![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
698 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. The Air Traffic Organization (ATO) is managed by a(n) ________.
A. Associate Administrator B. Vice President C. Chief Operating Officer D. Administrator |
C. Chief Operating Officer
|
|
|
2. According to their location, ATO air traffic control facilities are assigned to one of ________.
A. nine regions B. three service areas C. eleven FAA primary offices D. four FAA Headquarters divisions |
B. three service areas
|
|
|
3. The primary Navigational Aids (NAVAIDs) for the nation’s airways in the National Airspace System (NAS) are ________.
A. marker beacons B. VORs/VORTACs C. Non Directional Beacons (NDBs) D. Instrument Landing Systems (ILSs) |
B. VORs/VORTACs
|
|
|
4. The primary mission of the Traffic Management System (TMS) is to ________.
A. regulate air traffic procedures B. balance system demand with system capacity C. implement the use of state-of-the-art equipment D. ascertain controller stress and workload |
B. balance system demand with system capacity
|
|
|
5. The mission of the _______ is to balance air traffic demand with the system’s capacity to ensure that the maximum and most efficient utilization of the NAS is maintained.
A. Traffic Management System (TMS) B. Air Route Traffic Control Center (ARTCC) C. Automated Flight Service Station (AFSS) D. FAA Headquarters |
A. Traffic Management System (TMS)
|
|
|
6. The primary function of the Traffic Management Unit (TMU) is to ______.
A. monitor and balance traffic flows within their area of responsibility in accordance with traffic management directives B. ensure maximum efficiency in the utilization of the total National Airspace System, thereby producing a safe, orderly, and expeditious flow of traffic C. manage the flow of air traffic throughout the National Airspace System to achieve optimum use of the navigable airspace and minimize the effect of air traffic delays D. manage the flow of tower traffic by ensuring that traffic demand does not exceed operationally minimal levels of traffic |
A. monitor and balance traffic flows within their area of responsibility in accordance with traffic management directives
|
|
|
7. The primary purpose of the Air Traffic Control System is to ________.
A. prevent collision and organize and expedite the flow of traffic B. provide traffic advisories C. monitor holding patterns D. advise pilots of altitude deviations of 300 feet or more |
A. prevent collision and organize and expedite the flow of traffic
|
|
|
8. The air traffic facility that has no direct authority over Instrument Flight Rules (IFR) or Visual Flight Rules (VFR) traffic is the ________.
A. Airport Traffic Control Tower (ATCT) B. Terminal Radar Approach Control (TRACON) C. Automated Flight Service Station (AFSS) D. Air Route Traffic Control Center (ARTCC) |
C. Automated Flight Service Station (AFSS)
|
|
|
9. The facility primarily responsible for conducting pilot briefings is the ________.
A. ATCT B. ARTCC C. ATCSCC D. AFSS |
D. AFSS
|
|
|
10. Which position in the Automated Flight Service Station (AFSS) records and disseminates Hazardous Inflight Weather Advisory Service (HIWAS) summaries?
A. In Flight B. Broadcast C. Flight Data/NOTAM Coordinator D. Preflight |
B. Broadcast
|
|
|
11. Which of the following duties is not the function of the Clearance Delivery position in the tower?
A. Operating communication equipment B. Processing and forwarding flight plan information C. Compiling statistical data D. Issuing clearances and ensuring accuracy of readback |
C. Compiling statistical data
|
|
|
12. The ________ position in the ATC terminal option is normally responsible for issuing control instructions to aircraft and vehicles operating on the airport movement area (other than active runways).
A. Local Control B. Ground Control C. Clearance Delivery D. Flight Data |
B. Ground Control
|
|
|
13. In a Terminal Radar Approach Control (TRACON) facility, who has the responsibility for the safe and efficient operation of a sector?
A. Facility Manager B. Radar Position C. Radar Associate Position D. Radar Team |
D. Radar Team
|
|
|
14. The ATC facility that provides air traffic control services to aircraft on IFR flight plans during the en route phase of flight is ________.
