![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
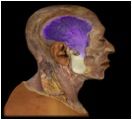
Temporalis
|
O: temporal fossa
I: coronoid process This muscle is involved with the elevation, retraction and lateral and medial excursion of the mandible. (i.e. mastication/chewing) |
|
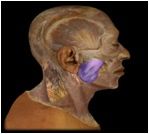
Masseter
|
O: zygomatic arch
I: lateral surface of mandibular ramus and angle This muscle is involved in the elevation of the mandible, with smaller roles in protration, retraction, and lateral and medial excursion. |
|
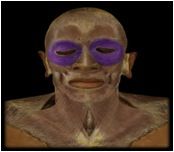
Orbicularis oculi
|
O: lacrimal & frontal bone
I: upper and lower eyelids, skin around margin or orbit This muscle functions as the sphincter of the eyelids: closes the eye in blinking, squinting and sleep and also aids in the flow of tears. |
|
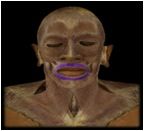
Orbicularis Oris
|
O: modiolus of mouth (around the corners of the mouth)
I: submucosa and dermis of lips This muscle encircles the mouth, closes lips, protrudes lips as in kissing, and is uniquely developed for speech in humans. |
|
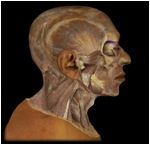
Levator Palpebrae Superioris
|
O: lesser wing of the sphenoid in posterior wall of orbit
I: upper eyelid This muscle elevates the upper eyelid and opens the eye |
|
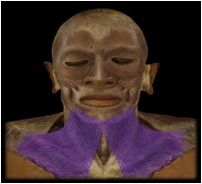
Platysma
|
O: fascia of deltoid and pectoralis major
I: mandible, skin and subcutaneous tissue of lower face This muscle is thin and covers most of the neck muscles. It draws the lower lip and angle of mouth downward in expressions of horror or surprise and may aid in opening the mouth widely. |
|
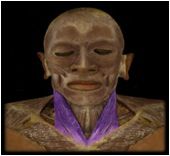
Sternocleidomastoid
|
O: manubrium of sternum and clavicle
I: mastoid process This muscle (marked number 28 in photo) is used for movements like looking over one's shoulder (unilateral action), rotating the head left and right, and moving the head straight forward and down (bilateral action). |
|
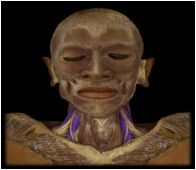
Scalenes
|
O: transverse processes of all cervical vertebrae
I: ribs 1-2 These muscles flex the neck and can be used to aid in breathing if the spine is fixed. |
|
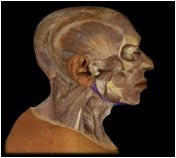
Digastric
|
O: mastoid notch of temporal bone and mandible
I: hyoid bone via fascial sling This muscle depresses the mandible when the hyoid is fixed and elevates the hyoid when mandible is fixed. It is involved in opening the mouth widely as in yawning or ingesting food. |
|
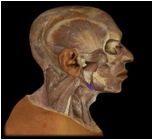
Stylohyoid
|
O: styloid process
I: hyoid bone This muscle elevates and retracts the hyoid, elongating floor of mouth. It has roles in speech, chewing, and swallowing which are not yet completely understood. |
|
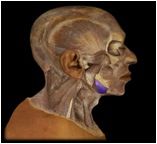
Mylohyoid
|
O: near inferior margin of mandible
I: hyoid bone This muscle spans the mandible from side to side and forms the floor of the mouth. It elevates the floor of the mouth in the initial stages of swallowing. |
|
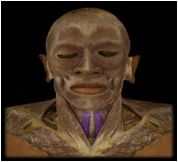
Sternohyoid
|
O: manubrium of sternum & clavicle
I: hyoid bone Function: depresses the hyoid after it's been elevated. |
|
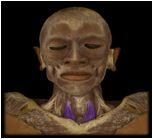
Sternothyroid
|
O: manubrium of sternum & costal cartilage
