![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
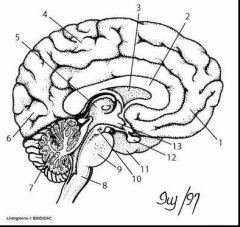
|
1. Frontal lobe 2. Corpus callosum 3. Ventricle 4. Parietal lobe 5. Thalamus 6. Occipital lobe 7. Cerebellum 8. Brain stem 9. Pons 10. Pineal gland 11. Temporal lobe 12. Pituitary gland 13. Hypothalamus |
|
|
Parts of brain |
Cerebral hemisphere or cerebrum. Diencephalon (hypothalamus, thalamus, sometimes pituitary). Brain stem Cerebellum |
|
|
Cerebral hemisphere or cerebrum |
Two lateral hemispheres which form the most obvious external feature of the brain. Sensory areas consciously interpret sensory impulses. Motor areas control voluntary muscular movement. Divided into lobes
|
|
|
Cerebellum |
Receives information from balance system of inner ear, sensory nerves, and auditory and visual systems. Memory storage of learned motor patterns. Cerebellum and cerebrum work together in assessing movement |
|
|
Thalamus (diencephalon) |
Relay stations for all sensory impulses (except smell) to the cerebral cortex. Processes and transmits movement and sensory information. |
|
|
Hypothalamus (diencephalon) |
Grouping of nuclei that lie along the base of the brain near pituitary gland. Responsible for hunger, thirst, emotions, temp regulation. Also controls pituitary gland by secreting hormones, which gives the hypothalamus heaps of control over many body functions |
|
|
Pituitary gland (diencephalon) |
Controls release of hypothalamic hormones. Secretes hormones regulating endocrine activity. Posterior lobe - Oxytocin, antidiuretic hormone Anterior lobe - FSH, LH, prolactin |
|
|
Pons |
Bridges two hemispheres of the cerebellum. Contains involuntary somatic and visceral motor centres, especially those related to respiration. |
|
|
Medulla oblongata |
Relays sensory impulses to the thalamus. Relays motor impulses from frontal lobe. |
|
|
CSF |
Cerebrospinal fluid. Produced by series of choroid plexus in the lumens of the ventricles. Cushioning, buoyancy, removes wastes in brain. |
|
|
Frontal lobe |
Front of brain. Reasoning, movement/ motor skills (like car engine), expressive language and higher cognitive skills. Damage can cause problems with sexual habits, socialization, attention and increased risk taking. |
|
|
Parietal lobe |
Middle section. Tactile sensory information - being aware of sensations (touch, pain) |
|
|
Occipital lobe |
Back portion of brain. Main role is interpreting visual stimuli and information. Damage can cause problems with recognising objects and words, and identify colours |
|
|
Temporal lobe |
Bottom section of brain. Mainly hearing/ sound, formation of memories. Damage can cause problems with memory, speech, language skills. |
|
|
Meninges |
Membranes surrounding brain and spinal cord and retain CNS (dura, arachnoid, pia) |
|
|
Dura mater |
Most superior of the meningeal layers. Name means "hard mother" in Latin. Tough and inflexible. |
|
|
Arachnoid mater |
Middle layer of the meninges. The subarachanoid space lies between the arachnoid and pia mater. It is filled with cerebrospinal fluid |
|
|
Pia mater |
Innermost layer of the meninges. Adheres closely to the brain, running down into the sulci and fissures of the cortex. Fuses with the membranous lining of the ventricles to form structures called the choroid plexes which produce cerebrospinal fluid. |
|
|
Types of tissue in CNS |
Grey matter - peripherally located in the cortex of the cerebellum, but centrally located in the medulla of rhe spinal cord and cerebrum White matter - peripherally located in the cortex of the spinal cord and cerebrum, laterally located in the medulla of the cerebellum |
|
|
Brain divided into three areas - |
Forebrain: cerebrum and diencephalon Midbrain: Hindbrain: medulla oblongata, pons, cerebellum |
|
|
LOBES |
Frontal (rostral) Parietal (dorsal) Occipital (caudal) Temporal (lateral) Olfactory (ventrorostral) |

