![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a habitat?
|
Where a plant or animal lives
|
|
|
All the animals and plants living in a habitat makes up a ____
|
community
|
|
|
How is the distribution of organisms measured.
|
Transect line
|
|
|
How is distribution of organisms displayed?
|
Kite diagram
|
|
|
What can cause zonation?
|
Exposure on a seashore or trampling near a footpath.
|
|
|
What do food chains show?
|
Interdependance
|
|
|
What does the capture-recapture method ensure?
|
-No deaths or reproduction
-Identical sampling methods for both samples -Markings don't affect the survival of woodlice |
|
|
How can you make a quadrat estimation more accurate?
|
Bigger quadrat and more samples
|
|
|
How does the capture-recapture method work?
|
Some animals are trapped, e.g. using pitfalls. They are marked in some harmless way then released. Traps are used a few days later.The numbers of marked and unmarked animals caught in the traps are recorded.
|
|
|
What equation is used to estimate population size using the capture recapture method?
|
(number 1st sample x number 2nd sample)
DIVIDED BY number in 2nd sample previously marked |
|
|
Balanced symbol equation for photosynthesis?
|
6CO2 + 6H2O --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
|
|
|
What is glucose used for in plants?
|
-Respiration
-Converted to cellulose to make cell walls -Converted to proteins for growth & repair -Converted to starch, fats and oils for storage |
|
|
Why is starch used for storage?
|
It is insoluble and does not move from storage areas. Unlike glucose it doesn't impact water concentration by osmosis.
|
|
|
What are the two main stages of photosynthesis?
|
1. Water is split up by light energy, releasing oxygen gas and hydrogen ions
2. C02 gas combines with the hydrogen ions producing glucose and water |
|
|
What did Greek scientists think plants did to get minerals?
Because for some reason we need to know what some crusty ass old person thought about soil and crud like that. I'm not bitter. |
Plants took minerals out of the soil to grow and gain mass. But Van Helmont's study on a willow tree shut this down
|
|
|
What is Priestly's experiment show?
|
Plants produce oxygen
|
|
|
What modern experiments have we done to prove that light energy splits water?
|
Chlorella and an isotope of oxygen (18O).
|
|
|
How is the rate of photosynthesis increased?
|
-More carbon dioxide
-More light -Higher temp to increase enzyme action |
|
|
How are some plant cells adapted to photosynthesis?
|
-Outer epidermis is transparent & there's no chloroplasts to there's no light barrier
-Upper palisite has most of the chloroplasts because its get the most light -Spongy mesophyll cells are loosely spaced so diffusion of gasses between cells can happen -They're also large so large amounts of gas can enter and exit cells |
|
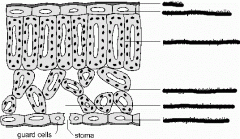
what dis
|
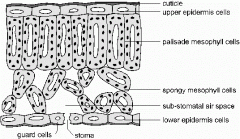
|
|
|
How are leaves adapted to make photosynthesis efficient?
|
-Stomata for entry and exit -Spongy cells covered in water to dissolve gas -Large surface area-Thin so gas diffuses easily -Chlorophyll and other pigments so light from all over the spectrum can be used -Vascular bundles: support & chemical transport -Specialised guard cells control CO2 , oxygen and water loss |
|
|
How do chlorophyll maximise use of the Sun's energy?
|
Different pigments absorb light of different wavelengths. There's chlorophyll, carotene and xanthophylls for example.
|
|
|
What is diffusion?
|
The net movement of particles in gas or liquid from an area of high concentration to low concentration.
|
|
|
How does water, oxygen and carbon dioxide enter the cell membrane?
|
Through diffusion.
|
|
|
How can the rate of diffusion be increased?
|
-Shorter distance for molecules to travel
-Steeper concentration gradient (greater difference between the two areas) -Greater surface area |
|
|
What is osmosis?
|
The net movement of water across a partially permeable membrane from an areas of high water concentration to low.
|
|
|
What causes osmosis?
|
Random movement of water molecules which is not restricted by a partially permeable membrane
|
|
|
What needs to be present for osmosis to take place?
|
A partially permeable membrane
|
|
|
What is turgor pressure?
|
Water pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall of plant, bacteria, and fungi cells
|
|
|
Why do plants wilt?
|
When too much water leaves the cell, it loses turgor pressure- which is what keeps the plant rigid.
|
|
|
When does a cell become flaccid?
|
When the cell loses water and becomes plasmolysed.
|
|
|
What happens when too much water leaves a cell?
|
It shows crenation by shrinking into a scalloped shape
|
|
|
What happens when too much water enters the cell?
|
Swell up and burst- AKA lysis
|
|
|
What are the xylem and phloem made of?
|
Specialised plant cells. Vascular bundles in wide leaved plants.
|
|
|
What does the xylem do?
|
Carry water and minerals from the roots to the leaves
|
|
|
What does the phloem do?
|
Carry food substances such as sugars up and down stems to growing storage tissues.
