![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
96 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How are Vascular anomalies divided?
|
Vascular Malformations and Vascular Tumors.
Vascular Malformations include: Slow Flow (Capillary malformations**MC**, venous malformations, lymphatic malformations) Fast Flow: AV Malformations Vacular tumors include Infantile hemangioma Vascular Tumors |
|
|
How are Vascular malformations different than vascular tumors WRT Gender prevalence, Natural History, Pathology, Immunophenotype, Hematology
|
Vascular malformations: no gender prevalence, persistent and lifelong, no increase in cell turnover, GLUT-1 negative, LIC/DIC risk -- Tx with LMWH
Vascular Tumors: F>M 3:1, postnatal proliferation, slow involution over years, increase in cellular turnover (+ markers of proliferation), GLUT-1 positive, KMS not linked to hemangiomas |
|
|
Name the some Capillary Malformations?
|
Port wine stains
Telangiectasias Nevus flammeus |
|
|
What two syndromes have capillary malformations
|
HHT
Sturge-Weber |
|
|
Occult spinal dysraphisms must be ruled out in what setting?
|
midline PWS
|
|
|
Name the types and assoc of Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis?
|
Type I: CM + epidermal nevus
Type II: CM + Mongolian spots + nevus anemicus MC type (85%) Type III: CM + nevus spilus + nevus anemicus Assoc. w/ multiple granular cell tumors Type IV: CM + Mongolian spots + nevus spilus + nevus anemicus Type V: CM + CMTC + Mongolian spots Subtype a = only skin anomalies Subtype b = skin + systemic abnormalities (intracranial/visceral vascular anomalies, ocular abnormalities, choroidal melanoma, hemihypertrophy) |
|
|
What does "Subtype a" designate in Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis?
|
Only skin anomalies are seen
|
|
|
What does "Subtype b" designate in Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis?
|
Subtype b = skin + systemic abnormalities (intracranial/visceral vascular anomalies, ocular abnormalities, choroidal melanoma, hemihypertrophy)
|
|
|
Name the Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis that has: CM + epidermal nevus
|
Type I
|
|
|
Name the Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis that has:
CM + Mongolian spots + nevus anemicus |
Type II -- MC form -- 85%
|
|
|
Name the Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis that has:
CM + nevus spilus + nevus anemicus Assoc w/ multiple granular cell tumors |
Type III
|
|
|
Name the Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis that has:
CM + Mongolian spots + nevus spilus + nevus anemicus |
Type IV
|
|
|
Name the Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis that has:
CM + CMTC + Mongolian spots |
Type V
|
|
|
Name the most common form of Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis
|
Type II
|
|
|
Name the Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis that has:
Assoc w/ multiple granular cell tumors |
Type III
|
|
|
What are the major findings in Sturge Weber syndrome?
|
Facial PWS (V1 -- forehead, upper eyelid)
Ipsilateral ocular involvement (Buphthlamos (congenital glaucoma) Ipsilateral leptomeningeal changes: CVM in pia mater MC in occipital region Seizures |
|
|
What is Buphthalmos?
|
Congenital glaucoma -- seen in Sturge Weber
|
|
|
CVMs in the pia mater seen in what dz?
|
Sturge Weber syndrome
|
|
|
Developmental delay
Contralateral hemiplegia, hemiparesis Migraines Attention deficit Neurologic findings that are sometimes seen in what? |
Sturge Weber Syndrome
|
|
|
"Tram-track" calcifications, Cerebral atrophy, convoluted calcifications in what d/o?
|
Sturge-Weber syndrome (Leptomeningeal CVM)
|
|
|
What % of infants with V1 have PWS?
|
10-15%
|
|
|
What types of PWSs have increased risk of Sturge-Weber?
|
If V1, 2, and 3 are involved
If Bilateral Involvement is seen |
|
|
Name the dz w/ Classic triad:
CM Venous/lymphatic malformation Limb hypertrophy |
Klippel-Trenaunay Syndrome
|
|
|
What is the classic triad seen in Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome?
|
Classic triad:
CM Venous/lymphatic malformation Limb hypertrophy |
|
|
Name the syndrome:
Overgrowth of affected limb CAVM Fast-flow lesion Warm, pink flat geographic stain w/ thrill/bruit Multiple AV connections in underlying skin & muscle Lytic bone lesions CHF w/ hemodynamically significant AVM Poor prognosis after puberty |
Parkes-Weber Syndrome
|
|
|
What syndrome can have the following:
Lytic bone lesions CHF w/ hemodynamically significant AVM |
Parkes-Weber syndrome
|
|
|
Prognosis for Parkes-Weber Syndrome?
|
Poor prognosis after puberty
|
|
|
What disorders have the following complications?