I: thyroid cartilage of larynx The function of this muscle is to depress the larynx after it's been elevated in swallowing and vocalization; aid in singing low notes. |
|
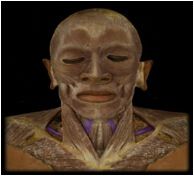
Omohyoid
|
O: superior border of scapula
I: hyoid bone This muscle depresses the hyoid after it's been elevated |
|
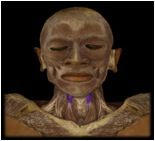
Thyrohyoid
|
O: thyroid cartilage of larynx
I: hyoid bone This muscle depresses the hyoid and when the hyoid is fixed, it elevates the larynx as in singing high notes. |
|
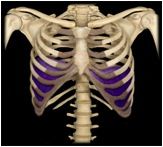
Diaphragm
|
O: xiphoid process of sternum. ribs and costal cartilages 7-12, lumbar vertebrae
I: central tendon This muscle is the prime mover of inspiration (intake of air during respiration) and contracts in preparation for sneezing, coughing, etc. |
|
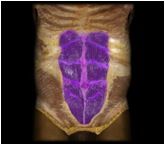
Rectus abdominus
|
O: pubic symphysis and superior margin of pubis
I: xiophoid process, costal cartilages 5-7 This muscle (labeled number 56 in photo) flexes the lumbar region of the vertebral column, producing forward bending at the waist. |
|
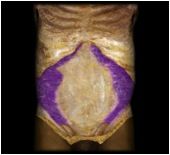
Transversus abdominus
|
O: inguinal ligament, iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia, costal cartilages 7-12
I: linea alba, pubis, aponeurosis of internal oblique This muscle compresses abdominal contents, with the same effects as external oblique, but does not contribute to the movements of the vertebral column. |
|
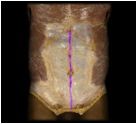
Linea alba
|
Not a muscle but rather, a median line of the abdomen which is made of other connective tissue.
|
|
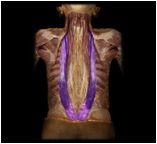
iliocostalis
|
The most lateral parallel column of the erector spinae.
|
|
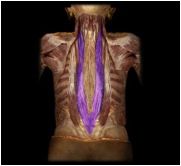
longissimus
|
A parallel column of the erecor spinae which is just medial to the iliocostalis.
|
|
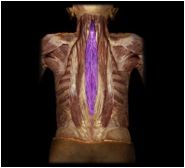
spinalis
|
The most medial parallel column in the erector spinae.
|
|
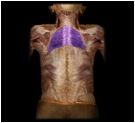
Rhomboideus major
|
O: spinous processes of vertebrae T2-T5
I: medial border of scapula This is one of the muscles that retract the scapula and braces the choulder; fixes scapula during arm movements. (larger & more inferior of the two) |
|
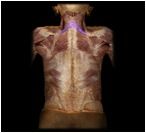
Rhomboideus minor
|
O: spinous processes of vertebrae C7-T1
I: medial border of scapula This is one of the muscles that retract the scapula and braces the shoulder; fixes the scapula during arm movements. (smaller & more superior of the two) |
|
|
Levator Scapulae
|
O: transverse processes of vertebrae C1-C4
I: superior angle to medial border of scapula This muscle elevates the scapula if the cervical vertebrae are fixed; flexes the neck laterally if scapula is fixed, retracts scapula and braces shoulder; rotates scapula and depresses apex of shoulder. |
|
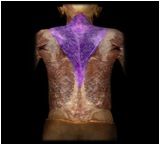
Trapezius
|
O: external occipital protuberance, medial 1/3 of superior nuchal line, nuchal ligament, spinous process of vertebrae C7-T3 or T4
I: acrominon of scapula; lateral 1/3 of clavicle. |
|
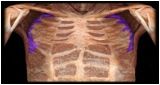
Serratus Anterior
|
O: all or nearly all ribs
I: medial border of scapula |
|
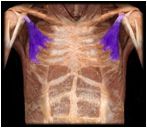
Pectoralis Minor
