![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
444 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Name the three ATO service areas. |
Eastern, Western, Central |
|
|
|
Each FAA primary office, except the ATO, is managed by a(n) _________. A. Administrator B. Associate Administrator C. Director |
B. Associate Administrator |
|
|
|
The FAA ATO is managed by a(n) _________. A. Administrator B. Vice President C. Chief Operating Officer |
C. Chief Operating Officer |
|
|
|
The primary purpose of the ATC system is to __________ between aircraft operating in the system, to _______ and _______ the flow of traffic, and to provide support for national security and homeland defense. |
-prevent a collision -organize -expedite |
|
|
|
_________ is given to _____________ and ____________. Second priority is to provide support to national security and homeland defense. |
-First priority -separating traffic -issuing safety alerts |
|
|
|
For everything else, good judgment shall be used in prioritizing duties. Provide ________________ to the extent possible. |
additional services |
|
|
|
ATC service to aircraft is provided on a “first come, first served” basis , EXCEPT: |
• Aircraft in distress have priority over all other aircraft • Civilian air ambulances • Military air evacuation flights (when requested by the pilot) • Active Search and Rescue (SAR) missions • Presidential aircraft • Flight Check aircraft • Special military and civilian operations • Diverted flights |
|
|
|
____________ procedures are used in preference to _____________ procedures when workload, communication and equipment capabilities permit. |
-Automation -non-automation
|
|
|
|
_____________ is used in preference to _____________ when it will be to an operational advantage, and workload, communications, and equipment permit. |
-Radar separation -non-radar separation |
|
|
|
____________ is used in preference to ______________ when an operational advantage will be gained. |
-Non-Radar separation -radar separation |
|
|
|
There are five basic positions in an AFSS: |
- Flight Data/NOTAM Coordinator - Broadcast - Preflight - En Route Flight Advisory Service (EFAS) - Inflight |
|
|
|
AFSSs provide radar traffic advisories to VFR aircraft A. True B. False |
B. False |
|
|
|
The AFSS position that initiates required search and rescue situations is the __________ position. A. Preflight Position B. Inflight Position C. Flight Data/NOTAM/Coordinator |
C. Flight Data/NOTAM/Coordinator |
|
|
|
The AFSS position that provides airport advisories is the ___________ position. A. Inflight B. Preflight C. EFAS |
A. Inflight |
|
|
|
Briefs pilots on weather, NOTAMs, and restrictions along proposed route; applies VFR not recommended (VNR) procedures |
Preflight |
|
|
|
Makes recordings of weather and flight information, such as Hazardous Inflight Weather Advisory Service (HIWAS) |
Broadcast |
|
|
|
Issues airport advisories, relays ATC clearances, advisories, or requests to pilots, monitors and restores NAVAIDs, activates and closes flight plans, assists pilots of lost aircraft |
Inflight |
|
|
|
Disseminates IFR and VFR flight plans, initiates search and rescue, disseminates NOTAMs, performs Customs notification |
Flight Data/ NOTAM/ Coordinator |
|
|
|
Provides en route aircraft with timely and pertinent weather data; uses radio call sign “Flight Watch” |
En Route Flight Advisory Service |
|
|
|
There are six positions in the tower: |
- Flight Data - Clearance Delivery - Local Control - Ground Control - Tower Coordinator - Tower Associate |
|
|
|
Performs interfacility/intrafacility coordination, advises the Tower Positions of actions required to accomplish objectives |
Tower Coordinator |
|
|
|
Initiates control instructions, has responsibility for control of active runways, ensures separation, one of the two “Tower Positions” |
Local Control |
|
|
|
Assists the Tower Positions by performing coordination and helps to ensure separation by maintaining awareness of tower traffic |
Tower Associate |
|
|
|
Compiles statistical data, processes and forwards flight plan information, reports weather information |
Flight Data |
|
|
|
Initiates control instructions, has responsibility control of aircraft and vehicles on taxiways and runways that are not active, ensures separation, one of the two “Tower Positions” |
Ground Control |
|
|
|
Issues clearances and ensures accuracy of pilot readback. |
Clearance Delivery |
|
|
|
There are four basic positions in the TRACON radar sector team: |
- Radar Flight Data - Radar Associate - Radar Controller - Radar Coordinator |
|
|
|
There are four basic positions in the ARTCC: |
- Radar Flight Data - Radar Associate - Radar Controller - Radar Coordinator |
|
|
|
The position that is in direct communication with aircraft is _______. A. Radar Associate Position B. Radar Flight Data Position C. Radar Position D. Radar Coordinator Position |
C. Radar Position |
|
|
|
The position responsible for compiling statistical data and forwarding flight plan data is _______. A. Radar Associate Position B. Radar Flight Data Position C. Radar Position D. Radar Coordinator Position |
B. Radar Flight Data Position |
|
|
|
The position responsible for ensuring separation, initiating control instructions, managing flight strip information, and assisting the Radar Position with coordination is the _______. A. Radar Associate Position B. Radar Flight Data Position C. Radar Position D. Radar Coordinator Position |
A. Radar Associate Position |
|
|
|
The Radar Coordinator position is responsible for _______. A. interfacility/intrafacility coordination B. direct communication with aircraft C. Compiling statistical data D. Issuing control instructions to aircraft |
A. interfacility/intrafacility coordination |
|
|
|
From what facility would you receive landing clearance? A. TRACON B. AFSS C. ATCT |
C. ATCT |
|
|
|
Name the two types of facilities that are referred to as “Terminal”. |
ATCTs and TRACONs |
|
|
|
The first level of supervision for any ARTCC ATC specialist is known as: |
Front Line Manager |
|
|
|
Generally, the first contact made to an ATCT by a departing IFR aircraft is the _______position. A. Flight Data B. Clearance Delivery C. Ground Control D. Tower Associate |
B. Clearance Delivery |
|
|
|
The mission of the TMS is to ______ air traffic ______ with system _______. |
-balance -demand -capacity |
|
|
|
The operation of the TMS is the responsibility of the__________________________________. |
ATC System Command Center |
|
|
|
Monitoring and balancing air traffic flows within their area of responsibility is the primary function of the _______________. |
TMU |
|
|
|
Assigns times for aircraft inbound to the same airport to cross an arrival fix for that airport |
Arrival Sequencing Program (ASP) |
|
|
|
Routings other than the filed flight plan; designed to keep aircraft clear of special use airspace, congested airspace, or weather areas |
Reroutes |
|
|
|
Overrides all other TMS programs. Aircraft remain on the ground indefinitely |
Ground Stop (GS) |
|
|
|
Assigns departure times to achieve a constant flow of aircraft departing from several airports and flying over the same point |
Departure Sequencing Program (DSP) |
|
|
|
Aircraft are held on the ground until a specified time |
Ground Delay Program (GDP) |
|
|
|
Assigns departure times that will facilitate integration into the en route traffic stream |
En Route Sequencing Program (ESP) |
|
|
|
Let me know that you have received and understood my message. |
ACKNOWLEDGE |
|
|
|
An error has been made in the transmission and the correct version follows. |
CORRECTION |
|
|
|
Used by ATC when prompt compliance is required to avoid the development of an imminent situation. |
EXPEDITE |
|
|
|
A question relating to the quality of the transmission or to determine how well the transmission is being received. |
HOW DO YOU HEAR ME? |
|
|
|
Used by ATC when compliance with an action is required to avoid an imminent situation. |
IMMEDIATELY |
|
|
|
The message will be repeated. |
I SAY AGAIN |
|
|
|
“No” or “Permission not granted” or “That is not correct.” |
NEGATIVE |
|
|
|
My transmission is ended; I expect a response. |
READ BACK |
|
|
|
I have received all of your last transmission. It should not be used to answer a question requiring a “yes” or “no” answer. |
ROGER |
|
|
|
Used to request a repeat of the last transmission. Usually specifies transmission or portion thereof not understood or received.
|
SAY AGAIN
|
e.g., “Say again all after ABRAM VOR.”
|
|
|
Means the controller or pilot must pause for a few seconds, usually to attend to other duties of higher priority.
|
STAND BY
|
Also means to “wait” as in “stand by for clearance.” If a delay is lengthy, the caller should re-establish contact.
|
|
|
Indicates inability to comply with a specific instruction, request, or clearance. |
UNABLE |
|
|
|
Movement areas in an airport are: |
Runways Taxiways Other selected areas of an airport/heliport |
|
|
|
PAVEMENT MARKINGS COLOR:
White |
Runways and landing areas (including heliports) |
|
|
|
PAVEMENT MARKINGS COLOR:
Yellow |
Taxiways, closed and hazardous areas, and holding positions |
|
|
|
RUNWAY THRESHOLD MARKINGS
4 STRIPES = 6 STRIPES = 8 STRIPES = 12 STRIPES = 16 STRIPES = |
4 STRIPES = 60 feet 6 STRIPES = 75 feet 8 STRIPES = 100 feet 12 STRIPES = 150 feet 16 STRIPES = 200 feet |
|
|
|
How would you number a runway with a magnetic heading of 094°?
|
runway 9
|
|
|
|
How would you number a runway with a magnetic heading of 004°? |
36 |
|
|
|
What runway marking consists of 4 to 16 longitudinal white stripes of uniform dimensions arranged symmetrically on either side of the runway centerline?