Venous thromboembolism in up to 22% (check D-dimers) Coagulopathy Pulmonary embolism Stasis dermatitis Leg ulcers Bleeding |
Klippel-Trenaunay & Parkes-Weber
|
|
|
% of venous thromboembolisim in Klippel-Trenaunay & Parkes-Weber
|
22%
|
|
|
Name the disorder:
Asymmetrical gigantism of extremities & digits Slow flow vascular anomalies Capillary, venous, lymphatic Cerebriform connective tissue nevus of palms & soles Benign hamartomatous lesions (lipomas, epidermal nevi) |
Proteus Syndrome
|
|
|
Name the disorder:
Asymmetrical gigantism of extremities & digits |
Proteus Syndrome
|
|
|
Name the disorder:
Cerebriform connective tissue nevus of palms & soles |
Proteus Syndrome
|
|
|
Benign hamartomatous lesions (lipomas, epidermal nevi)
|
Proteus Syndrome
|
|
|
Name some clinical findings of Proteus Syndrome
|
Asymmetrical gigantism of extremities & digits
Slow flow vascular anomalies Capillary, venous, lymphatic Cerebriform connective tissue nevus of palms & soles Benign hamartomatous lesions (lipomas, epidermal nevi) |
|
|
Mutation found in Proteus Syndrome
|
PTEN gene
|
|
|
Name this disorder:
Sporadic Clusters of tiny telangiectases in annular or serpiginous pattern Favors extremities Young females 90% F, 80% < 20 yo Palms, soles, mm spared |
Angioma Serpiginosum (Hutchinson Type)
|
|
|
Name the disorder:
Congenital & acquired forms Primarily females Face, neck, chest, arms Dermatomal distribution (trigeminal & upper cervical) or in Blaschko’s lines +/- prominent halo of vasoconstriction May be due to increase in estrogen receptors on bld vv in affected areas |
Unilateral Nevoid Telangiectasia
|
|
|
Name the dz:
Cutaneous vascular syndrome w/ reticulated pattern that persists after re-warming |
Cutis Marmorata Telangiectatica Congenita
|
|
|
This disorder can have the following findings:
+/- Atrophic depressions over joints Up to 50% w/ associated abnormalities (in the diffuse form of the dz): Limb hypoplasia on affected side Ocular: glaucoma, retinal pigmentation or detachment Neuro: macrocephaly, sz, hydrocephalus, psychomotor retardation |
Cutis Marmorata Telangiectatica Congenita (CMTC)
|
|
|
In the diffuse form of CMTC, what other abnormalities can be seen (up to 50% of cases)?
|
Limb hypoplasia on affected side
Ocular: glaucoma, retinal pigmentation or detachment Neuro: macrocephaly, sz, hydrocephalus, psychomotor retardation |
|
|
What is Adams-Oliver Syndrome?
|
CMTC
Distal transverse limb defects Aplasia cutis congenita (scalp) |
|
|
Eponym for Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia?
|
Osler-Weber-Rendu
|
|
|
What dz has Inheritance & Gene defects:
AD; endoglin & ALK1; TGF-beta receptors expressed by vascular endothelium |
HHT
|
|
|
Name the defect and gene in HHT?
|
Inheritance & Gene defects?
AD; endoglin (ENG, HHT1) & ALK1 (HHT2) TGF-beta receptors expressed by vascular endothelium |
|
|
What are some common clinical findings in HHT?
|
Epistaxis
Mat-like & papular telangectasias on face, lips, tongue, palms, fingers GI/GU tract hemorrhage &/or iron deficiency anemia |
|
|
Eponym for Ataxia Telangiectasia
|
Louis-Barr syndrome
|
|
|
Inheritance and Gene Defect in Louis-Barr syndrome?
|
Ataxia telangiectasia:
ATM (AR) |
|
|
Initial presenting symptom in Louis-Barr syndrome?
|
Ataxia
(aka Ataxia telangiectasia) |
|
|
In Ataxia Telangiectasia, where do the telangiectasias normall appear?