|
O: ribs 3-5 and overlying fascia
I: coracoid process of scapula |
|
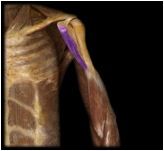
Coracobrachialis
|
O: coracoid process of scapula
I: medial aspect of humeral shaft This muscle flexes and medially rotates the arm; resists deviation of arm from frontal plane during abduction. |
|
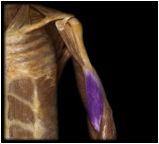
Brachialis
|
O: anterior surface of distal half of the humerus
I: coracoid process (of scapula) and tuberosity of the ulna This muscle, located deep to the biceps brachii, is the prime mover, or agonist, of elbow flexion. |
|
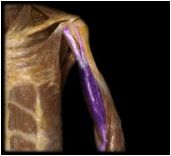
Biceps Brachii
|
O: Long head: superior margin of the glenoid cavity (scapula) Short head: coracoid process (scapula)
I: tuberosity of radius, fascia of forearm This muscle is the synergist in elbow flexion and is involved with rapid or forceful supination of forearm |
|
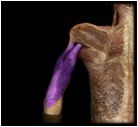
Triceps Brachii
|
O: Long head: inferior margin of glenoid cavity and joint capsule; Lateral head: posterior surface of proximal end of humerus; Medial head: posterior surface of entire humeral shaft
I: olecranon; fascia of forearm Located on the posterior side of the arm, this muscle functions to extend the elbow and the long head of this muscle extends and adducts humerus |
|
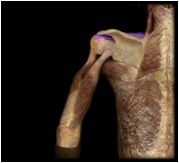
Supraspinatus
|
O: supraspinous fossa of scapula
I: lesser tubercle of humerus Located just superior to the spine of the scapula, this muscle aids in the abduction of arm and resisits downward slippage of humeral head when arm is relaxed or carrying weight |
|
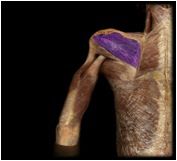
Infraspinatus
|
O: infraspinous fossa of scapula
I: greater tubercle of humerus Located just inferior to the spine of the scapula, this muscle modulates action of the deltoid, preventing humeral head from sliding upward; rotates humerus laterally |
|
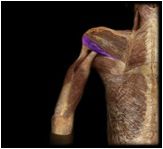
Teres minor
|
O: lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the scapula
I: greater tubercle of humerus; posterior surface of joint capsule Located just inferior to the infraspinatus, this muscle modulates the action of the deltoid, preventing humeral head from sliding upward as arm is abducted; rotates humerus laterally. |
|
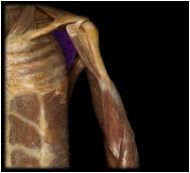
Subscapularis
|
O: subscapular fossa of scapula
I: lesser tubercle of humerus, anterior surface of joint capsule This muscle is deeper than the other muscles of the rotator cuff (on the deeper side of the scapula) and it modulates action of the deltoid, preventing humeral head from sliding upward as arm is abducted; rotates humerus medially. |
|
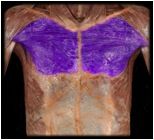
Pectoralis major
|
O: medial half of clavicle, costal cartilages 1-7, aponeurosis of external oblique
I: lateral lip of intertubercular sulcus of humerus |
|
|
Latissimus dorsi
|
O: vertebrae T7-L5, lower 3 or 4 ribs, iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia
I: floor of intertubercular sulcus of humerus |
|
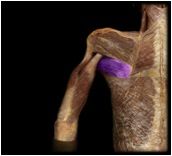
Teres major
|
O: Scapula (inferior angle and lateral border)
I: Intertuberclular groove of Humerus Action: Medial rotation, adduction and extension of arm |
|
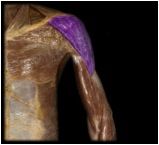
Deltoid
|