A. Threshold B. Touchdown Zone C. Aiming Point |
A. Threshold
|

|
|
|
An unusable portion of the runway which appears usable and is marked with large yellow chevrons identifies a _________.
A. blast pad B. closed runway |
A. blast pad
|

|
|
|
The centerline of a taxiway is marked with a ______ line. A. dashed yellow B. continuous yellow C. continuous white |
B. continuous yellow |
|
|
|
A runway with a non-precision approach does not have which of the following runway markings:
A. Threshold B. Designator C. Touchdown Zone D. Aiming Point |
C. Touchdown Zone
|
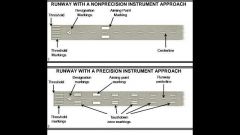
|
|
|
Runway numbers and letters determined from the approach direction. |
Runway designators |
|
|
|
Consists of two rectangular white stripes, markings one on each side of the runway centerline and approximately 1,000 feet from landing threshold.
|
Runway aiming point
|
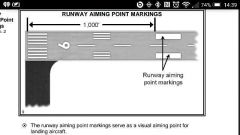
|
|
|
Consists of a single continuous yellow line, 6 inches to 12 inches in width. Provides a visual cue to permit taxiing along a designated path. |
Taxiway centerline |
|
|
|
These signs have a red background with a white
inscription and are used to denote an entrance to a runway, critical area, or areas where an aircraft is prohibited from entering. |
Mandatory Instruction Signs
|

|
|
|
Areas not under control of ATC on the airport. |
Nonmovement area |
|
|
|
Lighting circuits will be disconnected, and touchdown markings are obliterated and yellow crosses are placed at each end of the runway and at 1,000 foot intervals.
|
Permanently closed runways and taxiways
|

|
|
|
AIRPORT BEACONS
Lighted land airport color? |
Flashing white and green |
|
|
|
AIRPORT BEACONS
Lighted water airport color ? |
Flashing white and yellow |
|
|
|
AIRPORT BEACONS
Lighted heliport color? |
Flashing white, yellow, and green |
|
|
|
AIRPORT BEACONS
Military airport color? |
Two quick white flashes followed by a green flash |
|
|
|
An airport identified by a flashing white and yellow rotating beacon is _______. A. lighted land B. lighted water C. military |
B. lighted water |
|
|
|
The basic minimum altitude separation between IFR aircraft is:
|
- 1,000 feet for aircraft up to and including FL410.
- 2,000 feet for aircraft above FL410 up to and including FL600. - 5,000 feet for aircraft flying above FL600. |
|
|
|
IFR aircraft are vertically separated from fuel dumping aircraft by the following criteria: |
− 1,000 feet above the fuel dumping aircraft (through FL410); Exception: Between FL290 and FL410 – 2,000 feet above the fuel dumping aircraft if either aircraft is Non-RVSM − 2,000 feet above the fuel dumping aircraft (above FL410) − 2,000 feet below the fuel dumping aircraft (regardless of altitude) |
|
|
|
The standard minima for non-radar longitudinal separation is ___________. |
10 minutes or 20 miles if using DME. |
|
|
|
What is the minimum degree of divergence that may be assigned for the departure divergence rule? |
45 degrees |
|
|
|
To clear an aircraft to change altitude at a specified time or fix is a way to establish what type of separation? |
longitudinal |
|
|
|
Special Use Airspace
QUESTION: What is the vertical separation needed below the area? Above the area? |
500 feet below; 1,000 feet above |
|
|
|
The minimum terminal radar separation required for two aircraft 30 NM from the antenna is ______ miles. A. 1 B. 3 C. 5 |
B. 3
|
|
|
|
The minimum en route radar separation required for two aircraft below FL600 is ______ miles. A. 3 B. 5 C. 10 |
B. 5 |
|
|
|
For a tower facility to provide visual separation between two arriving IFR aircraft, the following condition must exist: A. One of the aircraft must be visually observed by the tower. B. Both aircraft must be visually observed by the tower. C. The pilots of both aircraft must see each other. |
B. Both aircraft must be visually observed by the tower. |
|
|
|
A ____________ is a predetermined maneuver which keeps an aircraft within a specified airspace while awaiting further clearance from air traffic control. Also used during ground operations to keep aircraft within a specified area or at a specified point while awaiting further clearance from air traffic control. |
holding procedure |
|
|
|
___________ refers to measures designed to adjust the flow of traffic into a given airspace, along a given route, or bound for a given airport, so as to ensure the most effective utilization of airspace. |
Flow control |
|
|
|
A ________ is a specified fix identifiable to a pilot by NAVAIDs or visual reference to the ground used as a reference point in establishing and maintaining the position an aircraft while holding. |
holding fix |
|
|
|
A ____________ is the fix, point, or location to which an aircraft is cleared when issued an air traffic clearance.
|
clearance limit
|
|
|
|
_____________________ refers to the time a pilot can expect to receive clearance beyond a clearance limit. |
Expect Further Clearance (EFC) |
|
|
|
If you had two aircraft at FL310, would you be correct in assigning one of the aircraft FL320 in order to achieve vertical separation? |
Yes, unless one of the aircraft is Non-RVSM equipped, you would need 2,000 feet vertical separation. |
|
|
|
If you were holding two aircraft at different fixes, one at 6,000 feet, and one at 7,000 feet, but the holding pattern airspace(s) overlapped each other, would you have separation? If so, what kind? |
Yes, vertical separation. |
|
|
|
Which type of separation in the en route environment, other than visual, would allow you to place two aircraft with the least distance between aircraft?
|
Vertical separation - 1,000 feet
|
|
|
|
The facility responsible for accepting, formatting, classifying, and disseminating NOTAMs is ________. A. AFSS B. Terminal C. Center |
A. AFSS |
|
|
|
Consists of information that requires wide dissemination via telecommunication and pertains to:
− En route navigational aids − Civil public-use airports listed in the Airport Facility Directory (AFD) − Facilities − Services |
NOTAM D
|
|
|
|
Consists of information that is regulatory in nature pertaining to flight including, but not limited to:
− Changes to IFR charts − Procedures − Airspace usage |
FDC NOTAM
|
|
|
|
Two types of radar systems are: |
- Primary radar - Secondary radar |
|
|
|
_________ is a radar system in which a minute portion of a radio pulse transmitted from a site is reflected by an object and then received back at the site for processing and display at an air traffic control facility. |
Primary radar |
|
|
|
The four major components of a primary radar system are: |
- Transmitter - Antenna - Receiver - Radar Display |
|
|
|
Features which improve primary radar presentation are: |
- Moving Target Indicator (MTI) - Polarization |
|
|
|
_________ is a pattern produced on the radar scope by ground returns which may degrade other radar returns in the affected area.
