![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What causes myasthenia graves? |
1. Autoantibodies, +/- complement towards Ach receptors |
|
|
What type of HSR is myasthenia gravis? |
1. Type II |
|
|
What are the ssx of myasthenia gravis? |
1. Progressive muscle weakness with exercise 2. Gets better with rest 3. Only skeletal muscles affected 4. "Better in the morning" |
|
|
What is neonatal myasthenia? |
1. Generalized muscle weakness due to passively transferred IgG |
|
|
How do you dx myasthenia gravis? |
1. Circulating anti-AchR antibodies 2. Thymoma on x-ray and histology 3. Abnormal electrical activity in muscles 4. Administration of edrophonium resolves ssx |
|
|
How do you tx myasthenia gravis? |
1. Cholinesterase inhibitors 2. Corticosteroids 3. Immunosuppressive drugs 4. IV immune globulin |
|
|
What is Addison disease? |
1. Adrenocrotical insufficiency |
|
|
What type of HSR is Addison disease? |
1. Type II |
|
|
What is the presentation of Addison disease? |
1. Hyperpigmentation of mucous membranes 2. Overproduction of corticotrophin and melanocyte-stimulating hormone 3. Vitiligo |
|
|
How do you dx Addison disease? |
1. ACTH stimulation test 2. Blood chemistries 3. Adrenal gland atrophy |
|
|
How do you tx Addison's? |
1. Hydrocrotisone |
|
|
What is bullous pemphigoid? |
1. Chronic subepithelial blistering skin disease 2. Rare involves mucous membrane |
|
|
What type of HSR are bullous pemphigoid/pemphigus vulgaris? |
1. II |
|
|
What antigens cause bullous pemphigoid? |
1. IgG to hemidesmosomal antigens |
|
|
What are the ssx of bullous pemphigoid? |
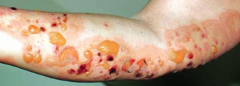
1. 65 y/o 2. Blisters are tense 3. Preceded by urticaria
|
|
|
How do you dx bullous pemphigoid? |
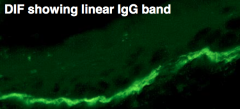
1. DIF of lesion bx shows IgG and complement in linear band at dermal-epidermal junction |
|
|
What is involved in pemphigus vulgaris? |
1. Skin and mucous membranes |
|
|
What causes the lesions in pemphigus vulgaris? |
1. IgG to keratinocyte desmogleins |
|
|
What is the presentation of pemphigus vulgaris? |
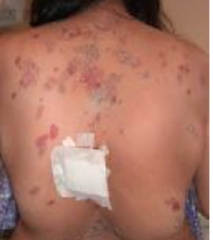
1. 50-60 y/o 2. Flaccid blisters are painful but don't itch |
|
|
How do you dx pemphigus vulgaris? |
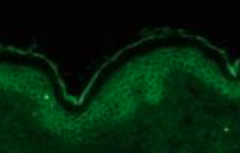
1. DIF shows IgG or IgM and C3 on surface of keratinocytes |
|
|
What causes Graves disease? |
1. Autoabs against TSH receptor |
|
|
What are the autoabs in Graves? |
1. Thyroperoxidase 2. Thyroglobulin 3. Na-I symporter |
|
|
What is the presentation of Graves disease? |
1. Goiter 2. Exophthalmos 3. Pretibial myxedema |
|
|
What type of HSR is Graves? |
1. II |
|
|
How do you dx Graves? |
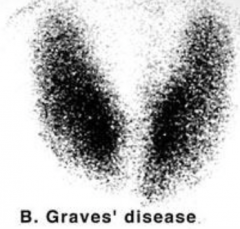
1. Anti-TSH receptor Ab 2. Low TSH 3. Increased T3 and T4 4. Increased radioactive uptake 5. Pretibial myxedema |
|
|
What causes Hashimoto? |
1. TH1 infiltration destroys thyroid gland
|
|
|
What antibodies are present in Hashimoto? |
1. Thyroid peroxidase 2. Thyroglobulin |
|
|
What are the ssx of Hashimoto? |
1. Goiter 2. Ssx of hypothyroidism |
|
|
How do you dx Hashimoto? |
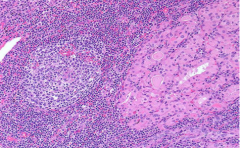
1. Elevated TSH 2. Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin 3. Diffuse lymphocytic and plasma cell infiltrate in follicles |
|
|
How do you tx Hashimoto? |
1. Levothyroxine 2. Surgery |
|
|
What is RA? |
1. Destructive disease 2. MC= hands and feet 3. Bone erosion in joints |
|