O: acrominon and spine of scapula; clavicle
I: deltoid tuberosity of humerus |
|
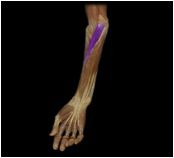
Pronator teres
|
O: humeral shaft near medial epichondyle; coronoid process of ulna
I: lateral surface of radial shaft This superficial muscle of the forearm assists the pronator quadratus in pronation but only during rapid or forceful action. |
|
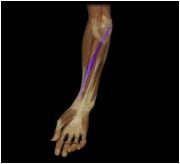
Flexor carpi radialis
|
O: medial epichondyle of humerus
I: base of metacarpals II-III This superficial muscle of the forearm flexes the wrist anteriorly and aids in the radial flexion of wrist |
|
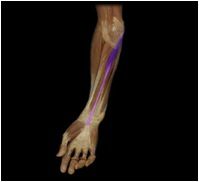
Palmaris longus
|
O: medial epichondyle of humerus
I: flexor retinaculum, palmar aponeurosis This superficial muscle of the forearm anchors the skin and fascia of the palmar region |
|
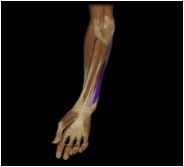
Flexor carpi ulnaris
|
O: medial epichondyle of humerus; medial margin of olecranon; posterior surface of ulna
I: pisiform, hamate, metacarpal V This superficial muscle of the forearm flexes the wrist anteriorly and aids in ulnar flexion of wrist. |
|
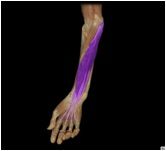
Flexor digitorum superficialis
|
O: medial epichondyle of humerus; ulnar collateral ligament; coronoid process; superior half of the radius
I: middle phalanges II-V This superficial muscle of the forearm flexes the wrist, metacarpophanangeal, and interphalangeal joints depending on the action of other muscles |
|
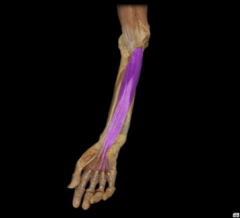
Flexor digitorum profundus
|
O: proximal 3/4 of ulna, coronoid process, interosseous membrane
I: distal phalanges II-V This deep muscle of the forearm flexes the wrist, metacarpophalangeal, and interphalangeal joints, and is the sole flexor of the distal interphalangeal joints. |
|
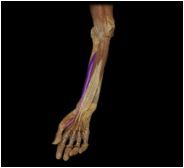
Flexor pollicis longus
|
O: radius, interosseous membrane
I: distal phalanx I This deep muscle of the forearm flexes the phalanges of the thumb. |
|
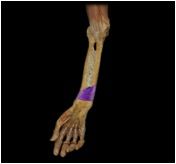
Pronator quadratus
|
O: anterior surface of the distal ulna
I: anterior surface of the distal radius This deep muscle of the forearm is the prime mover of forearm pronation and it also resists separation of the radius and the ulna when force is applied to forearm through wrist (as in doing push ups) |
|
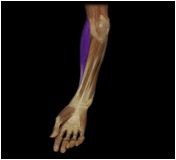
Brachioradialis
|
O: lateral distal humerus
I: near styloid process of radius This muscle flexes the forearm. |
|
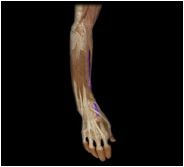
Extensor carpi radialis longus
|
O: humerus
I: second metacarpal This posterior muscle of the forearm extends and abducts the hand. |
|
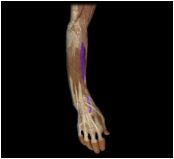
Extensor carpi radialis brevis
|
O: humerus
I: 3rd metacarpal This posterior muscle of the forearm extends and abducts the hand. |
|
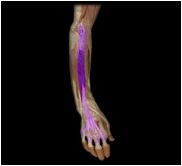
Extensor digitorum
|
O: humerus
I: distal phalanx II-V (via extensor hood) This muscle of the posterior forearm extends the wrist and fingers. |
|
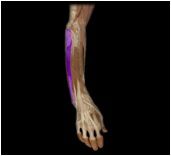
Extensor carpi ulnaris
|
O: humerus and ulna
I: 5th metacarpal This posterior forearm muscle extends and adducts the hand |
|
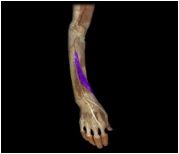
Abductor pollicis longus
|
O: radius, ulna
