![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How does the addition of MANGANESE change the properties of steel?
|
Increases Toughness and Hardness
Used for components subject to wear and abrasion Surface hardens with wear/cold working while core retains it's toughness |
|
|
How does the addition of NICKEL change the properties of steel?
|
Increases Toughness and Corrosion Resistance
|
|
|
How does the addition of CHROMIUM change the properties of steel?
|
Increases Hardness and Corrosion Resistance
Chromium oxide forms on the surface, protecting from corrosion 11% chromium or more is classed as stainless steel |
|
|
How does the addition of COBALT change the properties of steel?
|
Reduces Hardness
Increases Tensile Strength at high temperatures |
|
|
How does the addition of MOLYBDENUM change the properties of steel?
|
Increases Toughness and Hardness
Increases Creep Resistance, especially at high temperatures Increases Corrosion Resistance in stainless steels |
|
|
How does the addition of TUNGSTEN change the properties of steel?
|
Increases Hardness, especially at high temperatures
|
|
|
How does the addition of VANADIUM change the properties of steel?
|
Increases Hardness
Increases Creep Resistance, especially at high temperatures Increases Corrosion Resistance |
|
|
Describe Borax
|
Fluxes in brazing are based on borax
Also known as Sodium Borate A mineral that converts water (H2O) into hydrogen (H) when heated, preventing oxidization Mixed with ammonium chloride for brazing steel |
|
|
Describe 'Deflection'
|
The ability to withstand a load without flexing out of shape permanently
|
|
|
Describe 'Toughness'
|
The ability to withstand the impact of a blow
|
|
|
Describe 'Hardness'
|
The ability to withstand wear, indentation or scratching
|
|
|
Describe 'Conductivity'
|
The ability to pass heat or electricity through it
|
|
|
Describe 'Dielectric Strength'
|
The ability to insulate from electricity
|
|
|
Describe 'Creep'
|
The tendency to deform under stress over time
|
|
|
Describe 'Metal Fatigue'
|
Caused by repeated loading to the materials elastic limits
|
|
|
Describe 'Tensile Strength'
|
The ability to withstand being pulled apart or stretching
|
|
|
Describe 'Elesticity'
|
The ability to return back to it's original shape
|
|
|
Describe 'Ductility'
|
The property that allows material to be drawn into wire or tube
|
|
|
Describe 'Malleability'
|
The ability to be formed or bent into shape without fracture or failure
|
|
|
Describe 'Brittleness'
|
The tendency to fracture without bending or changing shape
|
|
|
Describe 'Shear Strength'
|
The ability to withstand offset loads
|
|
|
Describe 'Compressive Strength'
|
The ability to withstand squashing forces
|
|
|
What are the main types of MMA electrode flux coatings?
|
Class (C) - Cellulosic
Class (B) - Basic Class (R) - Rutile Class (RR) - Heavy Rutile |
|
|
What are added to brazing filler materials and why?
|
Silver - Improves fluidity and strength
Silicon - Acts as a de-oxidizer Nickel - Improves strength Manganese - Improves strength |
|
|
What do fluxes contain that are suitable for brazing aluminium?
|
Alkaline chlorides
Fluorides |
|
|
What do fluxes contain that are suitable for brazing manganese?
|
Alkaline chlorides
Fluorides |
|
|
What do fluxes contain that are suitable for brazing silver?
|
Boric acid, potassium borates, fluorides
|
|
|
What do fluxes contain that are suitable for brazing high temperature ferrous metals?
|
Boric acid, alkaline borates
|
|
|
What do fluxes contain that are suitable for brazing iron and steel?
|
Borax, ammonium chloride
|
|
|
What is the difference between an element, a molecule and a compound?
|
Elements are the different types of atoms (copper, hydrogen etc.)
Molecules consist of atoms made from a single chemical element (oxygen O2 etc.) Compounds consist of atoms made from different elements (Water H2O etc.) |
|
|
What is the term for when a length of material expands due to it's temperature being raise by 1º
|
Coefficient of linear expansion
|
|
|
What residue is left after brazing or hard soldering with borax?
