![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
119 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Whats ecosystem? |
Such as garden is made up of all plants and animals living there and their surrounding |
|
|
|
Whats habitat? |
Where a plant/animal lives |
|
|
|
All the plants and animals living in the garden make up the _____ ? |
Community |
|
|
|
The number of a particular plant or animal present in the community is called what? |
Population |
|
|
|
Examples of natural ecosystems ? |
Native woodlands Lakes |
|
|
|
What means biodiversity? |
The sum of different type of species in specific place. A lot of different species means it's a good biodiversity |
|
|
|
Natural ecosystem (E.g. lakes and native woodlands) is a good or bad biodiversity? |
Good as it has many different types of species |
|
|
|
Artificial ecosystem (E.g. fish farms) is a good or bad biodiversity? |
Bad as it has low amount of different species |
|
|
|
Remember! |
The distribution of organisms can be mapped using a transect line. A long lengjt of string is laid across an area such as path or sea shore. At regular intervals the organisms in a square frame called a quadrant can be counted (for animals) or assessed for percentage cover (for plants). The data can be displayed as a kite diagram |
|
|
|
What happens in artificial ecosystems that doesn't in natural ecosystems? |
In artificial ecosystem, humans deliberately keep and protect only one species (such as salmon in fish farm ) and remove any other organism that would compete with it and lower the yield. |
|
|
|
Whats zonation? |
gradual change in the distribution of species across a habitat is called zonation. |
|
|
|
What can show zonation? |
A transect line in kite diagram |
|
|
|
What can cause zonation? |
Changes in abiotic (not biological) factors such as exposure on a sea shore or trampling near a footpath, cause zonation |
|
|
|
How does food chains and food webs show that plants and animals are interdependent? |
Because of all the energy being transferred from one organism to another. The exchanges of gasses in photosynthesis and respiration ensures an overall balance of these gases. An ecosystem is therefore self supporting in all factors apart from having to have the sun as an energy source. |
Related to gases. |
|
|
When using the capture-recapture method, it assumes what 3 things? |
- there are no deaths or reproduction and no movement of animals into and out of the area - identical sampling methods are used for both samples - the markings do not affect the survival of the woodlice |
|
|
|
Photosynthesis equation |
CO2 + H2O -> C6H12O6 + O2 |
|
|
|
What can your body do with simple sugars such as glucose? |
• used in respiration, releasing energy • converted into cellulose to make cell walls • converted into proteins for growth and repair • converted into starch, fats and oils for storage |
|
|
|
Why is starch used as storage? |
Because it's insoluble and does not move from storage areas. |
|
|
|
What does starch not affect in our body that glucose does? |
unlike glucose, It doesn't affect the water concentration of cells and cause osmosis . |
|
|
|
Photosynthesis is a two staged process. Whats the process? |
- Water is split up by light energy releasing oxygen gas and hydrogen ions - carbon dioxide gas combines with the hydrogen ions producing glucose and water |
|
|
|
Whats isotopes? |
Same element with different amount of neutrons E.g. O18 |
|
|
|
Rate of photosynthesis can be increased by what 3 things? |
More carbon dioxide More light A higher temperature which increases enzyme action |
|
|
|
When do plants respire? And at daytime what takes place? |
Plants respire at all times by taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide . In day time they also photosynthesis |
|
|
|
Respiration cannot be noticed in day time but only at night. Why? |
Daytime: photosynthesis takes place and the rate of gas exchange in photosynthesis is much are than respiration in terms of quantities.
Night; photosynthesis doesn't take place at night |
|
|
|
What does limiting factor mean in photosynthesis ? |
Since photosynthesis depends on light, temperature and carbon dioxide, a lack of one of these factors will limit the rate of photosynthesis. they are called limiting factors. |
|
|
|
What specialised cells does green leafs have? |
Outer epidermis Upper palisade layer Spongy mesophyll cells |
There's 3 of them... |
|
|
How are outer epidermis in green leafs adapted for efficient photosynthesis? |
The outer epidermis lacks chloroplasts and so you s transparent; there are no barriers to the entry of light |
|
|
|
How are upper palisade layer in green leafs adapted for efficient photosynthesis ? |
The upper palisade layer contains most of the leafs chloroplasts, as they will receive most of light |
|
|
|
How are spongy mesophyll cells in green leafs adapted for efficient photosynthesis? |
The spongy mesophyll cells are loosely spread so that diffusion of gases between cells and the outside atmosphere can take place.
