![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How are weld sizes indicated? |
Throat Thickness - represented by the letter 'a'
Leg Length - represented by the letter 'z' Deep Penetration Throat Thickness - represented by the letter 's' |
|
|
What is the numerical representation for MMA with covered electrode?
|
111
|
|
|
What are the purposes of an MMA electrode?
|
Produce a gaseous shield
Increase arc temperature Give good arc transfer and stability Control reactions during welding Produce slag which retards the cooling rate and protects the weld from atmospheric contamination Improves mechanical and chemical properties of the weld |
|
|
Selection of the type of MMA electrode depends on what?
|
Parent metal
Depositing correct cross sectional weld size Type of current Service requirements e.g. strength or wear resistance Joint specification requirements Enabling the operator to gain access to the root of the weld Welding position |
|
|
What are the main types of MMA electrode flux coatings?
|
Class (C) - Cellulosic
Class (B) - Basic Class (R) - Rutile Class (RR) - Heavy Rutile |
|
|
What is the typical MMA current setting when using 2mm diameter electrode? |
40 - 60 amps
|
|
|
What is the typical MMA current setting when using 2.5mm diameter electrode? |
60 - 90 amps
|
|
|
What is the typical MMA current setting when using 3.2mm diameter electrode? |
90 - 130 amps
|
|
|
What is the typical MMA current setting when using 4mm diameter electrode? |
120 - 180 amps
|
|
|
What is the typical MMA current setting when using 5mm diameter electrode?
|
150 - 220 amps
|
|
|
What is the typical MMA current setting when using 6mm diameter electrode? |
220 - 320 amps
|
|

Describe 'Ohm's Law'
|
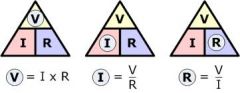
V = I x R (voltage = current x resistance)
or I = V/ R (current = voltage / resistance) or R= V/I (resistance = voltage / current) Resistance is measured in Ohms |
|
|
Describe the formula for calculating electrical power
|
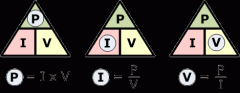
P = V x I (power = voltage x current)
or V + P / I (voltage + power / current) or I = P / V (current = power / voltage) |
|
|
Within the UK what welding standards are most adopted?
|
BS 4872 - Mild steel 6-12mm flat/horizontal/vertical |
|
|
International System for Units |
Ohms - Ω
|
|
|
International System for Units
How is electrical frequency measured? |
Hertz - Hz
1Hz = 1 cycle/s |
|
|
International System for Units
How is electrical current measured? |
Amperes (Amps) - A
|
|
|
International System for Units
How is electrical potential measured? |
Volts - V
|
|
|
International System for Units |
Watts - W
|
|
|
What is Coefficient of linear expansion?the term for when a length of material expands due to it's temperature being raise by 1º |
The term for when a length of material expands due to it's temperature being raise by 1º
|
|
|
How can heat distortion be controlled?
|
Reduce the amount of welded joints
Reduce the amount of weld - stitch joints Use correct cross- sectional weld sizes for the strength required Use smallest suitable angle of preparation (U rather than V, double U rather than single U) Use MIG or MAG Balance heat during welding Increase welding speed Preset component to an angle which allows for distortion Restrain components with clamps (can increase residual stress) Restrain components with welded supports (can increase residual stress) Tack Weld Use Chills - strips of metal that conduct heat away Welding sequencing Pre-heat the structure to 150ºc - 200ºc |
|
|
Identify the welding position PA
|
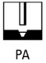
Flat position
|
|
|
Identify the welding position PB
|

Horizontal Vertical position
|
|
|
Identify the welding position PC
|
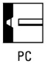
Horizontal position
|
|
|
Identify the welding position PD
|

