyme-controlled reactions take place on the cytoplasm
|
|
|
What does the cell membrane do?
|
Holds the cell together and controls what comes in and out
|
|
|
What do the mitochondria do?
|
They contain the enzymes needed for aerobic respiration and where the reactions take place
|
|
|
What do plant cells have that animal cells don't have?
|
A strong rigid cell wall - made of cellulose and supports and strengthens the cell
Vacuole - contains cell sap Chloroplasts - where the reactions for photosynthesis take place (contain the enzyme chlorophyll) |
|
|
How many cells are yeast microorganisms made up of?
|
One
|
|
|
Describe the structure of a yeast cell
|
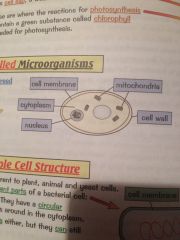
|
|
|
What replaces a nucleus in a bacteria cell?
|
A circular molecule of DNA which floats around in the cytoplasm
|
|
|
Describe the structure of a bacteria cell
|
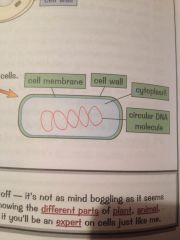
|
|
|
What is a protein?
|
An enzyme that speeds up chemical reactions
|
|
|
What is a substrate?
|
A molecule that is changed in a reaction
|
|
|
What is the active site?
|
The place in every enzyme where a substrate joins in on the enzyme
|
|
|
What is the 'lock and key' model?
|
The substrate has to be the correct shape to fit the active site
|
|
|
What happens if the temperature of an enzyme gets too hot or the pH is too high/low?
|
Some of the bonds holding the enzyme together break which changes the shape of the active site so the substrate no longer fits - it's denatured
|
|
|
What is respiration?
|
A series of chemical reactions that release energy by breaking down large food molecules
|
|
|
What is the energy released from respiration used to power?
|
Movement - energy to make muscles contract
Active transport - energy to move substances in and out of cells Synthesis of large molecules - made by joining smaller molecules together e.g glucose and nitrogen make amino acids |
|
|
What is aerobic respiration?
|
Respiration with oxygen
Releases more energy per glucose molecule than anaerobic Used most of the time |
|
|
What is the word equation for aerobic respiration?
|
Glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water (+energy)
|
|
|
What is the symbol equation for aerobic respiration?
|
C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 + 6H2O
|
|
|
What is anaerobic respiration?
|
Respiration without oxygen
|
|
|
Give examples of anaerobic respiration
|
(Humans) vigorous exercise means your body can't supply enough oxygen to your muscle cells
(Plants) if a plants soil becomes waterlogged (Bacteria) if it gets under your skin - there's very little oxygen |
|
|
What can glucose make,
|
Animals and bacteria-
Lactic acid Plant cells and some microorganisms - Ethanol and carbon dioxide |
|
|
What is fermentation?
|
When microorganisms break down sugars into other things as they respire anaerobically
|
|
|
Give examples of fermentation
|
Alcohol - yeast ferment sugar to form ethanol
Biogas - microorganisms ferment plant and animal waste which contain carbohydrates and produce carbon dioxide Bread - yeast ferments the carbohydrates and releases carbon dioxide causing it to rise |
|
|
What is photosynthesis?
|
A series of chemical reactions that she energy from sunlight to produce food
|
|
|
What is the word equation for photosynthesis?
|
Carbon dioxide + water = glucose + oxygen
|
|
|
What is the symbol equation for photosynthesis?
|
6CO2 + 6H2O = C6H12O6 + 6O2
|
|
|
In what three main ways do plants use glucose?
|
For respiration
To make chemicals for growth - cellulose for cell walls, chlorophyll, and combines with nitrogen to make amino acids Stored as starch - stored in roots, stems and leaves for when photosynthesis is slower (e.g winter) |
|
|
What three factors affect the rate of photosynthesis?
|
Light
Cabin dioxide Temperature |
|
|
Why does a light graph only go up to a certain point?
|
Light provides the energy needed for photosynthesis
But it will stop increasing because the temperature or CO2 will be a limiting factor |
|
|
Why is temperature the limiting factor usually?
|
Because the temperature can't exceed 45 degrees as this would denature them
|
|
|
How do you take a transect and what do they do?
|
They investigate how something changes across an area
You run a tape measure between two fixed points and collect the data you want across it |
|
|
Name 3 ways of collecting data
|
Light metre
Quadrat Identification key |
|
|
What is a light metre?
|
A sensor that accurately measures light level e.g compare plants in areas with different levels of light
|
|
|
What is a quadrat?
|
A square frame divided into a grid of 100 squares so you can estimate the percentage cover of something
|
|
|
What is an identification key?
|
A series of questions asked so that you can use them to figure out what a plat is
|
|
|
What is diffusion?
|
The passive overall movement of particles from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration
|
|
|
What is osmosis?
|
The movement of water from a dilute to a more concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane
|
|
|
An example of osmosis
|
Water passes through a partially permeable membrane and the concentrate sucrose solution gets more dilute as more water moves in
|
|
|
What is active transport?
|
The movement of chemicals across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to higher concentration using energy released by respiration
|
|
|
An example of active transport?
|
Plants take in minerals like nitrates through their roots and the concentration of minerals in root cells is higher than in the soil around them
|