|
Ground Clutter
|
|
|
|
Two types of polarization are: |
- Linear - Circular |
|
|
|
Name the components of a primary radar system. |
Transmitter, antenna, receiver, and radar display |
|
|
|
What are two types of radar jamming: |
- Passive jamming - Active jamming |
|
|
|
What type of polarization would be used to reduce areas of heavy precipitation from the radar display? |
Circular Polarization |
|
|
|
Requires no equipment in the aircraft |
Primary radar |
|
|
|
Displays only objects in motion |
MTI |
|
|
|
Focuses, broadcasts, and collects reflected radio energy |
Antenna |
|
|
|
Depicts the position and movement of objects that reflect radio energy |
Radar display |
|
|
|
Reduces or eliminates echoes from precipitation |
Circular Polarization |
|
|
|
Normal radar transmission that will cause an echo from anything that has mass |
Linear Polarization |
|
|
|
Radar indications of aircraft or objects that do not exist |
False targets |
|
|
|
Appearance of clutter on the radar display caused by moisture in the air bending the radar beam |
Anomalous Propagation |
|
|
|
Occurs when warmer air is trapped on top of cooler air |
Temperature inversion |
|
|
|
Appearance of clutter on the radar display that results from two radar systems operating on similar frequencies |
Electronic radar interference |
|
|
|
Appearance of clutter on the radar display caused by dropping large amounts of chaff |
Passive radar jamming |
|
|
|
Clutter pattern achieved by electronic disruption of the radar operating frequency |
Active radar jamming |
|
|
|
Area directly above the antenna that is not included in the signal pattern |
Blind zone |
|
|
|
Amplifies and converts reflected radio energy into video |
Receiver |
|
|
|
The secondary radar system consists of five major components: |
- Interrogator - Antenna - Transponder - Decoder - Radar Display |
|
|
|
Which component of the secondary radar system is located in the aircraft? |
Transponder |
|
|
|
What are the five major components of the secondary radar system? |
Interrogator, transponder, antenna, decoder, and radar display |
|
|
|
Name some advantages and disadvantages of secondary radar. |
Advantages: Less vulnerable to blind spots, provides longer range, and display not degraded by weather echoes or ground cover
Disadvantages: Only displays aircraft with transponders, does not provide weather information, and return is affected by aircraft orientation |
|
|
|
Which document prescribes air traffic control procedures and phraseology used by the FAA? A. FAA Order JO 7110.65 B. FAA Order JO 7210.3 C. FAA Order JO 7110.10 |
A. FAA Order JO 7110.65 |
|
|
|
Which document prescribes flight service procedures and phraseology used by the FAA? A. Flight Service Phraseology Guide B. FAA Order JO 7210.3 C. FAA Order JO 7110.10 |
C. FAA Order JO 7110.10 |
|
|
|
Which document provides direction and guidance for operating and managing air traffic facilities and offices? A. FAA Order JO 7110.65 B. FAA Order JO 7210.3 C. FAA Order JO 7350.8 |
B. FAA Order JO 7210.3 |
|
|
|
Which document contains the approved words and phrase contractions used by personnel in the FAA? A. FAA Order JO 7350.8 B. Aeronautical Information Manual C. FAA Order JO 7340.2 |
C. FAA Order JO 7340.2 |
|
|
|
Which document lists the location identifiers authorized by the FAA, Department of the Navy, and Transport Canada? A. FAA Order JO 7350.8 B. FAA Order JO 7340.2 C. Aeronautical Information Manual |
A. FAA Order JO 7350.8 |
|
|
|
Which document provides the aviation community with basic flight information and ATC procedures for use in the United States NAS? A. FAA Order JO 7350.8 B. FAA Order JO 7340.2 C. Aeronautical Information Manual |
C. Aeronautical Information Manual |
|
|
|
Responsibility for approval of a LOA rests with the A. Service Area Office. B. Flight Inspection Field Office. C. General Aviation District Office. |
A. Service Area Office. |
|
|
|
Who may be delegated the authority to approve a LOA? |
ATREPs and Air Traffic Managers (ATMs) |
|
|
|
One purpose of SOPs is to: A. specify jurisdictional boundaries for each position/sector. B. establish coordination between facilities. C. coordinate between government and nongovernment facilities. |
A. specify jurisdictional boundaries for each position/sector. |
|
|
|
Which of the following would not require the development of a LOA? A. Interfacility coordination B. Intrafacility coordination C. Airport emergency services |
B. Intrafacility coordination |
|
|
|
The primary source of lift on an airfoil is created by a differential in ________. A. temperature B. pressure C. reaction |
B. pressure |
|
|
|
The statement, “the internal pressure of a fluid decreases at points where the speed of the fluid increases” is a part of ________. A. Bernoulli’s Principle B. Newton’s Law of Motion C. Hindenberg’s Theory |
A. Bernoulli’s Principle |
|
|
|
is the direction of the airflow produced by an object moving though the air. |
Relative wind |
|
|
|
Types of airfoils on aircraft are: (6)
|
Wing
Propeller Helicopter rotor Horizontal stabilizer Vertical tail surfaces Fuselage |
|
|
|
The three principle airfoils that produce lift on an aircraft are: |
Wing Horizontal tail surfaces Propeller (lift produced in a forward direction) |
|
|
|
PARTS OF AN AIRFOIL:
|
Leading edge
Trailing edge Chord line |
|
|
|
The ______ is the curvature of the airfoil from the leading edge to the trailing edge. |
camber |
|
|
|
FORCES ACTING ON AN AIRPLANE IN FLIGHT |
Lift, Weight, Thrust, and Drag |
|
|
|
What are the three principle airfoils? |
wings, horizontal tail surface, propeller |
|
|
|
What is the curvature of the airfoil from the leading edge to the trailing edge? |
Camber |
|
|
|
Three key properties of the atmosphere that affect air density, and aircraft performance are: |
Temperature Altitude Water Vapor (humidity) |
|
|
|
Increased density altitude, such as in mountainous and high terrain areas with warm humid air, can greatly reduce aircraft performance, including: |
Longer takeoff roll Longer landing roll Slower climb rate Reduced engine power output Landing speed increased |
|
|
|
An aircraft has three axes of rotation, they are: |
− Longitudinal Axis (Roll) − Lateral Axis (Pitch) − Vertical Axis (Yaw) |
|
|
|
PRIMARY CONTROL SURFACES: |
Ailerons (controls roll) Elevator (moves as a unit; controls pitch) Rudder (controls yaw) |
|
|
|
Which two movements are controlled by the control yoke? |
Roll and pitch |
|
|
|
Which of the following is a primary control surface? A. Variable-pitch propeller B. Flap C. Rudder |
C. Rudder |
|
|
|
The extension of flaps causes an increase in ________. A. stall speed B. airspeed C. drag |
C. drag |
|
|
|
The three primary types of icing are: |
structural icing pitot-static system icing carburetor icing. |
|
|
|
The rotor blade of a helicopter is an airfoil and functions the same as a wing on a conventional aircraft. Name the three devices that control the rotor blade. |
Throttle, Collective, & Cyclic |
|
|
|
Lift is created as air flows smoothly over an airfoil. A stall occurs when the ________ of ________ is exceeded. |
critical angle; attack |
|
|
|
Air stops flowing smoothly over an airfoil between _________ and ________ degrees angle of attack. |
15; 20 |
|
|
|
What are the three primary causes of stalls? |
Insufficient airspeed; excessively violent flight maneuvers; severe wind shear |
|
|
|
The greatest wake turbulence is associated with which aircraft configuration? A. Heavy, clean, fast B. Heavy, dirty, slow C. Heavy, clean, slow |
C. Heavy, clean, slow |
|
|
|
The strength of these vortices will diminish with:
|
Time Distance |
|
|
|
If you have an aircraft on approach to an airport and a similar aircraft cruising during wake turbulence effect? |
An aircraft on approach to an airport |
|
|
|
Of speed, configuration, and weight, which one has the greatest impact on wake turbulence? |
Weight |
|
|
|
What is the name for the turbulent phenomenon created by aircraft passing through the atmosphere? |
Wake turbulence |
|
|
|
The circular patterns created by wake turbulence are often known as what? |
‘Wake Vortex’ or ‘Wingtip Vortices’ |
|
|
|
For fixed-wing aircraft, vortices begin at what stage of flight? |
At rotation or when lift begins. |
|
|
|
When do fixed-wing aircraft stop generating vortices? |
At touchdown or when lift ends. |
|
|
|
When observing an aircraft from behind, the circulation of vortices off the right wingtip is _______ and _______ off the left wingtip. |
counterclockwise; clockwise |
|
|
|
Vortices from large aircraft will sink approximately 300 feet to 500 feet per minute and level off approximately ______ feet below the flight path. A. 100 to 300 B. 500 to 1000 C. 1000 to 2000 |
B. 500 to 1000 |
|
|
|
With no wind, vortices within 100 feet to 200 feet of the ground will move ________ to ________ knots laterally across the ground. |
2; 3 |
|
|
|
For landing aircraft, crosswinds of 1 to 5 knots tend to ________ the lateral movement of one vortex while ________ the movement of the other. |
stall; increasing |
|
|
|
Hazardous conditions occur when the induced roll exceeds the level of ______. |
roll control of the aircraft |
|
|
|
Counter control is most effective and roll is minimal when the wingspan and the ailerons extend beyond the ________ of the vortex. |
outer edges |
|
|
|
A hovering helicopter creates a downwash from its main rotors that can travel up to how far? |
Up to 3 times the diameter of its rotors |
|
|
|
What must a helicopter be doing in order to generate wingtip vortices? |
It must be in a forward flight. |
|
|
|
Why is the controller not responsible for anticipating the existence or effects of wake turbulence? |
Because it is unpredictable |
|
|
|
Wake turbulence has the greatest impact on ATC in the areas of _______.