|
|
|
What is translocation?
|
The transport of food substances via the phloem.
|
|
|
Xylem structure?
|
They're dead cells with no living cytoplasm meaning a hollow lumen. Their cellulose walls have extra thick lignin. No, that's not a typo. That lignin is for strength and support.
|
|
|
What is the structure of the phloem?
|
Living cells arranged in columns.
|
|
|
What is transpiration?
|
Evaporation and diffusion of water inside leaves.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of transpiration in plants?
|
Create a continuous flow of water from the roots to the leaves in xylem cells for cooling by evaporation, photosynthesis, and turgor pressure.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of root hairs?
|
Produce a large surface area for osmosis.
|
|
|
How do you increase the rate of transpiration?
|
-Higher light intensity to open stomata
-Increase temp to increase evaporation -More air movement moves away water vapour -Decrease humidity allowing more water to evaporate |
|
|
How is leaf structure adapted to reduce water loss?
|
-Waxy cuticle covering outer epidermis and most stomatal openings
-Guard cells change size of stomatal openings -Guard cells contain chloroplasts which make sugars and increase turgor pressure -Fewer/smaller stomata |
|
|
What are nitrates needed for in plants?
|
To make amino acids/proteins for cell growth
|
|
|
What are phosphates needed for in plants?
|
Involved in respiration and growth.
Phosphorus: Used to make DNA and cell membranes. |
|
|
What are potassium compounds needed for in plants?
|
Involved in respiration and photosynthesis.
Potassium: Help enzyme action to speed up the former. |
|
|
What are magnesium compounds needed for in plants?
|
Involved in photosynthesis.
Magnesium: Used to make chlorophyll, which is essential for photosynthesis. |
|
|
What does lack of nitrates cause?
|
Poor growth and yellow leaves
|
|
|
What does lack of phosphate cause?
|
Poor root growth and discoloured leaves.
|
|
|
What does lack of potassium cause?
|
Poor flower and root growth and discoloured leaves.
|
|
|
What does lack of magnesium cause?
|
Yellow leaves
|
|
|
How do minerals enter a cell?
|
Taken up by root hair cells by active transport.
|
|
|
Explain the process of active transport in plants
|
Dissolved molecules move across a cell membrane from a lower to a higher concentration (against concentration gradient) & requires energy from the cell, unlike osmosis. Carrier proteins pick up specific molecules and take them through the cell membrane.
|
|
|
Explain active transport in humans
|
It takes place during the digestion of food in the small intestine. Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars such as glucose. The glucose is absorbed by active transport into the villi, to be passed into the bloodstream and taken around the body.
|
|
|
Give some example of detritivores
|
Earthworms, maggots, woodlice
Saprophyte (fungus) |
|
|
What are detritivores?
|
Organisms that feed on decaying material.
|
|
|
How do detritivores increase the rate of decay?
|
Breaking up the decaying matter and so increasing surface area for further microbial breakdown.
|
|
|
What is extracellular digestion?
|
Fungi produce enzymes to digest food outside their cells and then reabsorb the simple soluble substances.
|
|
|
How does canning preserve food?
|
Heated to kill bacteria then sealed in a vacuum to prevent entry of oxygen and bacteria.
|
|
|
How does cooling preserve food?
|
Slow down bacterial and fungal growth and reproduction.
|
|
|
How does freezing preserve food?
|
Kill some bacteria and slow down others.
|
|
|
How does drying foods preserve it?
|
Removes water so bacteria cannot feed and grow.
|
|
|
How does adding salt or sugar preserve food?
|
Will kill some bacteria and fungi as the high osmotic concentration will remove all water from them.
|
|
|
How does adding vinegar preserve food?
|
Very acidic conditions kill most bacteria and fungi.
|
|
|
What are the disadvantages of insecticides, fungicides and herbicides?
|
-Enter and accumulate in food chains leading to a lethal dose for the predators.
-Harm organisms that aren't pests. -Some take a long time to break down and be harmless |
|
|
What do organic farmers do to avoid using chemicals?
|
Use compost
Crop rotation to avoid build up of soil pests Varied seed planting time |
|
|
What is biological control?
|
Using living organisms to control pests, for example ladybirds eat aphids.
|
|
|
What risks does use of biological control present?
|
-The predators can kill useful things too
-Build up of the predator can mean they themselves become a pest- e.g. cane toads in Australia. |
|
|
Explain the hydroponic process
|
Crops are planted in an inert material such as gravel/sand or water. Fertiliser solution is then pumped with water through the material where the roots get it. There's water being pumped in too. Water and minerals are extracted the other side then reused.
|
|
|
What crop is often made with hydroponics?
|
Tomatoes
|
|
|
What are the benefits of using hydroponics?
|
Better control over mineral levels and disease.
Many plants grown in small space. |
|
|
Benefits of intensive farming?
|
Good efficiency and less energy used to keep things warm because animals are kept in such grossly overcrowded places!
|