I: trapezium; first metacarpal This posterior forearm muscle abducts and extends the pollex (thumb) |
|
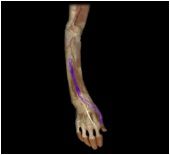
Extensor pollicis longus
|
O: ulna
I: distal phalanx of pollex This posterior forearm muscle extends the thumb and abducts the wrist |
|
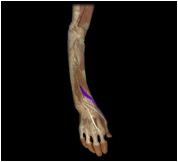
Extensor pollicis brevis
|
O: radius
I: proximal phalanx of pollex This posterior forearm muscle extends the thumb and abducts the wrist |
|
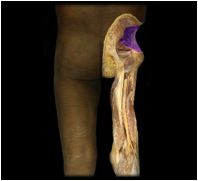
Gluteus minimus
|
O: gluteal lines on posterior ilium
I: greater trochanter of femur This muscle abducts and medially rotates the thigh. |
|
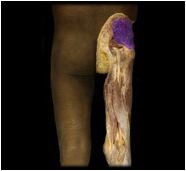
Gluteus medius
|
O: iliac crest
I: greater trochanter of femur This muscle abducts and medially rotates the thigh (used when shifting weight to stand on one foot) |
|
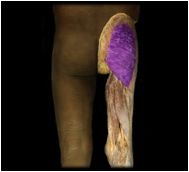
Gluteus maximus
|
O: iliac crest, sacrum, coccyx
I: gluteal tuberosity of femur iliotibial band This muscle extends and abducts the thigh |
|
|
Tensor fasciae latae
|
O: iliac crest, anterior superior iliac spine
I: iliotibial tract This gluteal muscle extends knee, aids in abduction/medial rotation of femur, and laterally rotates tibia. |
|
|
Iliopsoas
|
O: ilium, T12-L5
I: iliacus, lesser trochanter of femur These muscles include the iliacus and psoas major and it's function is flexion at the hip. The two muscles share a common tendon to the lesser trochanter of the femur. |
|
|
Psoas major
|
O: bodies and intervertebral discs of vertebrae T12-L5, transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae
I: lesser trochanter of the femur This muscle flexes the thigh at the hip when the trunk is fixed. (or vise versa -- flexes the trunk at the hip when the thigh is fixed, as in sitting up in bed or bending forward in a chair) |
|
|
Iliacus
|
O: iliac crest and fossa, superolateral region of sacrum, anterior sacroiliac and iliolumbar ligaments
I: lesser trochanter of the femur This muscle flexes the thigh at the hip when the trunk is fixed. (or vise versa -- flexes the trunk at the hip when the thigh is fixed, as in sitting up in bed or bending forward in a chair) |
|
|
Pectineus
|
O: superior ramus of pubis
I: spiral line of femur This medial muscle of the thigh flexes and adducts the thigh. |
|
|
Adductor brevis
|
O: body and inferior ramus of pubis
I: linea aspera and spiral line of femur This medial muscle of the thigh adducts the thigh. |
|
|
Adductor longus
|
O: body and inferior ramus of pubis
I: linea aspera of femur This medial muscle of the thigh adducts and medially rotates the thigh; FLEXES the thigh at hip |
|
|
Adductor magnus
|
O: inferior ramus of pubis; ramus and tuberosity of ischium
I: Linea aspera (femur), adductor tubercle (femur) gluteal tuberosity, and medial supracondylar line of femur. This medial muscle of the thigh adducts and medially rotates the thigh; EXTENDS the thigh at hip |
|
|
Gracilis
|
O: body and inferior ramus of pubis
I: medial surface of tibia This medial muscle of the thigh flexes and medially rotates tibia at knee. |
|
|
Vastus intermedius
|
O: anterior and lateral surfaces of femoral shaft
I: patella and tibia This "quad" muscle is located in the anterior (extensor) compartment of the thigh and its function is to extend the knee. This is the MIDDLE of the three muscles similar to it and with similar functions. |