A. damage and money B. resources and delays C. increased separation and traffic management delays |
C. increased separation and traffic management delays
|
|
|
|
What is the general speed range for CAT II aircraft? A. 100 - 160 knots B. 160 - 250 knots C. 250 - 500 knots |
B. 160 - 250 knots |
|
|
|
What category do helicopters fall under? |
CAT I |
|
|
|
What category do turbojet engine aircraft fall under? |
CAT III |
|
|
|
A twin-engine, turboprop aircraft weighing 12,500 pounds or less will fall under which category? |
CAT II |
|
|
|
An aircraft capable of 300,000 pounds of takeoff weight, but which currently only has a takeoff weight of 225,000 pounds, would fall into what weight class? |
Heavy |
|
|
|
An aircraft in the small weight class has a maximum certified takeoff weight of _______ pounds or less. |
41,000 |
|
|
|
If an aircraft has a 250,000 pound maximum certified takeoff weight, what would its weight class be? |
Large |
|
|
|
Aircraft weighing more than 41,000 lbs. maximum certified takeoff weight up to but not including 300,000 lbs. |
Large Weight Class |
|
|
|
A large multi-engine turbojet aircraft. |
Category III |
|
|
|
Aircraft capable of takeoff weights of 300,000 lbs. or more whether operating at that weight or not. |
Heavy Weight Class |
|
|
|
Small aircraft weighing 12,500 lbs. or less, single-engine, propeller-driven, and all helicopters. |
Category I |
|
|
|
Aircraft weighing 41,000 lbs. or less maximum certified takeoff weight. |
Small Weight Class |
|
|
|
Small aircraft weighing 12,500 lbs. or less, twin-engine, and propeller-driven. |
Category II |
|
|
|
Aircraft normally operating at 10,000 feet MSL and below, speed between 100-160 knots with a climb rate of 1,000 feet per minute or less. |
CAT I Operating Characteristics |
|
|
|
Aircraft normally operating at below FL200, speed between 90-160 knots with a climb rate of 500-2,150 feet per minute. |
Helicopters |
|
|
|
Aircraft normally operating at FL240 and below, speed between 160-250 knots with a climb rate of 1,000-2,000 feet per minute. |
CAT II Operating Characteristics |
|
|
|
Aircraft normally operating at FL450 and below, speed between 300-550 knots with a climb rate of 2,000-4,000 feet per minute. |
CAT III Operating Characteristics |
|
|
|
Designators may have as many as ________ characters, but no less than ________. A. 8; 4 B. 6; 3 C. 4; 2 D. 3; 1 |
C. 4; 2 |
|
|
|
An aircraft designator must consist of letters only.
A. True B. False |
B. False |
|
|
|
The first character in an aircraft designation must be a/an ________. A. number B. letter C. letter or number D. ‘N’ |
B. letter |
|
|
|
What are the nine generally-accepted identification features of aircraft? |
1. Size 2. Engine location and number 3. Engine type 4. Wing placement 5. Wing configuration 6. Tail configuration 7. Windows 8. Fuselage shape 9. Landing gear |
SEEWW TWFL |
|
|
What are two types of engines having propellers? |
Reciprocating and turboprop |
|
|
|
Turbojet engines are limited to what weight class of aircraft? |
Turbojet engines can be found on ALL weight classes of aircraft. |
|
|
|
What are the two basic types of landing gear? |
Tricycle and Conventional (aka ‘tail dragger’) |
|
|
|
What are the three basic wing placement positions? |
High-wing, Mid-wing, Low-wing |
|
|
|
What are the three basic wing shapes or configurations? |
Straight-wing, Swept-wing, Delta-wing |
|
|
|
How many basic tail configurations are there? Name them. |
FIVE 1. Conventional Tail 2. Forward Slant Vertical Stabilizer 3. Horizontal Stabilizer above the fuselage 4. “T” Tail (swept or straight) 5. “V” Tail |
|
|
|
What are the five basic aircraft window shapes? |
Teardrop, oval, round, square, and bubble canopy |
|
|
|
Which class of airspace does not require an ATC clearance? A. A B. B C. C |
C. C |
|
|
|
The airspace that generally extends from the surface to 10,000 feet MSL and surrounds a busy airport is designated as Class ________ airspace. A. A B. B C. C |
B. B |
|
|
|
The authority and responsibility for flying in Class G airspace belong to the _______. A. pilot B. military C. air traffic controller |
A. pilot |
|
|
|
The Special Use Airspace that overlies an aerial gunnery range located over land is called a _______ Area. A. Prohibited B. Restricted C. Warning |
B. Restricted |
|
|
|
What type of Special Use Airspace is found over international waters? A. Prohibited Area B. Controlled Firing Area C. Warning Area |
C. Warning Area |
|
|
|
Prohibited Area vertical airspace begins at _______. A. 3,000 feet B. the surface C. 1,500 feet |
B. the surface |
|
|
|
In what type of airspace would a high volume of pilot training take place? A. Restricted Area B. Controlled Firing Area C. Alert Area |
C. Alert Area |
|
|
|
Federal VOR airways class airspace? |
Class E |
|
|
|
Uncontrolled airspace is designated as what class airspace? |
Class G |
|
|
|
Jet routes are in what class airspace? |
Class A |
|
|
|
What determines the upper limits of Class G airspace? |
The base of the overlying controlled airspace |
|
|
|
What is one of the requirements for an aircraft operating in Class B airspace? |
ATC Clearance, Two-way communications, 4096 transponder with mode C |
|
|
|
VFR flight is not permitted in what class airspace? |
Class A |
|
|
|
Generally, that airspace from the surface to 2,500 feet above the airport elevation with an operational control tower is classified as what class airspace? |
Class D |
|
|
|
What type of Special Use Airspace is over the White House? |
Prohibited Area |
|
|
|
In what type of airspace would a high volume of pilot training take place?
|
Alert Area
|
|
|
|
What type of Special Use Airspace is found over international waters? |
Warning Area |
|
|
|
What type of Special Use Airspace is over an aerial gunnery range over land? |
Restricted Area |
|
|
|
What does “MOA” stand for? |
Military Operations Area |
|
|
|
Under whose authority are FARs issued? |
FAA Administrator |
|
|
|
Aircraft operating in the air or on airport movement areas are referred to as ________. A. air carriers B. air traffic C. air traffic control |
B. air traffic |
|
|
|
Authorization by air traffic control for the purpose of preventing collisions between known aircraft, and for an aircraft to proceed under specified traffic conditions within controlled airspace, is called an ATC _______. A. approval B. direction C. clearance |
C. clearance |
|
|
|
A level of constant atmospheric pressure related to a reference datum of 29.92 inches of mercury (stated in three digits) is referred to as ________. A. flight level B. aircraft altitude C. Mean Sea Level (MSL) altitude |
A. flight level |
|
|
|
Control of all air traffic within designated airspace by air traffic control is called ________ control. A. restricted B. precision C. positive |
C. positive |
|
|
|
Which aircraft operating within the United States are subject to FAR Part. 91? A. Military only B. Civilian C. All aircraft |
C. All aircraft |
|
|
|
When may pilots of two different aircraft operate as a formation flight? A. Authorization is obtained from air traffic control. B. Flight visibility is at least 3 miles. C. Prior arrangements are made, and no paying passengers are aboard. |
C. Prior arrangements are made, and no paying passengers are aboard. |
|
|
|
What is the maximum speed of VFR aircraft below Class B airspace? |
200 knots |
|
|
|
What is the maximum speed for an aircraft in Class C or D Airspace flying at less than 2,500 feet AGL and within 4 NM of the primary airport? A. 156 knots B. 200 knots C. 250 knots |
B. 200 knots |
|
|
|
What should the altimeter be set at in an aircraft maintaining FL310? A. 29.92 B. 31.00 C. altimeter setting within 100 NM of the aircraft |
A. 29.92 |
|
|
|
When may a pilot deviate from an ATC clearance?
A. At the pilot’s discretion B. In an emergency C. Under no condition |
B. In an emergency |
|
|
|
When should a pilot who deviates from an ATC clearance notify ATC of that deviation?
|
As soon as possible
|
|
|
|
What is true about filing a VFR flight plan? A. It is mandatory for all VFR flights. B. It is strongly encouraged. C. It is required for entering Class G airspace. |
B. It is strongly encouraged. |
|
|
|
When landing at an airport with an operational ATCT, an IFR flight plan ________. A. must be cancelled by the pilot B. is automatically cancelled C. remains open until departure |
B. is automatically cancelled |
|
|
|
TRUE or FALSE: Only VFR flight plans are used for search and rescue purposes |
False |
|
|
|
A VFR flight at 4,500 MSL within Class E airspace requires a flight visibility of how many SM(s)? A. 1 B. 3 C. 5 |
B. 3 |
|
|
|
The pilot must stay “clear of clouds” for VFR flights in which type of airspace? A. Class B airspace B. Class C airspace C. Class D airspace D. Class E airspace |
A. Class B airspace |
|
|
|
What is the distance from clouds for VFR flights in Class C and Class D airspace? A. 500 feet above, 1,000 feet below, and 2,000 feet horizontal B. 500 feet below, 2,000 feet above, and 1,000 feet horizontal C. 500 feet below, 1,000 feet above, and 2,000 feet horizontal |
C. 500 feet below, 1,000 feet above, and 2,000 feet horizontal |
|
|
|
What would be an appropriate VFR altitude on a magnetic course of 250 degrees, and more than 3,000 feet above the surface? A. 7,000 B. 7,500 C. 8,500 |
C. 8,500 |
|
|
|
VFR-On-Top is an IFR clearance.