|
A hard scale of copper borate
|
|
|
Describe Dead Mild Steel
|
Contains 0.05% - 0.15% carbon
Very ductile |
|
|
Describe Mild Steel
|
Contains 0.15 - 0.3% carbon
General purpose steel |
|
|
Describe Medium Steel
|
Contains 0.3% - 0.8% carbon
Brittle but capable of being hardened through heat treatment Cannot be cold formed |
|
|
Describe High Carbon Steel
|
Contains 0.8% - 1.4% carbon
Very brittle but very hard wearing when heat treated Also called tool steel |
|
|
Describe Wrought Iron
|
0.01% - 0.03% Carbon
More workable than cast iron Easily Welded Good corrosion resistance No longer normally produced - replaced by steel |
|
|
Describe Cast Iron
|
Contains 2% - 4% carbon
Dampens vibration Easily fractured High compressive strength but low tensile strength |
|
|
Describe Alloy Steel
|
Carbon steels that contain additional elements
Example: For bicycle frames alloy contains 10% chromium and 4% molybdenum, increasing tensile strength and stiffness |
|
|
What is at the centre of an atom and what does it consist of?
|
Nucleus, which consists of protons and neutrons
|
|
|
What surrounds a nucleus?
|
Electrons
|
|
|
Describe annealing of aluminium
|
Annealing is a softening process
The aluminium is heated to 550ºc then quenched Aluminium with less than 6% copper will remain malleable unless work hardened Aluminium with more than 6% copper will harden after 2 hrs, longer if refrigerated at -20ºc the annealed aluminium can be left to 'natural age hardening' or artificially hardened by heating to 130ºc - 200ºc |
|
|
What simple methods can indicate correct temperature for annealing aluminium?
|
soap or wood (e.g. matchstick) draws a black line on the surface, showing the material is ready for quenching
Temperature indicating crayons |
|
|
Describe strain hardening of aluminium
|
The material is cold rolled. The metals grain is elongated, reducing malleability and increasing tensile strength.
A letter 'H' and figures indicate hoe much strain hardening from soft, quarter hard, half hard, three quarter hard to hard Also called work hardening or cold working |
|
|
Describe 1000 series Aluminium
|
Pure aluminium
Soft Highly workable Good conductivity Good corrosion resistance Cannot be heat treated |
|
|
Describe 2000 series Aluminium
|
Contains copper
Used for machine parts Used as a base for more complex alloys Can be heat treated Good strength Lower corrosion resistance than other aluminium alloys |
|
|
Describe 3000 series Aluminium
|
Contains manganese
Used for pot, pans and heat exchange equipment
weldable Good ductility |
|
|
Describe 4000 series Aluminium
|
Contains silicon
High castability High strength Good corrosion resistance |
|
|
Describe 5000 series Aluminium
|
Contains magnesium
Relatively soft but quickly work hardened High tensile strength High corrosion resistance Weldable Can be heat treated Used in automobile and ship building |
|
|
Describe 6000 series Aluminium
|
Contains magnesium and silicon
High strength Corrosion resistant Can be work hardened Easily welded Suitable for anodising |
|
|
Describe 7000 series Aluminium
|
Contains zinc
Brittle High strength High rigidity Weldable Can be heat treated |
|
|
Describe silver solder
|
Tin / zinc / silver alloy
Good fluidity and strength Melting point 620ºc - 855ºc Often supplied in flat strips referred to as 'spelter' |
|
|
How does the addition of phosphorous affect copper brazing rods
|
The rod becomes self-fluxing
Essential for hard soldering of refrigeration pipework, where the presence of flux would lead to contamination and corrosion |
|
|
What is the temperature range for borax or fluoroborate fluxes?
|
Above 750ºc
|
|
|
What is the temperature range for fluoride fluxes?
|
Below 750ºc
|
|
|
What is the temperature range for alkali halide fluxes?
|
Below 580ºc
|
|
|
Shielding gas is usually made up from what gases?
|
Argon
Carbon Dioxide - CO2 Helium Oxygen |
|
|
Describe Cartridge Brass
|
70% Copper, 30% Zinc
Can be formed and drawn |
|
|
Describe Admiralty Brass
|
70% Copper, 29% Zinc, 1% Tin
Can be formed and drawn Has improved salt water resistance |
|
|
Describe Free Cutting Brass
|
58% Copper, 39% Zinc, 3% Lead
Not suitable for cold working Machinable Used for thread cutting |
|
|
Describe Bronze
|
Copper with 2%, 10% Tin
Suitable for casting |
|
|
Describe Gun Metal
|
88% Copper, 10% Tin, 2% Zinc
Bronze alloy Also called free cutting bronze Good for machining |
|
|
Describe Phosphor Bronze
|
89% Copper, 10% Tin, 0.25% Phosphorous
Improved fluidity when cast Used for machine bearings and marine fittings |
|
|
Describe Martensitic Stainless Steel
|
Contains 86% Iron, 12-18% Chromium, up to 1.2% Carbon, 0.5% Nickel
Can be hardened Unsuitable for welding Used for chef's knives, hard wearing shafts and spindles |
|
|
Describe Ferritic Stainless Steel
|
Contains 76% Iron, 12-30% Chromium, 0.1% Carbon, 1% Nickel
Tough and ductile Cannot be heat treated Unsuitable for welding Good corrosion resistance at high temperatures Used for furnace parts |
|
|
Describe Austenitic Stainless Steel
|
Contains around 86% Iron, 18% Chromium, 8% Nickel, up to 0.15% Carbon
Comes in a range of alloys with different properties Most commonly used Malleable Non magnetic Weldable |
|
|
Describe Duplex Stainless Steel
|
Contains around 61% Iron, 21% Chromium, 9% Nickel, 2% Magnesium, 3.5% Molybdenum
High Strength High Corrosion Resistance Called Duplex because structure consists of 50% ferrite and 50% austenite |
|
|
What is the melting point of soft solder?