|
|
|
|
How are leafs adapted for efficient photosynthesis? (Not related to specialised cells) |
* They are usually broad so that they have a large surface area to get as much light as possible. *They are usually thin so that gases can diffuse through easily and light can get to all cells |
2 basic points |
|
|
What do vascular bundles (veins) do in leaves for efficient photosynthesis? |
Leaves have a network of vascular bundles (veins) for support and transport of chemicals such as water and glucose |
|
|
|
What do guard cells do in leaves for efficient photosynthesis? |
Leaves have specialised guard cells which control the opening and closing of stomata therefore regulating the flow of carbon dioxide and oxygen as well as water loss. |
|
|
|
What controls stomata from opening and closing? |
Guard cells |
|
|
|
Why do plants have many pigments? |
By having many pigments (chlorophyll a and b, carotene and xanthophylls ) the plant cells can maximise the use of the sun's energy. Each pigment absorbs light of different wavelength. |
|
|
|
Whats diffusion? (Definition needs to be word by word) |
Diffusion is the net movement of particles in gas or liquids from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, resulting from the random movement of the particles. |
|
|
|
Diffusion explains how molecules of water, oxygen and carbon dioxide can enter and leave cells through cell membrane. Give example of diffusion regarding carbon dioxide and plants. |
If a plant cell is using up carbon dioxide, there is lower concentration of it inside the cell, so the carbon dioxide will enter by diffusion |
|
|
|
How are leaves adapted to increase the rate of diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide? |
- By having (usually) large surface area. - specialised openings called stomata which are spaced out - gaps between spongy mesophyll cells
|
|
|
|
The rate of diffusion is not fixed quantity. The rate can be increased by having what? (3 things) |
* a shorter distance for the molecule to travel * a steeper concentration gradient (greater difference in concentration between the two areas) * a greater surface area for the molecules to diffuse from or into |
|
|
|
Osmosis is a type of d......? |
Diffusion |
|
|
|
What does osmosis require to be present? |
It depends on the presence of a partially-permeable membrane that allows the passage of water molecules but not large molecules like glucose |
|
|
|
What's osmosis? (Word by word answer) |
Osmosis is the movement if water across a partially permeable membrane from an area of high water concentration (a dilute solution) to an area of low water concentration (a concentrated solution) |
|
|
|
How can we predict the net movement of water molecules during osmosis? |
By knowing the different concentrations of water inside and outside cells make it possible to predict the net movement of water molecules |
|
|
|
What stops plant cell from collapsing? |
By the pressure of water inside it that is pushing on the cell wall which is rigid and not elastic. |
|
|
|
Tip |
The entry of water into plant cells increases the pressure pushing on the cell wall, which is rigid not elastic. This turgor pressure supports the cell, stopping it, and the whole plant, from collapsing. When too much water leaves a cell, it loses this pressure and plant wilts. |
|
|
|
A plant cell full of water is to be _________ . When the cell loses water the fell contents shrink and become ________ and the cell is called ______ . |
A plant cell full of water is to be turgid . When the cell loses water the fell contents shrink and become plasnolysed and the cell is called flaccid. |
|
|
|
What will happen if animal cell lose too much water and when too much enters? |
Loses too much water = shrink and collapse Too much enter = swell up |
|
|
|
Animals lack a supporting cell wall and so when too much water enters, what might happen?(osmosis related) |
They will swell up and burst (lysis) |
|
|
|
Whats lysis? |
When animal cell gets too much water while it doesn't have cell wall to support it and as an result, swells up and bursts |
|
|
|
When too much water leaves animal cell, it shows what and by what? |
It shows cremation by shrinking into a scalloped shape |
|
|
|
Xylem and phloem are made of what? |
Specialised plant cells |
|
|
|
Where are phloem and xylem in plant? |
Both tissues are continuous from the root, through the stem and into the leaf |
|
|
|
What do xylem and phloem form? |
Vascular bundles (veins) |
|
|
|
What do xylem carry? |
Water and minerals from roots to the leaves. (Involved in transpiration ) |
|
|
|
What do phloem carry? |