A. True B. False |
A. True |
|
|
|
For SVFR operations, if the surface visibility is not reported, flight visibility must be at least: A. 2 SM B. 1 NM C. 1 SM |
C. 1 SM |
|
|
|
What is the correct altitude for a VFR aircraft on a magnetic course of 090 degrees? |
Odd plus 500 feet |
|
|
|
What is the correct altitude for a VFR aircraft on a magnetic course of 120 degrees? |
Odd plus 500 feet |
|
|
|
What is the correct altitude for a VFR aircraft on a magnetic course of 180 degrees? |
Even plus 500 feet |
|
|
|
What is the correct altitude for a VFR aircraft on a magnetic course of 285 degrees? |
Even plus 500 feet |
|
|
|
What is the correct altitude for a VFR aircraft on a magnetic course of 360 degrees? |
Odd plus 500 feet |
|
|
|
What is required before a person may operate aircraft in controlled airspace under IFR? A. File a flight plan B. File a flight plan and receive an ATC clearance C. File a flight plan and requested a clearance |
B. File a flight plan and receive an ATC clearance |
|
|
|
What is the minimum visibility for an IFR departure when the takeoff minimum at a civil airport is not prescribed for a twin-engine aircraft? A. 1/2 mile B. 1 mile C. 1 1/2 mile |
B. 1 mile |
|
|
|
An aircraft is cleared from Altus to the Enid airport by other than the filed routing. How will the pilot proceed if radio failure occurs? |
Via routing received in last ATC clearance |
|
|
|
If a route has not been assigned, or if ATC has not advised that a route may be expected, what action will the pilot take in the event of radio failure? |
Proceed by the route filed in the flight plan |
|
|
|
When there is a two-way radio failure, what is a pilot expected to do when the aircraft arrives at a clearance limit from which an approach begins? |
1. Commence descent and approach as close as possible to the EFC, if one has been received. 2. Without an EFC, begin descent and approach as near as possible to the ETA. |
|
|
|
When coordinates are used to define position, is latitude or longitude stated first? |
Latitude |
|
|
|
How would these coordinates be read? 1. 29°40'N, 35°53'W |
1. 29 degrees, 40 minutes, north (latitude), 35 degrees, 53 minutes, west (longitude) |
|
|
|
How would these coordinates be read? 2. 45°35'N, 82°43'22"E |
45 degrees, 35 minutes, north (latitude), 82 degrees, 43 minutes, 22 seconds, east (longitude) |
|
|
|
The reference line for measuring north-south distances is the _______. A. great circle B. prime meridian C. equator |
C. equator |
|
|
|
How many minutes are there in 1 degree of latitude? |
60 minutes |
|
|
|
The unit of measurement which equals 1 nautical mile is ________ statute miles. A. 0.87 B. 1.15 C. 1.5 |
B. 1.15 |
|
|
|
A time zone is established for every ________. A. 15 degrees of longitude B. 7 1/2 degrees of latitude C. 15 degrees of latitude |
A. 15 degrees of longitude |
|
|
|
An aircraft departs Oklahoma City at 9 P.M. (CST) and travels for 3 hours to arrive in Seattle, WA. (PST) What was the aircraft’s arrival time UTC? |
0600Z |
|
|
|
If it is 1300Z in Philadelphia (EST), what local time would it be in San Francisco (PST)? |
0500 local |
|
|
|
At 1 P.M. EDT in New York City, the time is _____ UTC. (Conversion factor is +5 EST). A. 1600 B. 1700 C. 1800 |
B. 1700 |
1 P.M. = 1300 DST. Add conversion factor = 5 hours. Subtract 1 hour for DST. |
|
|
An aircraft has a true airspeed of 200 KTS and is encountering a headwind of 40 kts. What is the aircraft’s ground speed? |
160 KTS |
|
|
|
An aircraft has a true airspeed of 180 KTS and encounters a tailwind of 30 kts. What is the aircraft’s ground speed? |
210 KTS |
|
|
|
An aircraft has a ground speed of 170 KTS and a headwind of 30 KTS. What is the aircraft’s ground speed? |
170 KTS |
|
|
|
An aircraft has a true airspeed of 320 knots and a tailwind of 40 knots. How far will the aircraft travel in 1 hour, 15 minutes? |
450 nautical miles |
|
|
|
The angular difference between true north and magnetic north at any given place is called ________. A. variation B. deviation C. isogonic line |
A. variation |
|
|
|
A line of equal magnetic variation is called a(n) ________ line. A. agonic B. magnetic C. isogonic |
C. isogonic |
|
|
|
What term denotes a magnetic compass error that is caused by materials within the aircraft which possess magnetic properties? |
Deviation |
|
|
|
True heading is true course corrected for effects of ________. A. magnetic variation B. compass error C. wind |
C. wind |
|
|
|
Navigation by reference to visible landmarks is called ________. A. dead reckoning B. pilotage C. radio navigation |
B. pilotage |
|
|
|
What method of navigation requires flying a predetermined course, taking into account the effects of wind? |
Dead reckoning |
|
|
|
How are all NDBs, except compass locators, identified? A. Three-letter identifier in Morse code B. Two-letter identifier in Morse code C. Aural tone |
A. Three-letter identifier in Morse code |
|
|
|
A VOR antenna transmission pattern is _______________. A. omni-directional B. nondirectional C. fan-shaped |
A. omni-directional |
|
|
|
A VOR station projects _______________. A. 360 usable true radials B. 360 usable magnetic radials C. an infinite number of bearings |
B. 360 usable magnetic radials |
|
|
|
The different classes of VORs are _______________. A. High, Low, Terminal B. High, Medium, Low C. High, Low, Compass Locator |
A. High, Low, Terminal |
|
|
|
A TACAN station projects _______________. A. 360 usable true radials B. 360 usable magnetic radials C. an infinite number of bearings |
B. 360 usable magnetic radials |
|
|
|
TACAN frequencies are in the _______________ band. A. L/MF B. VHF C. UHF |
C. UHF |
|
|
|
DME distance is displayed _______________. A. as slant range distance B. as horizontal distance C. in time to station |
A. as slant range distance |
|
|
|
What DME equipment on the ground is required to respond to the aircraft interrogator? A. Transmitter B. Transponder C. VOR |
B. Transponder |
|
|
|
What is the maximum non-radar lateral protected airspace of a victor airway? |
10 NM either side of centerline |
|
|
|
What is the upper limit of a low altitude VOR airway? A. Up to and including 18,000 feet MSL B. Up to, but NOT including 18,000 MSL C. Up to, but NOT including FL180 |
B. Up to, but NOT including 18,000 MSL |
|
|
|
The upper limit of the jet route structure is ________. A. up to and including FL600 B. up to but not including FL600 C. up to and including FL450 |
C. up to and including FL450 |
|
|
|
What instruments are affected by the pitot-static system? |
1. Airspeed indicator 2. Vertical speed indicator 3. Altimeter |
|
|
|
There are two fundamental properties of gyroscopic action: |
Rigidity in space Precession |
|
|
|
What may be obtained from the attitude indicator? A. Rate of turn B. Degrees of bank C. Height above sea level |
B. Degrees of bank |
|
|
|
The VOR course deviation needle indicates the aircraft’s position in relation to the selected ________. A. heading B. radial C. bearing |
B. radial |
|
|
|
The range displayed on the DME indicator is called ________ range. A. omni B. straight C. slant |
C. slant |
|
|
|
Airports with control towers are always depicted ____________. A. in the color blue B. by a circle with runway configurations shown C. with the letter “T” next to the airport |
A. in the color blue |
|
|
|
In the airport data “450 L 51 122.7,” the letter “L” indicates ____________. A. the category of NAVAID located at the airport B. a left-hand traffic pattern is standard at that airport C. the airport has runway lighting |
C. the airport has runway lighting |
|
|
|
In the airport data “4500 L 72 122.95,” “4500” is the ____________. A. airport elevation above sea level B. length of the longest runway C. height above sea level of the tallest obstruction within 5NM |
A. airport elevation above sea level |
|
|
|
A pilot can receive Hazardous Inflight Weather Advisory Service (HIWAS) broadcasts via the voice portion of a navigational aid if its communications box has a(n) _____________. A. frequency written above the box B. asterisk preceding the NAVAID frequency C. blue filled-in circle with a white H |
C. blue filled-in circle with a white H |
|
|
|
The boundary of Class B airspace is always depicted in what color? A. Magenta B. Blue C. Dark gray |
B. Blue |
|
|
|
The height of an obstruction is indicated on the chart in feet above _____________. A. Ground Level (AGL) B. Mean Sea Level (MSL) C. both ground level and sea level |
C. both ground level and sea level |
|
|
|
A major difference between a Sectional Aeronautical Chart and a Terminal Area Chart is that the Terminal Area Chart ______________. A. provides greater detail and a larger scale B. is used primarily for IFR flight in the terminal area C. uses a different set of symbols for manmade as well as topographical features |
A. provides greater detail and a larger scale |
|
|
|