|
What are the ssx of RA? |
1. Morning stiffness 2. Arthritis in > 3 joint areas 3. Rheumatoid nodules |
|
|
What is the mechanism behind RA? |
1. HLA-DR4 mutation 2. CD4 cells stimulate synovial cells, fibroblasts, osteoclasts, PMNs to produce cytokines, ROS, and NO 3. Damage to connective tissue 4. Pannus formation 5. Complement can be fixed |
|
|
What is the target of immunotx in RA? |
1. TNFa |
|
|
What antibody fixes complement in RA? |
1. RF |
|
|
How do you dx RA? |
1. Elevated ESR and CRP 2. Circulating RF 3. Radiographs showing erosions/decalcifications |
|
|
For what is Rituximab specific? |
1. CD20 2. Use to tx RA |
|
|
What type of HSR is SLE? |
1. III |
|
|
What causes SLE? |
1. IC of self DNA, Ab, and others 2. ICs fix complement 3. Lodge in various regions |
|
|
What complement deficiency contributes to development of SLE? |
1. C1, C2, and C4 |
|
|
What are the ssx of SLE? |
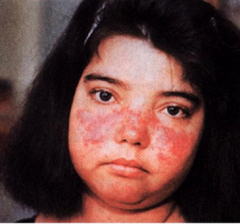
1. Erythema--- butterfly rash 2. Glomerulonephritis 3. Arthritis |
|
|
What are the MCC of death in SLE? |
1. Bacterial infection 2. Arteriosclerosis |
|
|
How do you dx SLE? |
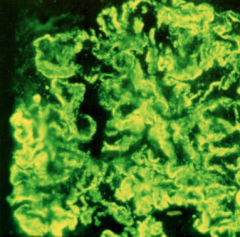
1. Lumpy-bumpy pattern on IF of kidney bx 2. Anti-dsDNA antibodies--- kidney damage and disease severity 3. Anti-Smith antibodies--- renal involvement |
|
|
How do you manage SLE? |
1. Avoid sunlight to prevent flares 2. Methotrexate for chronic 3. Prednisone, cyclophosphamide, etc. |
|
|
What is Sicca Syndrome? |
1. Chronic inflammatory disease mediated by CD4 infiltrate affecting exocrine glands 2. Principally lacrimal and salivary glands |
|
|
What are the ssx of Sicca? |
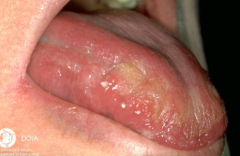
1. Xerophthalmia 2. Xerostomia with poor oral health 3. Xeroderma 4. Parotid swelling |
|
|
What are the risks of Sicca? |
1. Increases risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma 2. Maternal antibodies to SS-A/Ro increase risk of neonatal lupus and congenital heart block |
|
|
How do you dx Sicca? |
1. RF and ANA on 70% of patients 2. Schirmer test for tear produciton 3. Salivary gland bx shows aggregate of CD4 T cells |
|
|
What is Guillain-Barre syndrome? |
1. Ascending paralysis that affects the peripheral nerves 2. Follows infection or vaccination
|
|
|
What are the MC etiologic agents of GBS? |
1. Campylobacter 2. CMV 3. EBV 4. VZV 5. Mycoplasma |
|
|
What is the mechanism behind GBS? |
1. Lipid antigens of microbes demonstrate molecular mimicry with GM1 and GM1b in myelin 2. Inflammatory cellular response** leads to pathology |
|
|
How do you dx GBS? |
1. Abnormal nerve conduction tests 2. Elevated CSF protein w/o WBC elevation 3. Reduction in force vital capacity |
|
|
How do you tx GBS? |
1. Medical emergency--- closely monitor 2. Plasmapheresis or IVIG 3. PT and speech tx |
|
|
What is MS? |
1. Chronic or relapsing paralysis that attacks myelinated axons |
|
|
What are the ssx of MS? |
1. Dysarthria 2. Ataxia 3. Tremor 4. Paresthesias |
|
|
What is the mechanism behind MS? |
1. TH17 v. T reg for myelin basic protein 2. IL-17 induces killing of oligodendrocytes that comprise myelin sheath |
|
|
How do you dx MS? |
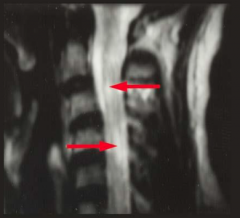
1. MRI: plaques of demyelination in white matter 2. Oligoclonal IgG bands detected by electrophoresis 3. IgG levels correlated with disease severity |
|
|
How do you tx MS? |
1. Methylprednisone 1. ABC tx---- avonex, betaserone, copaxone |

