![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define/Differentiate:
A. Oligiomenorrhea B. Polymenorrhea C. Menorraghia D. Metorrhagia E. Menometorrhagia |
A. Oligiomenorrhea: too few cycles per year
B. Polymenorrhea: too many cycles per year C. Menorraghia: bleeding is too heavy D. Metorrhagia: irregular interval of bleeding E. Menometorrhagia: too heavy and irregular |
|
|
Anovulatory bleeding ddx would include what conditions? (5)
|
- Chronic anovulation
- Hypothalamic anovulation - Hyperprolactinemia - Thyroid dysfunction - Premature ovarian failure |
|
|
What is the progesterone withdrawal test?
|
Pharmacologic progestin is given for a while, then withdrawn. If there is no withdrawal bleed, then it means either 1) the patient is pregnant or 2) no estrogen is present
The KEY thing to remember is that secretory (progesterone) changes only occur if endometrium primed by estrogen. |
|
|
With each of the following, state whether the levels of LH/FSH and Estrogen would be low/normal/high respectively, and what the outcome of progesterone withdrawal test would be.
A. hypothalamic amenorrhea B. chronic anovulation C. thyroid dz, increased prolactin levels D. premature ovarian failure E. Asherman's |
A. hypothalamic amenorrhea: LH/FSH low, Estrogen low, test light to no bleeding
B. chronic anovulation: normal across the board C. thyroid dz, increased prolactin levels: LH/FSH normal, estrogen normal to low, test variaible D. premature ovarian failure: LH/FSH high, estrogen low, test light to no bleeding E. Asherman's: LH/FSH normal, estrogen normal, test light to no bleeding |
|
|
What are some causes of hypothalamic amenorrhea? (4) hint: think you
|
- STRESS
- exercise amenorrhea (esp. gymnastics, ballet, distance running) - anorexia/bulimia - female athlete triad (amenorrhea, osteoporosis, disordered eating) MECH: Abnormal cortisol adn neurotransmitter levels change GnRH pulsatility, decrease LH and FSH. Decreased estrogen and increased risk osteoporosis is the consequences. |
|
|
What is the female athlete triad?
|
Amenorrhea, osteoporosis, disordered eating.
The female athlete triad can be a cause of hypothalamic amenorrhea. |
|
|
What are the treatment options for hyopthalamic amenorrhea?
|
Estrogen replacement (birth control pills, HRT)
If fertility is desired, pulsatile GnRH or exogenous gonadotropins If due to female athlete triad, correct caloric intake |
|
|
What are some causes of chronic anovulation?
|
***PCOS***
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding Stein-Leventhal Syndrome Remember, for PCOS there IS NO OTHER IDENTIFIABLE CAUSE FOR ANOVULATION |
|
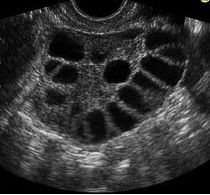
Your patient comes in complaining of hirsutism, central obesity and oligo-ovulation and oligomenorrhea. On ultrasound her ovaries look like this. What condition does this patient have?
|
PCOS! A form of chronic anovulation!
|
|
|
Hyperprolactinemia can present as [ what type of -menorrhea], and what two other signs?
|
- Oligomenorrhea/ Amenorrhea
- Galactorrhea - Visual field defects |
|
|
When evaluating for hyperprolactinemia,
A. what labs should you do? B. what imaging? C. what do you NEED to rule out? |
A. Prolactin, TSH
B. MRI C. very important to rule of stalk compressing lesion! |
|
|
What is the treatment for hyperprolactinemia?
|
-observation
- medical: dopamine agonists (bromocriptine, haloperidol), HRT, OCPs - surgical: transphenoidal resection (though want to avoid b/c knocks out pituitary so you'll have to supplement those for the rest of the patient's life |
|
|
Premature ovarian failure is defined as depletion of follicles before age 40.
True or False: Can wax and wane. |
TRUE
Ovary is not making functional follicles. Thus, the ovary is dysfunctional so ovary is not making estrogen. For some reason ovary cannot respond and make estrogen. Meanwhile, the pituitary is on overdrive pumping out LH and FSH trying to get the ovary to respond. Symptoms: oligo and amenorrhea, hot flashes, vaginal dryness |
|
|
What chromosomal abnormality is associated with premature ovarian failure?
|
45 X0 (Turner's)
Other: Idiopathic, Mumps infection, iatrogenic, autoimmune |
|
|
When evaluating for primary ovarian failure, what can you order/screen for?
|
- karyotype
- screen for autoimmune disease (ANA) - screen for other endocrine dysfunction (Thryoid, Parathyroid, adrenal) |
|
|
True or False:
The treatment for primary ovarian failure is hormone replacement until average age of menopause. |
TRUE
via either HRT or OCPs |
|
|
Given choices of primary ovarian failure, hyperprolactinemia, menopause, PCOS, thyroid disease, match the symptoms below with the common condition.
A. nipple discharge (1) B. hot flashes (2) C. hirsutism / acne (1) D. heat / cold intolerance, hair changes (1) |
A. nipple discharge (1): hyperprolactinemia
B. hot flashes (2): menopause, POF C. hirsutism / acne (1): PCOs D. heat / cold intolerance, hair changes (1): thyroid disease |
|
|
What is Asherman's syndrome?
|
Rare complication of infection after D&C. Patient is ovulating just fine but intrauterine scarring is occuring causing amenorhea or hypomenorrhea.
Treated with: hsyteroscopy followed by estrogen. |
|
|
Heavy menstrual bleeding is defined as (numerically) more than ________ mL blood loss per cycle. Since this is hard for people to estimate, and since every woman is her own average, mostly we rely on patient's subjective reporting that she is having heavy bleeding.
|
> 80 mL
|
|
|
Intrauterine device Mirena is approved for heavy menstrual bleeding treatment and has excellent pregnancy protection. Must be changed how often?
|
Every 5 years
Heavy bleeding can also be treated surgically by endometrial ablation or hysterectomy. These, though, are usually when childbearing years are done. |

