![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What layer of the brain has a delay in maturation in ADHD? |

Outer layer of the cortex. |
|
|
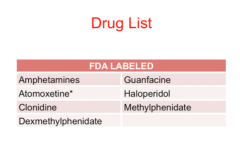
What are the drugs used to treat ADHD? |
|
|
|
What is treatment failure of ADHD often the result of? Do stimulants have a long or short half life? What are the four phases of management? |

|
|
|
True or false. There is often little overall difference between agents in initial response.
What drugs do you usually start with? |

True
Stimulants |
|
|
How do you combat appetite suppression? |
Decreases with time Time meals when medication has worn off |
|
|
How to combat delayed sleep onset? |
Decrease afternoon dose, Rarely consider clonidine or trazodone |
|
|
How to combat "wearing off" phenomenon? |
Use a 4pm dose of short acting agent Switch to longer acting agent |
|
|
How to combat tics? |
Check for Tourettes Observe simple Stop stimulant and substitute with central alpha-agonist if severe. |
|
|
How to combat depression? |
If they occur with dosing, choose different agent. Make sure symptoms are legit. |
|
|
How to combat social withdrawal? |
"Zombie-like" behavior from excessive dosing Decrease dose or time intervals |
|

Which phase? |
Maintenance |
|

Which phase? |
Termination phase |
|
|
Releases DA and NE |
Amphetamines |
|
|
Selective NE reuptake inhibitor centrally and peripherally |
Atomoxetine |
|
|
Block reuptake of DA and NE |
Dexmethylphenidate Methylphenidate |
|
|
Believed due to regulation of NE release from locus ceruleus. |
Clonidine |
|
|
Improved prefrontal cortical function through post-synaptic alpha-2-receptor agonist effects in PFC. |
Guanfacine |
|
|
Blocks post-synaptic D2 receptors |
Haloperidol |
|
|
Which are used as initial treatment in small children (disadvantage is bid-tid dosing to control symptoms throughout day)? Long or short acting?
Which are more convenient, confidential, and greater adherence, but offer greater problems with evening appetite and sleep? Long or short acting? |
Short-acting amphetamines Longer-acting amphetamines |
|
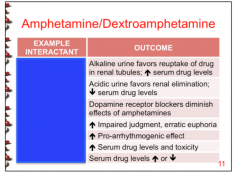
Identify the drug that causes the adverse effect.
Ammonium chloride, dextromethorphan, digoxin, MAOIs, CYP2D6 ind/inhib, acetazolamine, Na bicarbonate |
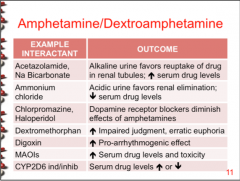
|
|
|
What are the four most common amphetamine adverse effects? |
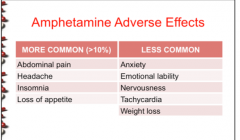
|
|
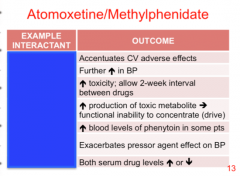
Identify the interactant: epinephrine, MAOIs, albuterol, alcohol, phenytoin, ergotamine, pseudoephedrine, CYP2D6 ind/inhib |
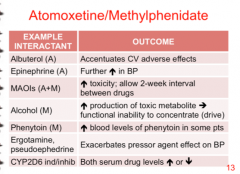
|
|
|
How do you distinguish atomoxetine from methylphenidate in terms of adverse effects? |
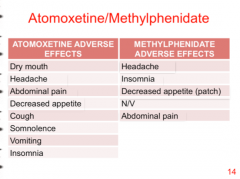
Dry mouth Cough Somnolence Vomiting
|
|

What are all of these? |
Absolute contraindications to stimulant use. NARROW ANGLE GLAUCOMA => pupil dilation can provoke acute attack of angle-closure glaucoma |
|
|
What is the most common co-morbid condition encountered in people with tics and Tourette syndrome?
1st, 2nd, and 3rd choice? |

|
|
|
Do antipsychotics reduce tics? Do they have a better or worse side-effect profile compared to alpha-2 agonist medications and behavioral therapy?
|

|
|
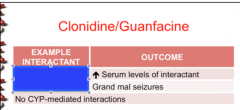
Identify the interactant: Cyclosporine Buproprion
|
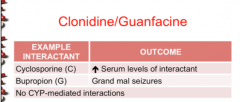
|
|
|
How is haloperidol metabolized? How can QT prolongation occur? |

|
|
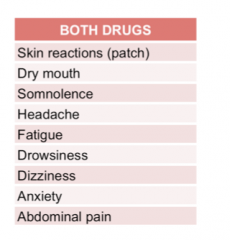
What drug class causes these effects? |
Alpha-2 agonists |
|

Overdose of what medication?
What is the management? |
ADHD (stimulants) Supportive => judicious use of BNZs |
|

What toxicity? Management? |
Atomoxetine Supportive => focus on sedation, control of dyskinesias and seizures |
|
|
What will clonidine overdose produce?
What do you give for this effect? |
Paradoxical short term hypertension => hypotension Give nitroprusside for HTN Atropine, dopamine (pressors) for support of HYPOtension. |
|
|
What drug causes drowsiness, lethargy, dry mouth, diaphoresis, hypotension or hypertension with overdose? |
Guanfacine
Use supportive therapy => focus on support of BP |