|
|
Vastus lateralis
|
O: femur, linea aspera, gluteal tuberosity
I: patella and tibia This "quad" muscle is located in the anterior (extensor) compartment of the thigh and its function is to extend the knee as well as retain the patella in groove on femur during knee movements. This is the most LATERAL of the three muscles similar to it. |
|
|
Vastus medialis
|
O: femus, linea aspera
I: patella and tibia This deeper "quad" muscle is located in the anterior (extensor) compartment of the thigh and its function is to extend the knee as well as retain the patella in groove on femur during knee movements. This is the most MEDIAL of the three muscles similar to it. |
|
|
Rectus femoris
|
O: anterior inferior iliac spine, superior part of acetabulum
I: patella, tibia (marked number 110 in photo) This "quad" muscle extends the knee; flexes the thigh at the hip; flexes the trunk on hip if flexed |
|
|
Sartorius
|
O: anterior superior iliac spine
I: proximal end of tibia (marked number 103 in photo) This "quad" muscle aids in knee and hip flexion, as in sitting or climbing, abducts and laterally rotates thigh. It's the thin, long muscle that looks diagonal as it crosses over the vastus medialis. |
|
|
Biceps femoris
|
O: Ischial tuberosity & Linea aspera of femur
I: fibula This posterior muscle of the thigh flexes the knee and and extends the hip. Essentially, it counteracts forward bending at the hip and elevates the trunk from stooping posture |
|
|
Semimembranosus
|
O: ischial tuberosity
I: tibia This posterior thigh muscle flexes the knee and counteracts forward bending at the hips. (deeper muscle) |
|
|
Semitendinosus
|
O: ischial tuberosity
I: tibia This posterior thigh muscle flexes the knee and counteracts forward bending at the hips. (more superficial muscle) |
|
|
Tibialis anterior
|
O: tibia
I: first metatarsal and cuneiform bone |
|
|
Extensor digitorum longus
|
O: lateral condyle of tibia, shaft of fibula, interosseous membrane
I: middle and distal phalanges II-V This lower leg muscle extends the toes, dorsiflexes the foot, and tautens planar aponeurosis. |
|
|
Extensor hallucis longus
|
O: anterior surface of middle of fibula, interosseous membrane
I: distal phalanx I This lower leg muscle extends the great toe and dorsiflexes the foot. |
|
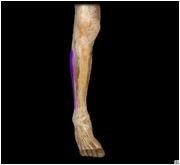
Fibularis (peroneus) longus
|
O: lateral surface of proximal 2/3 of fibula
I: first metatarsal and cuneiform This muscle maintains concavity of sole during toe off and tiptoeing, planar flexes, and everts the foot. |
|
|
Fibularis (peroneus) brevis
|
O: lateral surface of distal 2/3 of fibula
I: base of metatarsal V Maintains concavity of sole, may evert foot, limit inversion, and help steady. |
|
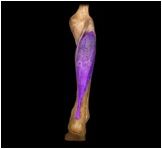
Soleus
|
O: fibula and tibia
I: calcaneus This lower leg muscle, located deep to the gastrocnemius, extends the ankle, plantar flexes the foot, and steadies the leg on ankle during standing |
|
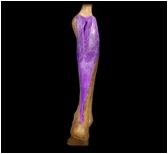
Gastrocnemius
|
O: condyles and popliteal surface of femur; capsule of knee joint
I: calcaneus This lower leg muscle, located superficial to the soleus, planar flexes the foot, flexes the knee, and is active in walking, running, and jumping. |