|
usu appear after age 4-5, most commonly on bulbar conjunctiva (also on face and ears)
|
|
|
Name the disease:
Chromosomal instability (t 7;14), growth retardation, immunodeficiency, pulmonary infections, sensitivity to ionizing radiation High risk for lymphomas, leukemia, breast cancer Deficiency of IgA & IgG w/ sinus/bronchial infxns Children: ↑ levels of CEA & alpha-fetoprotein Heterozygous carriers: ↑ risk of breast cancer |
Ataxia Telangiectasia
|
|
|
Name the types of angiokeratomas
|
Solitary papular angiokeratoma
-MC on LE in young adults; likely trauma-induced -May be mistaken for melanoma Angiokeratoma of scrotum/vulva (Fordyce spots) Angiokeratoma circumscriptum Clusters form a plaque, usually on extremities, present at birth Angiokeratoma of Mibelli Dorsal fingers/toes, elbows, knees in prepubescent children Rare, AD genodermatosis assoc w/ cyanotic hands & feet and family h/o chilblains Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum (bathing trunk distribution) |
|
|
These capillary malformations may be seen on the surface of CM in KTS
|
Angiokeratomas
|
|
|
Assoc w/ what mutation?
- Hyperkeratotic cutaneous CVM seen in subgroup of pts w/ cerebral CM (familial cerebral cavernomas) - Cutaneous lesion represents sign of brain involvement |
Mutation in CCM1 encoding KRIT-1
|
|
|
Name the disease:
Accumulation of globotriaosylceramide (ceramide trihexidose) |
Fabry's disease
|
|
|
Name the disease:
alpha-galactosidase A deficiency |
Fabry's disease
|
|
|
What is the best way to evaluate a Venous Malformation?
|
T2 weighted MRI
|
|
|
How would you treat cephalic VMs?
|
Sclerotherapy
Surgical Excision |
|
|
What sclerotherapy agent could you use to treat limb VMs?
|
- Pure Ethanol
- Ethibloc (zein, sodium amidotrizoate, oleum papveris, propylene glycol, ethanol) |
|
|
Name the syndromes associated with VMs
|
Familial Cutaneous & Mucosal Venous Malformation (CMVM)
Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome (BEAN syndrome) Maffucci Syndrome Glomangiomas & Familial Glomangiomatosis |
|
|
Name the disorder:
AD TEK gene “gain of function” mutation Activation of tyrosine kinase receptor (TIE2/TEK) Multiple lesions: skin, oral mucosa, muscles No intestinal VM’s |
Familial cutaneous & mucosal venous malformation (CMVM)
|
|
|
Name the disorder:
Sporadic Widely distributed dark blue papules/nodules Skin colored compressible nodules GI VM’s→hemorrhage, iron deficiency anemia CNS, lung, heart involvement less common |
Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome (Bean syndrome)
|
|
|
Name the disorder:
Rare, sporadic PTH/PTHrP mutation VM’s (MC on extremities) + enchondromas Risk of malignant transformation to chondrosarcoma Spindle cell hemangioma w/ VM on histo |
Maffucci Syndrome
|
|
|
Mutation in Maffucci Syndrome
|
Rare, sporadic
PTH/PTHrP mutation |
|
|
Clincal picture in Maffucci syndrome
|
VM’s (MC on extremities) + enchondromas
Risk of malignant transformation to chondrosarcoma Spindle cell hemangioma w/ VM on histo |
|
|
Mutation in: CMVM
|
AD
TEK gene "gain of function" Activation of tyrosine kinae receptor (TIE2/TEK) |
|
|
Mutation in Bean Syndrome
|
Sporadic
|
|
|
Clinical findings in Familial Cutaneous & Mucosal venous malformation
|
Multiple lesions: skin, oral mucosa, muscles
No intestinal VM’s as in Bean syndrome |
|
|
Clincal findings in Blue Rubber bleb nevus syndrome
|
Widely distributed dark blue papules/nodules
Skin colored compressible nodules GI VM’s→hemorrhage, iron deficiency anemia CNS, lung, heart involvement less common |
|
|
Name the disorder:
VM + glomus cells Small solitary lesions: Nail bed MC, sporadic Widely scattered blue-purple nodules or in segmental distribution Multiple lesions usually familial GLMN gene (AD) encoding glomulin Hyperkeratotic, painful to palpation, partially compressible, no involvement of viscera or joints |
Glomangiomas & Familial Glomangiomatosis:
New name: glomuvenous malformations |
|
|
Eponym for Glomangiomas & Familial Glomangiomatosis
|
Glomuvenous malformations
|
|
|
Describe Clinical findings in Glomangiomas & Familial Glomangiomatosis
|
VM + glomus cells
Small solitary lesions: Nail bed MC, sporadic Widely scattered blue-purple nodules or in segmental distribution Multiple lesions usually familial GLMN gene (AD) encoding glomulin Hyperkeratotic, painful to palpation, partially compressible, no involvement of viscera or joints |
|
|
What gene is associated with
Glomangiomas & Familial Glomangiomatosis? |
Glomangiomas & Familial Glomangiomatosis:
New name: glomuvenous malformations GLMN (AD) encoding glomulin |
|
|
Name the two types of congential Lymphedema
|
Milroy disease (congenital, type I):
FLT4 mutation (encoding VEGFR3) Meige lymphedema (late-onset, type II): FOXC2 gene (forkhead family transcription factor C2) |
|
|
Name the disease that has:
FLT4 mutation (encoding VEGFR3) |
Milroy Disease (congenital lymphedema, type I)
|
|
|
Name the disease that has:
FOXC2 gene (forkhead family transcription factor C2) mutation |
Meige lymphedema (late-onset, congenital lymphedema, type II)
|
|
|
Besides congenital lymphedema, Lymphedema is also seen in two other syndromes
|
Turner Syndrome
Noonan Syndrome |
|
|
Lymphatic malformations are due to what change in the lymphatics?