A. ATCT B. AFSS C. TRACON D. ARTCC |
D. ARTCC
|
|
|
15. The only en route sector team member whose duties do not include accepting handoffs is the ________ position.
A. Radar Coordinator B. Radar Associate C. Radar D. Radar Flight Data |
D. Radar Flight Data
|
|
|
16. When considering the duty priority of an air traffic controller, first priority is given to ________.
A. coordinating B. issuing traffic C. separating aircraft D. vectoring |
C. separating aircraft
|
|
|
17. Nonradar separation is used in preference to radar separation when ________.
A. an operational advantage will be gained B. the aircraft is not transponder equipped C. secondary radar is out of service D. controller is not radar qualified |
A. an operational advantage will be gained
|
|
|
18. “Presidential aircraft have priority over Flight Check aircraft” is an example of ________.
A. Operational Priority B. Procedural Preference C. Duty Priority D. Additional Services |
A. Operational Priority
|
|
|
19. All of the following represent uses of a non-movement area EXCEPT:
A. Loading Passengers B. Landing C. Maintenance D Parking |
B. Landing
|
|
|
20. A runway with a magnetic heading of 003 degrees should be designated Runway _______.
A. 0 B. 1 C. 3 D. 36 |
D. 36
|
|
|
21. An airport with three parallel runways with a magnetic heading of 216 degrees would have runway designations of ________.
A. 22R, 22C, 22L B. 21R, 21C, 21L C. 21R, 21L, 22C D. 22R, 22L, 21 |
A. 22R, 22C, 22L
(LP 3, p. 6) |
|
|
22. What runway marking extends the full-length runway pavement area?
A. Runway side stripes B. Dashed side stripes C. Runway centerlines D. Dashed centerlines |
A. Runway side stripes
(LP 3, p. 12) |
|
|
23. A(n) _______ consists of white arrows which point in the direction of landing, replacing the runway centerline, and beginning at the non-landing portion to the threshold bar.
A. stabilized area B. abandoned runway C. relocated threshold D. displaced threshold |
D. displaced threshold
(LP 3, p. 13) |
|
|
24. A _______ is identified by large chevrons pointing in the direction of the threshold.
A. blast pad B. closed runway C. relocated threshold D. dislocated threshold |
A. blast pad
(LP 3, p. 17) |
|
|
25. Runway ________ provide alignment guidance during takeoffs and landings, and consist of a line of uniformly spaced stripes and gaps.
A. aiming points B. centerlines C. thresholds D. touchdown zones |
B. centerlines
(LP 3, p. 7) |
|
|
26. What color are taxiway edge lights?
A. White B. Amber C. Blue D. Red |
C. Blue
(LP 3, p. 33) |
|
|
27. Civil land airports have rotating beacons that _______.
A. flash white and green B. flash two white and one green C. flash white D. flash green |
A. flash white and green
(LP 3, p. 29) |
|
|
28. Touchdown Zone Lighting (TDZL) and Runway Centerline Lights System (RCLS) are two types of _______.
A. Runway End Identifier Lights B. Taxiway lights C. In-runway lights D. Runway edge lights |
C. In-runway lights
(LP 3, p. 32) |
|
|
29. Threshold lights are ________.
A. white/yellow B. green/yellow C. white/red D. green/red |
D. green/red
(LP 3, p. 31) |
|
|
30. The two subsystems for disseminating aeronautical information are _______.
A. AIS and NOTAMs B. NFDC and NOTAMs C. NAS and NFDC D. AIS and AFSS |
A. AIS and NOTAMs
(LP 5, p. 3) |
|
|
31. Who is responsible for originating a NOTAM concerning a navigational aid?
A. Facility responsible for monitoring or controlling the navigational aid B. Center in whose area the outage occurs C. Terminal in whose area the outage occurs D. Automated Flight Service Station |
