![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
3 components of an amino acid |
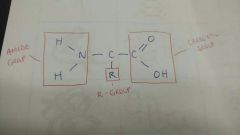
1. Amide group 2. Carboxyl group 3. R-group |
|
|
|
What are the bonds formed when amino acids link together? |
Peptide bonds |
|
|
|
6 functions of proteins |
1. Enzymes - Speed up rxns 2. Structural - Muscles, tendons, etc 3. Movements - Muscle fibres 4. Defense - Antibodies 5. Transport - Hemoglobin, channel proteins 6. Regulatory - insulin, hormones |
|
|
|
What gives proteins their shapes in each stage? |
Primary - Due to sequence of amino acids Secondary - Due to peptide bonds being polar; hydrogen bonds form Tertiary - Due to bonding between R-groups Quaternary - When 2 or more polypeptides (3e) connect together |
|
|
|
Describe denaturation |
- Weak hydrogen and ionic bonds holding tertiary structure together can easily be broken - Change in temp, pH, or presence of heavy metal ions can destroy the normal shape of protein - Makes the protein (ie. Enzyme) non-functional |
3 points |