Food substances such as sugars up and down stems to growing and storage tissues. This transportation is called translocation |
|
|
|
Phloem transport of food is called what? |
Translocation |
|
|
|
Xylem cells are called vessels. They are _____ cells and the lack of living cytoplasm leaves a ______ ______ . Their cellulose walls have extra _____ of lignin, giving great strength and support. |
Xylem cells are called vessels. They are dead cells and the lack of living cytoplasm leaves a hollow lumen . Their cellulose walls have extra thickening of lignin, giving great strength and support. |
|
|
|
Phloem are what cells and what about them? |
Phloem are living cells that are arranged in columns |
|
|
|
Xylem are involved in what process? |
Transpiration |
|
|
|
Phloem cells are in involved in what process? |
Translocation |
|
|
|
Whats transpiration? |
Transpiration is the evaporation (liquid -> gas) and diffusion of water from inside leaves. |
|
|
|
Remember |
Transpiration is the evaporation (liquid -> gas) and diffusion of water from inside leaves. This loss of water from leaves helps to create a continuous flow of water from the roots to the leaves in xylem cells |
|
|
|
Roots hair are what? |
Projections from root hair cells |
|
|
|
What do roots hair do? |
Produce large surface area for water uptake by osmosis |
|
|
|
By what process do root hairs take in water? |
Osmosis |
|
|
|
Transpiration ensures that plants have what? (2 things ) |
- water for cooling by evaporation - photosynthesis and support from cells turgor pressure and for transport of minerals |
|
|
|
What can increase the rate of transpiration ? |
* increase of light intensity = stomata being open * increase in temperature = increase of water evaporation * increase in air movement = blowing away air that contains the evaporation of water * decrease in humidity( amount of water vapour in atmosphere) = allowing more water to evaporate |
|
|
|
How does guard cells control stomata + How do plants deal with reducing water loss ? |
- Guard cells have chloroplasts so photosynthesis (in presence of water and light) will produce sugars causing turgor pressure onto plant cells to Increase as well as making them swell up. Due to the turgor pressure, the guard cells curve opening the stoma
- further reduction in water lose is by having fewer stomata, smaller stomata, the position of stomata (usually in the lower epidermis) , and their distribution
|
|
|
|
What minerals do plants need? (4) |
• nitrates = make proteins = cell growth • phosphates = respiration & growth • potassium = involved in respiration and photosynthesis • magnesium = involved in photosynthesis |
|
|
|
Nitrogen in plants is used to produce what? |
Amino acids to form proteins |
|
|
|
In plants phosphorus is used to make what? |
DNA |
|
|
|
In plants potassium is used to do what? |
To help enzymes action in photosynthesis and respiration (enzymes speed up chemical reactions ) |
|
|
|
In plants, magnesium is used for what? |
To make chlorophyll which is essential for photosynthesis |
|
|
|
In plant lack of nitrate = ? |
Poor growth and yellow leaves |
|
|
|
In plant lack of phosphate = ? |
Poor root growth and discoloured leaves |
|
|
|
In plants lack of potassium = ? |
Poor flower and root growth and discoloured leaves |
|
|
|
In plants lack of magnesium = ? |
Yellow leaves |
|
|
|
Minerals are usually in soil in what concentrations? |
Low |
|
|
|
Root hairs absorb what? |
Water |
|
|
|
Minerals are taken up by root hairs cells by active _____ |
Active transport |
|
|
|
Active transport in plants is what kind of system? |
A system of carriers transport selected minerals across the cell membrane |
|
|
|
Remember! |
Minerals uptake involves active transport ,rather than diffusion or osmosis |
|
|
|
Active transport enables minerals, present in the soil only in ____ concentrations , to enter root hairs already containing _____ amounts of minerals |
Active transport enables minerals, present in the soil only in low concentrations , to enter root hairs already containing higher amounts of minerals |
|
|
|
In plants, the uptake of minerals against a concentration gradient requires what? |
Energy from respiration |
|
|
|
3 examples of detritivores |
Earthworms Woodlice maggots |
|
|
|
What's detritivores? |
Organisms that feed on dead and decaying material (detritus) |
|
|
|
Detritivores feed on the dead and decaying material that is known as what? |
Detritus |
|
|
|
How do detritivores increase the rate of decay? |
By breaking up the detritus and so increase the surface area for further microbial breakdown |
|
|
|
The rate of decay can be increased by what 3 things? |