|
180ºc - 250ºc
Depending on the ratio of tin to lead |
|
|
What is an elastomer?
|
An elastic polymer, such as rubber
|
|
|
Describe natural rubber
|
Highly elastic
Excellent vibration absorption Good creep resistance ideal for tyres |
|
|
Describe Ethylene-propylene
|
Synthetic rubber
Known as EPM Chemically inert Good electrical insulation Resistant to cracking from age Ideal for insulating power leads |
|
|
How much carbon does steel need to contain for it to be heat treatable?
|
0.3% or more
|
|
|
How does heat treatment change the crystalline structure of metal?
|
Structure changes from body centre cubic (ferrite) to face centre cubic (austenite)
|
|
|
What are the three main groups of adhesives?
|
Solvent based - air drying, natural and synthetic
Thermoplastic - temperature setting, liquifies on warming, solidifies when cooled Chemical setting - relies on chemical reaction for curing, very strong, used for structural applications |
|
|
What was the first synthetic resin adhesive developed?
|
Phenol formaldehyde
|
|
|
Fluxes suitable for soldering carbon steel, brass, copper or tin contain what?
|
Zinc chloride
|
|
|
Fluxes suitable for tinning the soldering bit contain what?
|
Ammonium chloride (sal ammoniac)
|
|
|
Fluxes suitable for soldering zinc or galvanised steel contain what?
|
Hydrochloric acid
|
|
|
Fluxes suitable for soldering copper plated stainless steel contain what?
|
Phosphoric acid
|
|
|
What are the corrosive fluxes used in soldering?
|
Zinc chloride - used for carbon steel, brass, copper and tin plate
Ammonium chloride - used for cleaning the bit before tinning Hydrochloric acid - used for zinc an galvanised steel Phosphoric acid - used for copper plated stainless steel |
|
|
What are the non-crrosive fluxes used in soldering?
|
Natural resin - used for electrical components
Tallow - used for lead sheet and pipes |
|
|
What materials are spanners made from?
|
High carbon steel
Alloy steel containing chromium and vanadium Beryllium bronze (non-sparking) |
|
|
What qualities make a good filler alloy for brazing?
|
Achieve good bonding
Capable of good capillary action Melts at the right temperature Good resistance to corrosion Sufficient strength for the joint Compatible with the parent material |
|
|
What does LPG stand for?
|
Liquid petroleum gas
Also called propane or butane, which make up LPG in varying ratios |
|
|
Describe thermoplastics
|
Also known as thermo-softening plastic
Softens when heated then re-hardens upon cooling |
|
|
Describe thermosetting plastic
|
Irreversibly cures through heating or chemical reaction (e.g. two part epoxy).
Once hardened they cannot return to a liquid or softened state |
|
|
All carbon steels contain what additional elements?
|
Silicon
Sulphur Manganese Phosphorous |
|
|
What is Cementite?
|
A compound of iron and carbon
Also called Iron Carbide |
|
|
What is Pearlite?
|
Alternate layers of ferrite and cementite
|
|
|
How much Chromium does steel have to be classed as Stainless Steel?
|
Approximately 10-12% or more
|
|

What is this?
|
Universal Beam
|
|

What is this?
|
Universal Column
|
|

What is this?
|
Parallel Flange Channel
|
|
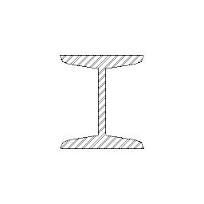
What is this?
|
Rolled Steel Joist
|
|
|
What is the formula for calculating drill speeds?
|
RPM = 30,000 / 3 x drill diameter
|

