![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
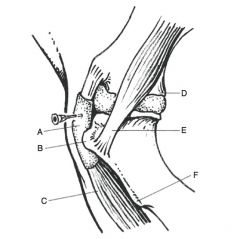
Examples of SQ bursae:
|
olecranon tuberosity, tuber calcanei, carpal hygroma
|
|
|
Location of SQ tuber calcanei bursa:
|
between the skin and the SDFT
|
|
|
Communication of SQ tuber calcanei bursa:
|
can communicate with (subtendinous) calcaneal bursa in 30% of horses
|
|
|
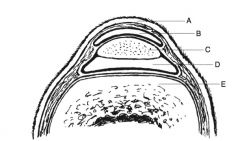
What is a carpal hygroma:
|
traumatically acquired soft tissue swelling on the dorsum of the carpus not associated with any joints or tendon sheaths
|
|
|
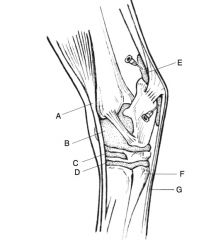
Examples of tubtendinous bursae:
|
navicular, bicipital, infraspinatus, calcaneal, trochanteric, cunean, LDE, CDE, ECR
|
|
|
Location of bicipital bursa:
|
between bilobed tendon of origin of biceps brachii muscle and M shaped tubercles of the cranioproximal humerus
|
|
|
Communication of bicipital bursa:
|
uncommon but can communicate with scapulohumeral joint
|
|
|
Radiographic changes of chronic bicipital bursitis:
|
mottled appearance to tubercles, demineralization of tubercles, periarticular osseous densities, osseous cysts in cranioproximal humerus, osteitis of bicipital groove, ossification of biceps tendon, calcification of bursa
|
|
|
Location of infraspinatous bursa:
|
between tendon of infraspinatous muscle and the caudal eminence of the greater tubercle of the proximal humerus
|
|
|
Cause of infraspinatous bursitis:
|
severe adduction of the forelimb and direct trauma
|
|
|
Location of (subtendinous) calcaneal bursa:
|
beneath the SDFT, extending 7 cm proximal and 9 cm distal to the point of the hock
|
|
|
Divisions of the (subtendinous) calcaneal bursa:
|
gastrocnemius and intertendinous, usually communicate
|
|
|
Causes of (subtendinous) calcaneal bursitis:
|
luxation of SDFT, avulsion or trauma to insertion of gastrocnemius on tuber calcanei, osteolytic lesions at the insertion of the gastrocnemius or plantar ligament
|
|
|
Complication of (subtendinous) calcaneal bursitis:
|
secondary osteitis or osteomyelitis of tuber calcanei
|
|
|
Location of trochanteric bursa:
|
beneath flat tendon of the middle gluteal muscle as it passes over the convexity of the greater trochanter of the femur
|
|
|
Location of cunean bursa:
|
between medial collateral ligament of the tarsus and the medial branch of the tibialis cranialis muscle
|
|
|
Communication of cunean bursa:
|
often with DIT joint
|
|
|
Location of LDE bursa:
|
beneath common origin of the LDE and PT over lateral surface of proximal tibia
|
|
|
Communication of LDE bursa:
|
always with lateral femorotibial joint
|
|
|
Location of ECR bursa:
|
beneath ECR tendon and over the 3rd carpal bone
|
|
|
Examples of subligamentous bursae:
|
supraspinous, atlantal (nuchal)
|
|
|
Location of supraspinous bursa:
|
beneath nuchal ligament over T3-4
|
|
|
Location of atlantal (nuchal) bursa:
|
between the nuchal ligament and rectus capitis dorsalis over C1
|