A. Facility responsible for monitoring or controlling the navigational aid
(LP, p. 11) |
|
|
32. A NOTAM that is widely disseminated and applies to civil components of the NAS is classified as a _______.
A. NOTAM D B. Military NOTAM C. Pointer NOTAM D. FDC NOTAM |
A. NOTAM D
(LP 5, p. 6) |
|
|
33. A NOTAM that consists of information that is regulatory in nature pertaining to flight, such as changes to IFR charts, is classified as a/an:
A. NOTAM D B. Military NOTAM C. Pointer NOTAM D. FDC NOTAM |
D. FDC NOTAM
(LP, p. 8) |
|
|
34. Responsibility for validating NOTAM data and operating the National NOTAM System belongs to _______.
A. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) B. NFDC C. ARTCCs D. AFSSs |
B. NFDC
(LP, p. 13) |
|
|
35. Who is responsible for observing and reporting the conditions of the landing area of an airport?
A. Airport manager/operator B. Tower controller C. Pilot D. Flight service specialist |
A. Airport manager/operator
(LP, p. 15) |
|
|
36. Types of Notices to Airmen (NOTAMs) are:
A. GENOT, RENOT and SERNOT B. PIREP, ALNOT and INREQ C. AIRMET, SIGMET and MIS D. FDC, POINTER and MILITARY |
D. FDC, POINTER and MILITARY
(LP 5, p. 5) |
|
|
37. What information is contained in the FAA Order JO 7110.65?
A. Prescribes air traffic procedures used by Flight Service specialists B. Prescribes air traffic procedures and phraseology used by air traffic controllers C. Provides direction and guidance for operating and managing Air Traffic facilities D. Contains approved words and phrase contractions used by the FAA |
B. Prescribes air traffic procedures and phraseology used by air traffic controllers
(LP 7, p. 8) |
|
|
38. What information is contained in the FAA Order JO 7210.3?
A. Prescribes air traffic procedures and phraseology used by Flight Service specialists B. Prescribes air traffic procedures and phraseology used by air traffic controllers C. Provides direction and guidance for operating and managing Air Traffic facilities D. Contains approved words and phrase contractions used by the FAA |
C. Provides direction and guidance for operating and managing Air Traffic facilities
(LP 7, p. 11) |
|
|
39. Revised, reprinted, or new pages in FAA Orders JO 7110.10, JO 7110.65, and JO 7210.3 are indicated by bold ________.
A. asterisks B. horizontal lines C. vertical lines D. stars |
C. vertical lines
(LP, p. 16) |
|
|
40. What information is contained in the FAA Order JO 7340.2?
A. Prescribes air traffic procedures and phraseology used by Flight Service specialists B. Prescribes air traffic procedures and phraseology used by air traffic controllers C. Provides direction and guidance for operating and managing Air Traffic facilities D. Contains approved words and phrase contractions used by the FAA |
D. Contains approved words and phrase contractions used by the FAA
(LP 7, p.13) |
|
|
41. When used in FAA Orders JO 7110.10, JO 7110.65, and JO 7210.3, the word “may” means that the procedure is ________.
A. recommended B. approved C. optional D. mandatory |
C. optional
(LP, p. 20) |
|
|
42. What information is contained in the FAA Order JO 7350.8?
A. Aeronautical Information Manual B. Lists location identifiers authorized by the FAA C. Provides direction and guidance for operating and managing Air Traffic facilities D. Contains approved words and phrase contractions used by the FAA |
B. Lists location identifiers authorized by the FAA
(LP 7, p. 15) |
|
|
43. In FAA Order 7110.65, the word used to specify that a procedure is mandatory is ________.
A. shall B. may C. should D. will |
A. shall
(LP 7, p. 20) |
|
|
44. Which contraction is used to identify General Notices issued by Washington Headquarters?
A. GANOT B. GENOT C. GENNOT D. GNOT |
B. GENOT
(LP, p. 17) |
|
|
45. In FAA Order 7110.65, the word used to specify that a procedure is recommended is ________.
A. shall B. may C. should D. will |
C.
(LP 7, p. 21) |
|
|
46. What document is used to consolidate instructions from different levels into a single directive to avoid having instructions scattered among several directives?