En Route Low Altitude Charts are published every ________. A. 28 days B. 56 days C. 6 months |
B. 56 days |
|
|
|
Which statement is true concerning En Route Low Altitude Charts? A. Areas of mountainous terrain are depicted. B. Military Training Routes include times of use. C. There are a total of 36 charts. |
C. There are a total of 36 charts. |
|
|
|
En Route Low Altitude Charts are for use below ________ feet MSL. A. 18,000 B. 12,500 C. 10,000 |
A. 18,000 |
|
|
|
Airports with approved Instrument Approach Procedures are depicted in ________ and ________. A. green, brown B. brown, blue C. blue, green |
C. blue, green |
|
|
|
When included in the airport data, (A) means ________. A. the airport is surrounded by Class A airspace B. alternate approach minimums are applicable at that airport C. Automatic Terminal Information Service (ATIS) is available |
C. Automatic Terminal Information Service (ATIS) is available |
|
|
|
A star (*) in the airport data could be used to indicate ________. A. part-time status of surrounding airspace B. pilot-controlled lighting C. presence of a rotating beacon on the field |
A. part-time status of surrounding airspace |
|
|
|
A frequency which is underlined within a communication box indicates that ________. A. no HIWAS broadcast is available through that facility B. there is no voice transmitted on that frequency C. a NOTAM is issued pertaining to an abnormal status situation |
B. there is no voice transmitted on that frequency |
|
|
|
A (T) depicted next to the facility name means ________. A. the facility is temporarily unmonitored B. Transcribed Weather Broadcasts are available C. the facility is a Terminal class NAVAID |
C. the facility is a Terminal class NAVAID |
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT found in a communication box? A. NAVAID frequency B. Symbol indicating the availability of ATIS broadcasts C. Morse Code identification of the NAVAID |
B. Symbol indicating the availability of ATIS broadcasts |
|
|
|
The OROCA ensures an aircraft of ________ coverage. A. obstruction clearance, but no NAVAID/communications B. NAVAID signal reception, but no communications C. communications coverage, but no NAVAID signal |
A. obstruction clearance, but no NAVAID/communications |
|
|
|
Light brown shading indicates the presence of ________. A. uncontrolled airspace B. controlled airspace C. a Warning Area |
A. uncontrolled airspace |
|
|
|
A Mode C Area, which requires an aircraft to have Mode C equipment onboard, is depicted by ________. A. solid blue shading inside of a solid blue outline B. a hatched blue line around the boundary C. a solid blue outline |
C. a solid blue outline |
|
|
|
An appropriate IFR altitude for an aircraft on a magnetic heading of 178° is ________. A. not able to be determined B. 15,000 feet C. 8,000 feet |
A. not able to be determined |
|
|
|
The primary purpose of an IFR Area Chart is to furnish ________. A. visual landmarks for use in congested areas B. terminal data for IFR flights C. navigation information using a smaller scale than the En Route Low Altitude Charts |
B. terminal data for IFR flights |
|
|
|
IFR Area Charts are published ________. A. every 56 days B. every 6 months C. at the same time as the Terminal Area Charts |
A. every 56 days |
|
|
|
Instrument Departure Procedures are preplanned IFR procedures that provide obstruction clearance and facilitate transition from the terminal environment to the en route environment. A. True B. False |
A. True |
|
|
|
TYPES OF SIDs |
• Pilot Navigational • Vector |
|
|
|
U.S. Terminal Procedure Charts are published every _____ days. A. 28 B. 56 C. 112 |
B. 56 |
|
|
|
After locating the correct volume, the specialist should verify A. whether the airport has a SID. B. the currency of the volume. C. whether the desired SID is a Vector or Pilot Navigational SID. |
B. the currency of the volume. |
|
|
|
What is the primary reason SIDs have been developed?
|
simplify clearance delivery, expedite traffic flow, and reduce pilot/controller workload.
|
SER
|
|
|
What must a pilot possess before accepting a STAR clearance? |
The approved chart for the STAR. |
|
|
|
An aircraft must be in instrument flight conditions to execute an Instrument Approach Procedure (IAP). A. True B. False |
B. False |
|
|
|
The ILS is designed to provide ________. A. An approach path with both course and vertical guidance B. 360 useable magnetic radials C. accurate long range navigation |
A. An approach path with both course and vertical guidance |
|
|
|
An approach is termed “precision” because it ________. A. lines the aircraft up with the active runway B. provides lateral and vertical guidance C. allows the aircraft to descend through the overcast safely |
B. provides lateral and vertical guidance |
|
|
|
Which of the following components of an ILS is designed to provide the pilot with course guidance to the runway centerline? A. Markers B. Glide path C. Localizer |
C. Localizer |
|
|
|
The purpose of the marker beacon is to ___________. A. provide directional information B. identify a particular location C. provide airborne radio direction finding |
B. identify a particular location |
|
|
|
An Instrument Approach Procedure (IAP) is designed to provide _______. A. an IFR descent to a point where the active runway is in sight B. an IFR descent to a point where a safe landing can be made C. altitude guidance to a descending aircraft |
B. an IFR descent to a point where a safe landing can be made |
|
|
|
There are two types of precision approaches: ILS and PAR. A. True B. False |
A. True |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the IAP Chart? |
To portray the aeronautical data required to execute Instrument Approach Procedures to airports |
|
|
|
What are the seven sections of the IAP Chart? |
1. Margin Information 2. Pilot Briefing Information 3. Planview 4. Airport Diagram 5. Missed Approach Icons 6. Profile View 7. Minimums Section |
|
|
|
Controllers are responsible for providing current prevailing visibility/RVR appropriate to the runway-in-use; however, they are not responsible for determining that landing minimums do or do not exist. A. True B. False |
A. True |
|
|
|
Sea level temperature |
15°C / 59°F |
|
|
|
Decrease of temperature with height (lapse rate) in the Troposphere |
2°C / 3.5°F / 1,000 feet |
|
|
|
Which layer of the atmosphere contains almost all clouds and precipitation? A. Troposphere B. Stratosphere C. Mesosphere |
A. Troposphere |
|
|
|
Which layer of the atmosphere is stable and generally devoid of significant weather? A. Troposphere B. Stratosphere C. Tropopause |
B. Stratosphere |
|
|
|
What is the value of sea level pressure in the standard atmosphere? A. 29.92 hectopascals B. 29.92 inches of mercury C. 1013.2 inches of mercury |
B. 29.92 inches of mercury |
|
|
|
Which two jet streams are commonly identified? A. Arctic and tropical B. Hot and Cold C. Polar and Subtropical |
C. Polar and Subtropical |
- Polar jet stream located between 30° and 60° latitude. - Subtropical jet stream located between 20° and 40° latitude. |
|
|
The ratio, usually expressed as a percentage, of water vapor actually in the air compared to the amount of water vapor the air could hold at a particular temperature and pressure. |
Relative Humidity |
|
|
|
What is the raw material for clouds and precipitation? A. Evaporation B. Dew point C. Water vapor |
C. Water vapor |
|
|
|
A parcel of air that has the capacity to hold more water vapor is ________. A. saturated B. unsaturated C. evaporated |
B. unsaturated |
|
|
|
When the ________ decreases to zero, the air becomes ________, and condensation will form dew, fog, or clouds. A. dew point, saturated B. temperature-dew point spread, saturated C. condensation, unsaturated |
B. temperature-dew point spread, saturated |
|
|
|
A parcel of ________ air expands and cools as pressure decreases with height. A. rising B. sinking C. stationary |
A. rising |
|
|
|
Which cloud form often produces widespread IFR weather? A. Cirriform B. Stratiform C. Cumuliform |
B. Stratiform |
|
|
|
Air flow around a low ________ in a counterclockwise motion and ________, causing the air to cool and eventually condense into clouds and precipitation. A. diverges, rises B. converges, sinks C. converges, rises |
C. converges, rises |
|
|
|
A Maritime Tropical (mT) air mass is ________ and ________. A. warm, moist B. warm, dry C. cold, dry |
A. warm, moist |
|
|
|
A ________ air mass moving over a ________ surface often produces unstable air associated with turbulence, good visibility, cumuliform clouds, and showers. A. hot, cool B. warm, cold C. cold, warm |
C. cold, warm |
|
|
|
Which front moves in such a way that warmer air replaces colder air? A. Cold front B. Warm front C. Stationary front |
B. Warm front |
|
|
|
What type of front has a steep slope which often leads to a narrow band of showers and thunderstorms if the rising air is unstable?