Increase in... ° temperature ° oxygen ° water |
|
|
|
Increase in temperature will increase rate of decay - why? |
Increasing the temperature to an optimum of 37°C for bacteria or 25°C for fungi will increase their rate of respiration. Higher temperature will denature enzymes |
|
|
|
Why increase in the amount of oxygen will increase rate of decay? |
Increasing the amount of oxygen, bacteria will use aerobic respiration to grow and reproduce faster |
|
|
|
Increasing the amount of water will increase the decay rate - why? |
Increasing the amount of water will allow material to be digested and absorbed more efficiently and increase growth and reproduction of bacteria and fungi |
|
|
|
Example of fungi that's detritivores |
Saprophyte |
|
|
|
What'S extracellular digestion? |
Fungi produce enzymes to digest food outside their cells and then reabsorb the simple soluble substances. This type of digestion is called extracellular digestion |
|
|
|
When it comes to canned food, how do they reduce the rate of decay? |
Heated to kill bacteria and then sealed in a vacuum to prevent entry of oxygen |
|
|
|
Why do we freeze as well as cool down our food? |
Cooling food will slow down bacterial and fungal growth and reproduction Freezing food will kill some bacteria and fungi and slow down their growth and reproduction |
|
|
|
How does drying food decrease rate of decay? |
Drying foods removes water so bacteria cannot feed and grow |
|
|
|
How does adding salt or sugar decrease rate of decay in food? |
Adding sugar or salt will kill some bacteria and fungi, as the high osmotic concentration will remove water from them |
|
|
|
How does adding vinegar to foods reduce rate of decay? |
Adding vinegar will produce very acid conditions killing most bacteria and fungi |
|
|
|
Methods we use to decrease rate of decay in foods? |
° foods sealed in a vacuum can ° cooling food ° freezing food ° drying food ° adding salt or sugar to food ° adding vinegar to food |
|
|
|
Remember! |
Keeping food cool in a refrigerator only slows down the growth of bacteria. It doesn't stop it completely |
|
|
|
3 pesticides |
Insecticides fungicides Herbicides |
Insects fungi and herbs |
|
|
Disadvantages of using pesticides (fungicides, herbicides, insecticides) ? |
• they can enter and accumulate in food chains causing a lethal dose to predators • they can harm other organisms living nearby which are not pests • some are persistent (take a very long time to break down and become harmless) |
3 points |
|
|
Organic farming doesn't use what that intensive farming do? |
Artificial fertilisersPesticides s Pesticides |
|
|
|
Instead of fertilisers and pesticides, organic farming uses what? |
Manure Compost |
|
|
|
What is crop rotation for? |
To avoid build up of soil pests |
|
|
|
What method do people use for organic farming to avoid build up of soil pests? |
Crop rotation |
|
|
|
Why do seed planting vary throughout year in organic farming? |
To get a longer crop time and avoid certain times of the life cycle of insect pests |
|
|
|
differences between products from intensive and organic farming? |
Organic farming = smaller crops and produce more expensive but people believe organic food is most healthy and tastes better Intensive = bigger, cheaper |
|
|
|
Whats biological control? With 1 E.g. |
Using living organisms to control pests. E.g. using ladybirds and wasps to eat alphids which damage plants |
|
|
|
Advantage of biological control? |
Unlike insecticides, they dont need replacing once introduced |
|
|
|
Disadvantage of biological control? |
- introduce new species to the area such as new pests |
|
|
|
In what is intensive farming efficient at? |
Producing large crop yields cheaply |
|
|
|
What are the concerns regarding intensive farming? |
Intensive farming methods raise concerns about animal cruelty as animals are kept in small areas and about the effects of extensive use of chemicals on soil structure and other organisms |
|
|
|
Common method in intensive farming to grow plants? |
Method where crops are grown without soil using hydroponics |
|
|
|
What's hydroponics system? |
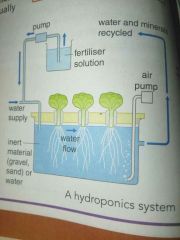
This system uses a regulated recycling flow of aerated water containing minerals and is usually done in glasshouse and polytunnels |
|
|
|
Tip |
Hydroponics is a form of intensive farming |
|
|
|
Where is hydroponics usually done in? |
Glasshouse Polytunnels |
|
|
|
Advantages of hydroponics ? |
- better control over mineral levels and diseases - small amount of space needed for one plant - useful in areas that have low amount of rain |
|
|
|
Example of what crop is grown in hydroponics |
Tomatoes |
|

