![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Variation? |
Differences between individuals of the same species |
|
|
How can variation occur? |
Genetic Environmental |
|
|
Genetic factor example? |
Dimples |
|
|
Environmental factor example? |
Scars |
|
|
DNA? |
Molecules that code for genetic information and make up chromosomes |
|
|
Genes? |
Small section of DNA of a chromosome that determines a particular characteristic |
|
|
Order cell, chromosomes, DNA, genes and nucleus biggest to smallest? |
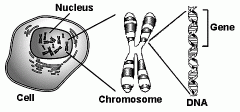
Cell Nucleus Chromosome DNA Gene |
|
|
What do genes carry? |
Information for you to develop |
|
|
What do different genes control? |
Different characteristics |
|
|
Chromosome? |
A long molecule found in the nucleus of all cells containing DNA |
|
|
Nucleus? |
Control centre of a cell and contains DNA |
|
|
Where are genes found? |
In sections of DNA In chromosomes which are located inside the nucleus of every cell |
|
|
What are chromosomes made of? |
DNA molecules |
|
|
What are DNA molecules made up of? |
Two very long strands which coil to form a double helix |
|
|
What do DNA molecules complete a full set of instructions for? |
How the organism should be constructed How each cell should function |
|
|
How do genes control the development of different characteristics? |
Genes issue instructions to the cell The cell carries out instructions by producing proteins |
|
|
Protein? |
Long organic compounds made of amino acids |
|
|
What can proteins formed inside a cell be? |
Structural Functional |
|
|
What are structural proteins for? |
Cell growth Repair |
|
|
Structural protein example? |
Collagen |
|
|
What are functional proteins for? |
Speed up chemical reactions |
|
|
Functional protein example |
Amylase |
|
|
What do chromosomes normally come in? |
Pairs |
|
|
What do both chromosomes in a pair have? |
Same sequence of genes |
|
|
How many chromosome pairs do human cells have? |
23 pairs |
|
|
How many individual chromosomes do human cells have? |
46 |
|
|
What is different bout the chromosomes in sex cells? |
They have single chromosomes= 23 individual chromosomes |
|
|
Allele? |
An alternative form of a particular gene |
|
|
What do you inherit for each gene? |
One allele from father and one from mother |
|
|
Homozygous? |
Inheriting two alleles that are the same |
|
|
Heterozygous? |
Inheriting two alleles that are different |
|
|
Why do siblings look different? |
They randomly inherit different combinations of alleles |
|
|
Genotype? |
The genetic make-up of an organsism |
|
|
Phenotype? |
The characteristics shown by an individual |
|
|
Dominant allele? |
Controls the development of a characteristic even if it's present on only one chromosome in a pair |
|
|
Recessive allele? |
Controls the development of a characteristic only if a dominant allele isn't present If the recessive allele is present on both chromosomes in a pair |
|
|
How many sex chromosomes are there in a human body cell? |
One of the 23 pairs |
|
|
What gene determines the sex on the Y chromosome? |
Sex-determining region Y gene |
|
|
What happens if the sex-determining region Y gene isn't present? |
They embryo will develop into a female |
|
|
What happens if the sex-determining region Y gene is present? |
Testes begin to develop |
|
|
What do testes produce six weeks after fertilisation? |
A hormone called androgen |
|
|
What happens after androgen is produced? |
Specialised receptors detect the androgen Male reproductive organs begin to grow |
|
|
What happens if the Y chromosome is present but androgen isn't detected? |
The embryo develops female sex organs apart from the uterus The baby has a female body but is infertile |
|
|
What is Huntington's disease caused by? |
A dominant allele Heterozygous and homozygous alleles |
|
|
What is Cystic Fibrosis caused by? |
Recessive allele Homozygous allele |
|
|
What if a person possesses one allele for Cystic Fibrosis? |
They are a carrier Heterozygous allele |
|
|
What are the implications if an adult is genetically tested and the result is positive? |
Decide not to have children Adopt children Have children but to accept that they may also inherit disorder |
|
|
Why are children tested to see if they have disease-causing genes? |
To take preventative measures before prescribing certain drugs that may have a negative effect due to the genetic make-up Susceptibility of certain diseases Tailor healthcare To stop genetic disorders from being passed on, eliminating them |
|
|
How are fetuses tested? |
Amniocentesis Chorionic villus test |
|
|
How does amniocentesis occur? |
Fluid surrounding the fetus/placenta is injected out This can be tested for faulty alleles |
|
|
How does the chorionic villus test occur? |
Suction tube removes cells from chorionic villi |
|
|
What are the risks of testing fetuses? |
Miscarriage False negative/positive as it is not 100% reliable |
|
|
What are the implications if a fetus was tested and the result was positive? |
Termination Give birth and take care of child Tell family members they too may carry the faulty allele |
|
|
What are ethical concerns about testing fetuses? |
Termination The effects the information may have on an individual and relationships Not right to interfere with nature Who has the right to decide if a disorder is worth living with Confidentiality- employers/insurance companies causes discrimination |
|
|
What are the outcomes of a false positive? |
Termination when there is no disorder |
|
|
What are the outcomes of a false negative?
|
Parents not prepared when child is born with a disorder |
|
|
What are the benefits of embryo selection? |
Prevents babies from having genetic disorders |
|
|
How can embryos be produced? |
IVF |
|
|
What is done alongside IVF to check for a specific genetic disorder? |
Pr-implantation Genetic Diagnosis |
|
|
IVF and PGD steps? |
Ova harvested Fertilised Embryos divide into eight cell stage Single cell removed from each embryo Cells tested to see if they carry the alleles for a specific genetic disorder Healthy embryos implanted into uterus |
|
|
What are the ethical problems of embryo selection? |
Unnatural Pre-selection-reduces variation |
|
|
Asexual reproduction? |
New offspring are reproduced that are identical to the parent |
|
|
What organisms do asexual reproduction? |
Single-cell e.g. bacteria/plants |
|
|
How do single-cell organisms reproduce? |
Divide to form two new individuals |
|
|
What are the new individuals? |
Clones |
|
|
Clone? |
An organism genetically identical to the parent |
|
|
What is variation like in asexually produced organisms? |
No genetic variation Only environmental variation |
|
|
How can animal clones occur naturally? |
Identical twins- the cells of an embryo separate |
|
|
How can animal clones be produced artificially? |
Nucleus removed from an adult body cell Transferred into an empty unfertilised egg cell New individual will have exactly the same genetic information as the donor |
|
|
How do plants naturally produce clones? |
With bulbs and runners |
|
|
Bulb example? |
Daffodil |
|
|
Runner example? |
Strawberry plants |
|
|
What is the problem with asexually produced organisms? |
No genetic variation Susceptible to the same diseases as the parent plant |
|
|
Stem cells? |
A cell of a human embryo or adult bone marrow that has the ability to differentiate |
|
|
Specialised cell? |
It has a certain function |
|
|
What can stem cells be used for? |
Replace damaged tissues- Parkinson's disease/heart disease/other organ diseases Red blood cells- leukemia Insulin- diabetes |