Horizontal Overhead position
|
|
|
Identify the welding position PE
|
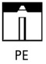
Overhead position
|
|
|
Identify the welding position PF
|
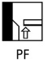
Vertical Upwards position
|
|
|
Identify the welding position PG
|
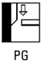
Vertical Downwards position
|
|
|
How can heat distortion be corrected mechanically?
|
Large sections with a press
Small parts with hammering, drifting or jacking Sheet metal with planishing |
|
|
How can heat distortion be corrected using heat? |
Heat uniformly to 650ºc then cooling normally
Heating the opposing side of the weld (bright red heat should not be exceeded) Heat small areas one at a time (bright red heat should not be exceeded) |
|
|
Which standards cover welding symbols?
|
BS EN 22553 welded, brazed and soldered joints - symbolic representation on drawings
|
|
|
Name the different types of heat distortion from welding
|
Angular |
|
|
What kind of voltage establishes an arc?
|
Open circuit voltage - OCV
Up to a maximum of 80V After the arc is established volts drop to around 20V (depending on settings) A voltage reduction device (VRD) is used to limit OCV and ensure a maximum of 80v for safety |
|
|
What is a rectifier?
|
An electrical device that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC)
|
|
|
What is a solenoid?
|
An electromagnet
Made from a soft iron shaft with insulated wire coiled around it When a current is passed through the wire the solenoid becomes magnetic The more wire coiled, the greater the magnetism created Clockwise wire direction is north polarity - negative Anti-clockwise wire direction is south polarity - positive |
|
|
Describe an AC/DC inverter
|
Silicon controlled rectifiers convert and reduce current
Power semiconductor unit inverts current back to AC at a higher frequency - 5,000-10,000 Hz Has a solid ferritic core transformer Up to 75% lighter and smaller than conventional power sources Experiences much less power loss, which increases duty cycle Improves arc and penetration Synergic pulse allows welding of thinner material with no spatter Can be used for AC or DC MMA, MIG/MAG, TIG and resistance welding |
|
|
Describe a DC welder generator
|
Powered by petrol or diesel
Used mainly onsite, where power is dangerous or unavailable Uses lower voltage, 20V - 40V Safer to use, especially outdoors Needs more maintenance due to moving parts Can cause the weld pool to pull to one side (arc blow) due to the magnetic current |
|
|
Describe an AC transformer |
A welding power unit that steps down the current from either 240V or 400V mains supply to 80V
Current flow is OCV - open current voltage Can be fan cooled or oil cooled Little voltage drop along cables, allowing the operator t weld further away from the power source Suitable for MMA and resistance welding |
|
|
What are the three most common colour coded plugs and sockets? |
Yellow 100V - 130V
Blue 200V - 250V Red 380V - 480V |
|
|
Describe an AC/DC transformer rectifier
|
Steps down the voltage
Increases the current Converts AC current to DC current Can be used for a variety of processes including MMA, MIG/MAG and TIG |
|
|
How much carbon does steel need to contain for it to be heat treatable? |
0.3% or more
|
|
|
How does heat treatment change the crystalline structure of metal?
|
Structure changes from body centre cubic (ferrite) to face centre cubic (austenite)
|
|
|
What power control characteristics are used for MMA and TIG welding? |
Constant current (drooping characteristics) - |
|
|
On an AWS electrode code E7018, what does 'E' represent? |
The electrode is for MMA welding and has a flux coating |
|
|
On an AWS electrode code E7018, what do the first two numbers '70' represent? |
Tensile strength (x 1000 psi = 70,0000 psi)
Tensile Strength is when the metal breaks. |
|
|
On an AWS electrode code E7018, what does the third number '1' represent? |
'1' designates all positions
'2' would designate only flat or horizontal positions |
|
|
On an AWS electrode code E7018, what does the fourth number '8' represent? |
The current required |
|
|
On an AWS electrode code E7018, what do the third and fourth numbers '18' together represent? |
Flux coating |
|
|
On a BS electrode code E46 4 B 32 H5, what does the letter 'E' represent? |
The electrode is for MMA welding and has a flux coating |
|
|
On a BS electrode code E46 4 B 32 H5, what do the first two numbers '46' represent? |
Yield strength (x 10 = 460 N/mm2)
Yield Strength is where the metal starts to deform plastically (when it doesn't spring back to it's original form after the load is released) |
|
|
On a BS electrode code E46 4 B 32 H5, what does the third number '4' represent? |
Minimum impact temperature (-40º) |
|
|
On a BS electrode code E46 4 B 32 H5, what does the second letter 'B' represent? |
Flux coating (Basic) |
|
|
On a BS electrode code E46 4 B 32 H5, what does the fourth number '3' represent? |
Recovery (105 - 125) and Current Type (AC + DC) |
|
|
On a BS electrode code E46 4 B 32 H5, what does the fifth number '2' represent? |
Welding Position
1 - All positions 2 - All positions except vertical down 3 - Flat. For fillet welds they can also be used in horizontal and vertical positions. 4 - Flat butt and fillet welds 5 - Vertical Down |
|
|
On a BS electrode code E46 4 B 32 H5, what do the last letter 'H' and number '5' represent? |
Hydrogen content in ml/100g (5ml/100g maximum)
Only indicated on low hydrogen rods |

