![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What happens within the ribosomes? |
Protein synthesis using amino acids
|
|
|
What happens in the mitochondria?
|
Respiration to release energy
|
|
|
What is the function of a cell membrane?
|
Controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell
|
|
|
What happens in the cytoplasm?
|
Chemical reactions, controlled by enzymes
|
|
|
What is in the nucleus?
What is the function of the nucleus? |
Genetic information
Controls all activity in the cell |
|
|
What is the purpose of a cell wall?
|
Strengthen the cell
|
|
|
What is the function of a chloroplast?
|
Contain chlorophyll which absorbs light for photosynthesis
|
|
|
What is in a permanent vacuole?
What is its purpose? |
Cell sap
Keep the cell turgid (enlarged with water) |
|
|
How is a red blood cell specialised?
|
No nucleus to provide more space
Packed full of haemoglobin to absorb oxygen Thin outer membrane to let diffusion of oxygen happen easily Shape increases surface area |
|
|
How is an ovum specialised?
|
Large cell to carry food reserves for the embryo
|
|
|
How is a white blood cell specialised?
|
Has the ability to change shape so it can destroy or engulf a pathogen successfully
|
|
|
What are the features of a bacterial cell?
|
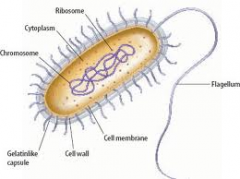
Single bacterium
No nucleus Cytoplasm Cell membrane Cell wall Flagellum |
|
|
What are the features of a yeast cell?
|
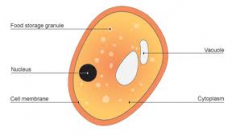
Single-celled fungus
Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell membrane Cell wall Vacuole |
|
|
What substances do cells have to constantly replace?
What substance do cells have to constantly remove? |
Oxygen and glucose for respiration
Carbon dioxide |
|
|
What can pass in and out of cells through diffusion?
|
Gases
Substances in a solution |
|
|
What is diffusion?
|
Spreading of the particles of a gas or substance in a solution
Net movement from an area of higher concentration to a region with a lower concentration |
|
|
What affects the rate of diffusion?
|
The greater the difference in concentration, the faster the rate of diffusion
|
|
|
To create a multicellular organism, what must happen?
|
The cells must differentiate to carry out different functions
|
|
|
If you differentiate a cell, what does it become?
|
A specialised cell that have a similar structure and function
|
|
|
What is a tissue?
|
A group of specialised cells
|
|
|
What does muscular tissue enable?
How does the tissue work in the stomach? |
Movement due to contraction
Contract to churn contents |
|
|
What is the purpose of glandular tissue?
How does this tissue work in the stomach? |
To produce substances such as enzymes and hormones
Produces digestive enzymes and acid |
|
|
What is the purpose of epithelial tissue?
How does this tissue work in the stomach? |
Covers some parts of the body such as organs
Lines the outside and inside of the stomach |
|
|
How do the following organs contribute to the digestive system?
Pancreas and salivary gland Stomach Small intestine Liver Large intestines |
Produce digestive juices
Digests food Digest and absorb soluble food Produces bile to break down fats Absorbs water form undigested food, producing faeces |
|
|
What is the purpose of epidermal tissue?
|
To cover the plant
|
|
|
What is the purpose of mesophyll tissue?
|
Carries out photosynthesis
|
|
|
What is the purpose of both xylem and phloem tissue?
|
Transport substances around the plant
|
|
|
Give examples of plant organs
|
Roots
Stem Leaves |
|
|
How is a leaf adapted to absorbing sunlight?
Chlorophyll? Large surface area? Thin? |
Absorb sunlight
Absorb more sunlight Easier for carbon dioxide to diffuse into the leaf cells |
|
|
What 3 factors affect the rate of photosynthesis?
|
Temperature
Carbon Dioxide concentration Light Intensity |
|
|
At what temperature are the enzymes that control photosynthesis destroyed?
|
45 degrees
|
|
|
What are the function of guard cells?
|
Control the opening and closing of stomata
Found in pairs Located in the leaves |
|
|
How is a root hair cell specialised?
|
Tiny hair extensions to increase surface area so that the plant can absorb more water
|
|
|
How is a xylem cell specialised?
|
Long, hollow cells to transport water through the stem
|
|
|
Where does diffusion occur?
|
Lungs
Small intestine |
|
|
Name 3 examples of plant organs
|
Stem
Leaves Roots |
|
|
What 4 things are needed for photosynthesis?
|
Water
Light Chlorophyll Carbon dioxide |
|
|
How do plants use glucose?