A. Cold front B. Warm front C. stationary front |
A. Cold front
|
|
|
|
The three necessary ingredients for precipitation formation are ________, lift, and a growth process. A. water vapor B. unstable air C. warm air |
A. water vapor |
|
|
|
Which precipitation type occurs when there is a deep layer aloft with above freezing temperatures, with a shallow layer of below freezing air at the surface? A. Snow B. Ice pellets C. Freezing rain |
C. Freezing rain |
|
|
|
What NWS entity provides consultation, forecast, and advice to Air Route Traffic Control Centers (ARTCCs) regarding weather impacts? A. Meteorological Watch Office (MWO) B. Weather Forecast Office (WFO) C. Center Weather Service Unit (CWSU) |
C. Center Weather Service Unit (CWSU) |
|
|
|
When an airplane is taking off into a headwind, gusts may cause it to ________. A. drift off the side of the runway B. bounce on the runway C. roll off the end of the runway |
B. bounce on the runway |
|
|
|
A variable wind can be hazardous on takeoff and landing because it could _______. A. cause engine failure B. cause the pilot to experience vertigo C. quickly become a crosswind or tailwind |
C. quickly become a crosswind or tailwind |
|
|
|
Which type of aircraft will perform better in adverse wind conditions, due to its higher takeoff and approach speeds? A. Larger airplanes B. Smaller airplanes C. Helicopters |
A. Larger airplanes |
|
|
|
Most aircraft accidents related to instrument weather involve pilots who ________. A. are instrument rated B. are not instrument rated C. have under 1,000 hours of flight time |
B. are not instrument rated |
|
|
|
Which precipitation types most commonly produce instrument weather? A. Rain, drizzle, and snow B. Hail, snow grains, and ice pellets C. Snow, snow grains, and ice crystals |
A. Rain, drizzle, and snow |
|
|
|
What type of turbulence momentarily causes slight erratic changes in altitude and/or attitude (pitch, roll, yaw)? A. Light B. Moderate C. Severe |
A. Light |
|
|
|
During what type of turbulence is the aircraft violently tossed about and practically impossible to control? A. Moderate B. Severe C. Extreme |
C. Extreme |
|
|
|
When the air is too dry for cumuliform clouds to form, _______ currents caused by uneven surface heating can still be active and cause turbulence. A. wind shear B. mechanical C. convective |
C. convective |
|
|
|
Which of the following clouds would provide visual proof that a mountain wave exists? A. Rotor cloud B. Towering Cumulus (TCU) C. Cumulonimbus (CB) |
A. Rotor cloud |
|
|
|
What generates turbulence between two wind currents of differing wind directions and/or speeds? A. Wind shear B. Obstructions to the wind flow C. Convective currents |
A. Wind shear |
|
|
|
High density altitude ________ an aircraft’s power and thrust. A. increases B. reduces C. does not alter |
B. reduces |
|
|
|
Three types of icing: |
Rime Clear (or glaze) Mixed |
|
|
|
ICING INTENSITY CLASSIFICATION: |
Trace, Light (LGT), Moderate (MOD), and Severe (SEV) |
|
|
|
Although ________ is the most common type of icing, it is the least serious because it is easier to remove. A. rime B. clear C. mixed |
A. rime |
|
|
|
With ________ ice, the rate of accumulation may create a problem if flight is prolonged (over 1 hour). Occasional use of deicing/anti-icing equipment removes/ prevents accumulation. A. trace B. light C. moderate |
B. light |
|
|
|
Aircraft icing potential is NOT dependent upon ________. A. aircraft type and design B. pilot rating C. meteorological factors |
B. pilot rating |
|
|
|
Which adverse effect of structural icing is LEAST significant to an aircraft? A. Increased drag B. Increased weight C. Decreased lift |
B. Increased weight |
|
|
|
Thunderstorm cell formation requires ________, unstable air, and lift. A. an inversion B. water vapor C. stratiform clouds |
B. water vapor |
|
|
|
It may be impossible to recover from ________ encountered at low altitude. A. a headwind B. a microburst C. an outburst |
B. a microburst |
|
|
|
Wind shear is especially dangerous when it is encountered ________. A. during takeoff and landing B. en route C. while in a holding pattern |
A. during takeoff and landing |
|
|
|
While an aircraft is on approach, a shear from a tailwind to a headwind causes airspeed to ________, the nose to pitch ________, and the aircraft to ________ the glideslope. A. increase, up, rise upward above B. increase, up, drop below C. decrease, down, drop below |
A. increase, up, rise upward above |
|
|
|
A TAF is a concise statement of the expected meteorological conditions significant to aviation for a specified time period within ________. A. 5 SM of an airport’s runway complex B. 30 SM of an airport’s runway complex C. an ARTCC’s airspace. |
A. 5 SM of an airport’s runway complex |
|
|
|
In a TAF, “FM121115” indicates ________ occurring on the 12th day of the month ________ UTC. A. a significant and rapid change; at 1115 B. temporary fluctuations; between 11-15 C. a 30% probability; 11-15 |
A. a significant and rapid change; at 1115 |
|
|
|
In a TAF, “TEMPO 1911/1915” indicates ________ occurring on the 19th day of the month ________ UTC. A. a significant and rapid change, at 1915 B. temporary fluctuations, between 11-15 C. a 30% probability, between 11-15 |
B. temporary fluctuations, between 11-15 |
|
|
|
In a TAF, “PROB30 1416/1420” indicates ________ occurring on the 14th day of the month ________ UTC. A. a significant and rapid change; at 1420 B. a 30% probability; between 14-20 C. a 30% probability; between 16-20 |
C. a 30% probability; between 16-20 |
|
|
|
Which product would provide a forecast of severe icing over Kentucky? A. AIRMET Tango B. AIRMET Zulu C. SIGMET |
C. SIGMET |
|
|
|
Which product would provide a forecast of sustained surface wind greater than 30 knots over Minnesota and Iowa? A. AIRMET Tango B. AIRMET Zulu C. SIGMET |
A. AIRMET Tango |
|
|
|
Which product would provide a forecast of IFR over Georgia and Alabama? A. AIRMET Sierra B. AIRMET Zulu C. SIGMET |
A. AIRMET Sierra |
|
|
|
Which product would be used to forecast an isolated severe thunderstorm 25 miles west of Hill City, Kansas (HLC)? A. AIRMET B. SIGMET C. Convective SIGMET |
C. Convective SIGMET |
|
|
|
Which product would provide a forecast of freezing levels over New England? A. AIRMET Sierra B. AIRMET Zulu C. SIGMET |
B. AIRMET Zulu |
|
|
|
Which product would provide a forecast for a squall line over the New York Oceanic Flight Information Region (FIR)? A. AIRMET Tango B. SIGMET C. Convective SIGMET |
B. SIGMET |
|
|
|
An unscheduled aviation weather product issued by CWSU meteorologists for ATC use to alert pilots of existing or anticipated adverse weather conditions within the next two hours is ________. A. a Center Weather Advisory (CWA) B. a Meteorological Impact Statement (MIS) C. an Airman’s Meteorological Information (AIRMET) |
A. a Center Weather Advisory (CWA) |
|
|
|
Which product would the Cleveland CWSU (ZOB) issue due to winds gusting greater than 45 knots in the wake of a cold front expected to enter the ZOB ARTCC airspace in six hours? A. AIRMET Tango B. Center Weather Advisory (CWA) C. Meteorological Impact Statement (MIS) |
C. Meteorological Impact Statement (MIS) |
|
|
|
The Wind and Temperature Aloft Forecast (FB) is used by Air Traffic Control (ATC) to help ________. A. vector aircraft B. calculate density altitude C. calculate fog and cloud formation potential |
A. vector aircraft |
|
|
|
What classification of PIREP would be used to report Severe Icing? |
Urgent (UUA) |
|
|
|
Who uses PIREPs to expedite traffic flow in the vicinity of the airport and to provide hazardous weather avoidance procedures? |
Towers and TRACONs |
|
|
|
When can you request a PIREP? |
Anytime |
|
|
|
When are you required to solicit a braking action PIREP? |
Whenever braking action advisories are in effect (terminal only). |
|
|
|
Under which of the following conditions are you required to solicit a PIREP? A. Ceilings are at or below 5,000 feet. B. A trace of icing is reported. C. It’s Fall and the geese are flying south. |
A. Ceilings are at or below 5,000 feet. |
|
|
|
What are the two classifications of emergencies? |
Distress and Urgency |
|
|
|
Who can declare an emergency for an aircraft? |
Pilot, ATC Personnel, and Aircraft Owner/Operator |
|
|
|
Which ELT system allows for the quickest response to an alert? A. 243.0 MHz B. 406 MHz C. 121.5 MHz |
B. 406 MHz |
|
|
|
The minimum information required for handling an emergency is________. A. aircraft identification and type, nature of the emergency, and pilot’s desires B. aircraft identification, altitude, fuel remaining in time C. aircraft identification and type, altitude, color of aircraft |
A. aircraft identification and type, nature of the emergency, and pilot’s desires |
|
|
|
If an aircraft declares an emergency while you are working it on your frequency, you should normally ________. A. assign the emergency frequency B. leave the aircraft on your frequency C. instruct the aircraft to change to an alternate frequency |
B. leave the aircraft on your frequency |
|
|
|
When a bomb threat has been received involving an aircraft you are working, you should inform the pilot of the threat and ____________. A. instruct the pilot to land as soon as possible B. assign Code 7700 C. comply with any pilot requests |
C. comply with any pilot requests |
|
|
|
The exclusive transponder code for hijacked aircraft is ____________. A. 7700 B. 7600 C. 7500 |
C. 7500 |
|
|
|
A provision for the effective utilization of all available facilities for search and rescue missions is called a ________. A. Search and Rescue Facility B. National Search and Rescue Plan C. Rescue Coordination Center |
B. National Search and Rescue Plan |
|
|
|
An operation to retrieve persons in distress, provide for their initial medical or other needs and deliver them to a place of safety defines a/an ________. A. Search B. Rescue C. Abduction |
B. Rescue |
|
|
|
Which facility has initial search and rescue responsibility for aircraft on a VFR flight plan? A. ARTCC B. RCC C. AFSS |
C. AFSS |
|
|
|
Which facility has search and rescue responsibility for aircraft on a Special VFR clearance? A. ARTCC B. RCC C. AFSS |
A. ARTCC |
|
|
|
Which air force base is responsible for search and rescue coordination for the inland region of the conterminous states? A. Fort Richardson B. Scott AFB C. Tyndall AFB |
C. Tyndall AFB |
|
|
|
What steps are taken when a facility having jurisdiction over a search area receives an ALNOT? |
- Conducts a communications search of airports - Notifies appropriate ATCT facilities - Requests search assistance from aircraft traversing the search area |
|
|
|
When is an aircraft on an IFR flight plan considered overdue? |
An aircraft is considered overdue when neither communications nor radar contact can be established and 30 minutes have passed since: - ETA over a specified or compulsory reporting point or at a clearance limit - Clearance void time |
|
|
|
What is the role of the Rescue Center Coordinator RCC?