|
Hyperplasia
(vs. lymphedema which is due to aplasia or hypoplasia of the lymphatics; can be congenital or acquired) |
|
|
Another name for Macrocystic LMs? where are they found?
|
aka cystic hygromas
MC on neck, axilla, lateral chest wall |
|
|
What Dz are assoc with hygromas?
|
Downs
Turners Noonan |
|
|
what is another name for Microcystic Lymphatic malformations?
|
Lymphangioma circumscriptum
|
|
|
What complications can arise from lymphatic malformations?
|
Mandibular overgrowth when bilateral
Cross bite, displacement of midline Airway compromise when parapharyngeal, laryngeal Dental caries w/ loss of teeth Speech impediment Poor lifetime prognosis for massive cervicofacial LM LIC on trunk & limbs |
|
|
Treatment options for Lyphatic malformations?
|
Microcystic LM’s
Excision May require STSG, tissue expanders Macrocystic LM’s Percutaneous sclerotherapy Picibani, OK 432 (killed bacteria) Ethibloc Pure ethanol Surgery second-line if sclero fails |
|
|
What is the MC location for AV malformation?
|
cephalic (70%)
|
|
|
Is there a gender prevalence in AV Malformations?
|
No
|
|
|
What % of AV malformations are congenital?
|
40%, visible at birth
|
|
|
What are some things that may worsen an AV Malformation?
|
Puberty
Pregnancy Trauma |
|
|
What is the staging system for AV Malformations?
|
Schobinger’s Staging:
1. Dormant – mimics PWS 2. Expansion – throbbing/thrills 3. Destruction – necrosis, ulcer, hemorrhage 4. Cardiac decompensation with stage 2 or 3 |
|
|
Where are AVMs commonly located?
|
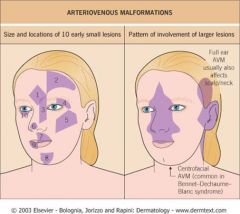
|
|
|
What are the syndromes associated with AVMs?
|
Cobb Syndrome
Parkes-Weber syndrome Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc (Wyburn-Mason's) |
|
|
Name the d/o:
Skin (20%), spinal & vertebral AVMs Red or red-brown stains mimicking PWS or throbbing masses w/ thrills Congenital or develop late in life after neuro signs Paraparesis & neuro deficits due to mass effect |
Cobb syndrome
|
|
|
Describe Cobb Syndrome
|
Skin (20%), spinal & vertebral AVMs
Red or red-brown stains mimicking PWS or throbbing masses w/ thrills Congenital or develop late in life after neuro signs Paraparesis & neuro deficits due to mass effect |
|
|
Name the d/o:
Multiple limb AVMs w/ Limb overgrowth |
Parkes-Weber Syndrome
|
|
|
Another name for Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc
|
Wyburn-Mason's
|
|
|
Name the d/o:
AVM w/ centrofacial, retinal & brain involvement Brain AVM asymptomatic or causes sz, hemiparesis |
Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc (aka Wyburn Masons')
|
|
|
Describe findings in Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc Syndrome
|
AVM w/ centrofacial, retinal & brain involvement
Brain AVM asymptomatic or causes sz, hemiparesis |
|
|
How would you treat an AV Malformation?
|
Conservative mgmt for stage 1 & 2
Head & neck stage 2 &3: wide excision after pre-op embolization (pure ethanol) AVM of limbs: Orthopedic evaluation Vascular treatments Elastic stockings, shoe-lift Amputation |