Name 4 things |
Changed into insoluble starch, stored in roots, leaves or stem
Respiration to provide energy Produce cellulose to strengthen cell wall Produce proteins, uses nitrate ions from soil |
|
|
What are proteins?
|
Molecules made from long chains of amino acids which are folded into a specific 3D shape
|
|
|
What 4 things do proteins act as?
|
Structural components for tissue
Hormones Antibodies Catalysts |
|
|
What are enzymes?
|
Biological catalysts made from proteins
|
|
|
What do catalysts do?
|
Increase the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy
|
|
|
What is specific to the enzyme that is vital for its function?
|
Shape
|
|
|
Why is it dangerous for humans to have a temperature?
|
High temperatures denature the shape of the active site within the enzyme so that they no longer work
|
|
|
What temperature do enzymes work best in?
|
37 degrees
|
|
|
How do digestive enzymes work?
|
Released from cells
They come into contact with food molecules Catalyse breakdown of large food molecules to smaller ones They turn insoluble substances into soluble substances so they can be absorbed in the bloodstream |
|
|
What are the 3 digestive enzymes?
|
Protease
Lipase Amylase |
|
|
Where is amylase produced?
|
Salivary glands
Pancreas Small intestine |
|
|
What does amylase digest?
|
Starch
|
|
|
What does amylase produce?
Where is this product produced? |
Sugars
Mouth and small intestine |
|
|
Where is protease produced?
|
Stomach
Pancreas Small intestine |
|
|
What does protease digest?
|
Proteins
|
|
|
What does protease produce?
Where is this product produced? |
Amino acids
Stomach and small intestine |
|
|
Where is lipase produced?
|
Pancreas
Small intestine |
|
|
What does lipase digest?
|
Lipids (fats and oils)
|
|
|
What does lipase produce?
Where are these products produced? |
Fatty acids and glycerol
Small intestine |
|
|
What is the function of mesophyll?
|
Tissue used to carry out photosynthesis
|
|
|
What is the function of epidermal tissue?
|
Cover outside of the plant
|
|
|
What is the function of xylem?
|
Transport water
|
|
|
What is the function of phloem
|
Transport nutrients
|
|
|
What 3 things affect photosynthesis?
|
Light intensity
Carbon dioxide levels Temperature |
|
|
Which two enzymes are in biological detergents and why?
|
Lipase- Break down oil and grease stains
Protease-Break down blood and food stains |
|
|
Where is bile produced?
|
In the liver
|
|
|
Where is bile stored?
|
Gall bladder
|
|
|
Where is bile realised into?
|
Small intestine
|
|
|
What is the function of bile?
Why is this important? |
It neutralises the acid that is added to food in the stomach
This means alkaline conditions are present which enzymes in the small intestines work best in |
|
|
Which enzyme is used in baby food and why?
|
Protease because it pre-digests protein
|
|
|
Which enzyme is used to convert starch into sugar syrup?
|
Amylase/Carbohydrase
|
|
|
Which enzyme is used to convert glucose into fructose?
|
Isomerase
|
|
|
Why are enzymes used in industry?
|
To bring about reactions at normal temperatures and pressures which would otherwise need more energy which raises costs
|
|
|
Where does aerobic respiration take place?
|
Mitochondria in the cytoplasm of cells
|
|
|
What is the aerobic respiration word equation?
|
Glucose + Oxygen = Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
|
|
|
What is the energy released during respiration used for?
Name 4 things |
Build larger molecules
Allow muscles to contract Maintain steady body temperature Build up amino acids from sugars, nitrates and nutrients |
|
|
During exercise, what changes does your body go through?
|
Heart rate increases
Rate and depth of breathing increases Arteries supplying blood to muscles dilate Bloodflow to muscles increase Supply of oxygen and sugar, removal of carbon dioxide increases |
|
|
What do muscles store glucose as?
|
Glycogen
|
|
|
What is the anaerobic respiration word equation?
|
Glucose = Energy + Lactic acid
|
|
|
Which releases more energy, anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration?
|
Aerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration releases less energy because the breakdown of glucose is incomplete |
|
|
What is oxygen debt?
|
It's the oxygen that's needed to oxidise lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water
|
|
|
What happens when muscles carry out vigorous activity for a long time?
|
They become fatigued, they stop contracting efficiently and hurt
|
|
|
How is lactic acid removed from the muscles?
|
By blood flowing through the muscles
|