|
Coordinate and conduct the physical search for the aircraft.
|
|
|
|
Who is responsible for canceling the ALNOT? |
The facility that issued the ALNOT |
|
|
|
MDA/DA ALTITUDES
1,320 Stated?
486 Stated? |
“MINIMUM DESCENT ALTITUDE, ONE THREE TWO ZERO.”
“DECISION ALTITUDE, FOUR, EIGHT, SIX” |
|
|
|
FIELD ELEVATION
2,817 feet Stated?
|
“FIELD ELEVATION, TWO EIGHT ONE SEVEN” |
|
|
|
SURFACE WIND
27015G35 Stated? |
“WIND TWO SEVEN ZERO AT ONE FIVE GUSTS THREE FIVE” |
|
|
|
HEADING
360 degrees Stated?
5 degrees Stated? |
“HEADING THREE SIX ZERO”
“HEADING ZERO ZERO FIVE”
|
|
|
|
RADAR BEACON CODE
1000 Stated?
3617 Stated? |
“SQUAWK ONE ZERO ZERO ZERO”
“SQUAWK THREE SIX ONE SEVEN” |
|
|
|
FREQUENCIES
243.0 Stated?
135.275 Stated?
302 kHz Stated?
|
“TWO FOUR THREE POINT ZERO”
“ONE THREE FIVE POINT TWO SEVEN”
“THREE ZERO TWO KILOHERTZ” |
|
|
|
FREQUENCIES
88
|
“TACAN CHANNEL EIGHT EIGHT” |
|
|
|
How do you identify an ATCT? |
State the name of the facility followed by the word “TOWER.” |
|
|
|
How are AFSSs identified? |
Name of station followed by the word “RADIO.” |
|
|
|
How is Oakland, California ARTCC identified? |
“OAKLAND CENTER.” |
|
|
|
What is the prefix for a domestic general aviation aircraft when the aircraft type, model name, and/or manufacturer’s name are unknown? |
“NOVEMBER” |
|
|
|
What is the phraseology for AAL52? |
“AMERICAN FIFTY-TWO” |
|
|
|
What is the call sign for a civilian air ambulance? |
“MEDEVAC” |
|
|
|
What are the letter prefixes for the following military services: Air Force, Army, and Navy? |
A, R, and VV |
|
|
|
Airway V12 = Jet Route J35 = IR Route IR531 = VR Route VR42 = Q Route Q136 = T Route T212 = |
“VICTOR TWELVE” “J THIRTY-FIFE” “I-R FIFE THIRTY-ONE” “V-R FORTY-TWO” “Q ONE THIRTY-SIX” “TANGO TWO TWELVE”
|
|
|
|
FIX PHRASEOLOGY
APE050037 |
“APPLETON ZERO FIFE ZERO RADIAL TREE SEVEN MILE FIX” |
|
|
|
What letter precedes the route number for a low altitude RNAV route? How is it pronounced? |
T; “TANGO” |
|
|
|
What is the phraseology to describe this position: SEA286007? |
“SEATTLE TWO EIGHT SIX RADIAL, SEVEN MILE FIX” |
|
|
|
What are seven types of coordination? |
- Radar handoffs - Radar point outs - Transfer of control - Runway crossings - Forwarding flight plan information - Arrival information (i.e., inbounds) - Clearances and instructions |
|
|
|
Radar identification is transferred from one controller to another but communications will not be transferred. This describes a...? |
Point-out |
|
|
|
After the relieving specialist has assumed responsibility for the sector, the relieved specialist _______. A. immediately leaves the area B. reviews all information for omissions or inaccuracies C. signs off the position and remains at the sector for 10 minutes |
B. reviews all information for omissions or inaccuracies |
|
|
|
If the specialist being relieved recognizes an inaccuracy immediately after relinquishing position responsibility, who should be notified? |
The relieving specialist. |
|
|
|
Before receiving a verbal briefing from the specialist being relieved, the relieving specialist shall _______. A. indicate that he/she has assumed position responsibility B. sign onto the position C. preview the position |
C. preview the position |
|
|
|
Briefing on applicable traffic is accomplished during which step of the briefing process? A. Preview the position B. Verbal briefing C. Visual briefing |
B. Verbal briefing |
|
|
|
Flight progress strips are used as an aid and are not a legal document. A. True B. False |
B. False |
|
|
|
Strips are ________ and ________ differently for each air traffic option. |
sized and formatted |
|
|
|
In comparison to the terminal strip, the en route strip is ______. A. larger with more blocks B. smaller with less blocks C. no different in size |
A. larger with more blocks
|
|
|
|
You should use authorized symbols or abbreviations for recording what three items? |
1. Clearances 2. Reports 3. Instructions |
|
|
|
Referring to your clearance abbreviations, what is the meaning of “Z”? |
Tower jurisdiction |
|
|
|
Referring to your miscellaneous abbreviations, what does the abbreviation “RX” stand for? |
Report crossing |
|
|
|
To delete any unused or unwanted symbols or items a/an ________ or ________ should be used. A. /; O B. X; − C. O; X |
B. X; − |
|
|
|
What prefix phrase should you use to relay a clearance to an aircraft through another aircraft? A. “ATC CLEARS.” B. “ATC RELAYS.” C. “ATC ADVISES.” |
A. “ATC CLEARS.” |
|
|
|
One reason a pilot-in-command of an aircraft may deviate from a clearance without an amended clearance is _______. A. an early departure is required B. instrument flight rules are in effect C. an emergency exists |
C. an emergency exists |
|
|
|
Provides aircraft or vehicles a route to follow while on movement area of airport |
Taxi clearance |
|
|
|
Authorizes aircraft to execute a particular procedure for the purpose of landing at an airport.
|
Approach clearance
|
|
|
|
Authorization for an aircraft to land. |
Landing clearance |
|
|
|
Authorizes the pilot to depart the airport. |
Takeoff clearance |
|
|
|
Changes previously issued clearance. |
Amended clearance |
|
|
|
Authorization for pilot to proceed from point of origin to point of destination. |
Departure clearance |
|
|
|
Clearance authorizing pilots to make intermediate stops while en route to a final destination.
|
Through clearance
|
|
|
|
Authorizes pilots to descend to any altitude above the minimum IFR altitude and execute a SIAP. |
Cruise clearance |
|
|
|
Provides for the mass movement of aircraft. |
Altitude reservation |
|