A. FAA Order JO 7110.65 B. Notices C. Supplements D. Changes |
C. Supplements
(LP, p. 18) |
|
|
47. Which document prescribes air traffic procedures and phraseology used by Flight Service specialists?
A. FAA Order JO 7210.3 B. FAA Order JO 7110.10 C. Aeronautical Information Manual D. Terminal Phraseology Guide |
B. FAA Order JO 7110.10
(LP, p. 6) |
|
|
48. Which document provides the aviation community with basic flight information and ATC procedures?
A. FAA Order JO 7340.2 B. FAA Order JO 7110.65 C. Aeronautical Information Manual D. FAA Order JO 7350.8 |
C. Aeronautical Information Manual
(LP, p. 19) |
|
|
49. When used in FAA Orders JO 7110.10, JO 7110.65, and JO 7210.3, the word “will” means ________.
A. recommended B. not a requirement for application of a procedure C. optional D. mandatory |
B. not a requirement for application of a procedure
(LP, p. 21) |
|
|
50. Many FAA orders are divided into chapters, sections, and ________.
A. groups B. subsections C. stanzas D. paragraphs |
D. paragraphs
(LP, p. 6) |
|
|
51. The lower limit of Class B airspace is ________.
A. 1,200 feet AGL B. 1,200 feet MSL C. 1,500 feet AGL D. the surface |
D. the surface
(LP, p. 6) |
|
|
52. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a Military Operations Area (MOA)?
A. Identified by the letter “M” plus a number B. Established outside Class A airspace C. Activities include low altitude, high-speed flight D. MOAs are depicted on Sectional Aeronautical and En Route Low altitude charts |
A. Identified by the letter “M” plus a number
(LP 9, p. 23) |
|
|
53. The upper vertical limit of Class A airspace is ________.
A. up to but not including FL450 B. FL450 C. up to but not including FL600 D. FL600 |
D. FL600
(LP, p. 5) |
|
|
54. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a Prohibited Area?
A. Established around residential areas for noise abatement B. Begins at the surface of the earth and extends upward to a defined altitude C. Established for security or other reasons associated with the national welfare D. Identified by the letter “P” plus a number |
A. Established around residential areas for noise abatement
(LP 9, p. 17) |
|
|
55. A Warning Area is established beyond ________ NM from the coast of the United States.
A. 1 B. 3 C. 5 D. 12 |
B. 3
(LP, p. 19) |
|
|
56. The upper limit of Class G airspace is ________.
A. 1200 AGL B. 1200 MSL C. the base of the overlying airspace D. the base of Class E airspace |
C. the base of the overlying airspace
(LP, p. 12) |
|
|
57. What airspace contains federal airways?
A. Class A B. Class C C. Class E D. Class G |
C. Class E
(LP, p. 11) |
|
|
58. What airspace is generally established from the surface to 4,000 feet above the airport elevation and has an operational control tower?
A. Class B B. Class C C. Class D D. Class E |
B. Class C
(LP, p. 8) |
|
|
59. Airspace of defined dimensions, confined activities, and limitations imposed on nonusers is identified as ________ airspace.
A. controlled B. Class E C. Special Use D. Class G |
C. Special Use
(LP, p. 15) |
|
|
60. What airspace generally extends upward to 10,000 feet MSL A. Class A
|
B Generally extends upward to 10,000 feet MSL A. Class A
(LP, p. 6) |
|
|
61.VFR aircraft need to receive a clearance from ATC to enter this airspace?
|
B VFR aircraft need to receive a clearance from ATC to B. Class B enter this airspace
(LP, p. 6) |
|
|
62. Which class of airspace requires all aircraft to be IFR?
|
A Requires all aircraft to be IFR
(LP, p. 5) |
|
|
63. No transponder is required in which class airspace?
|
D No transponder is required
(LP, p. 10 |
|
|
64. VFR aircraft are separated only from IFR aircraft in which airspace class?
|
C VFR aircraft are separated only from IFR aircraft
(LP, p. 8) |
|
|
65. A pilot operating above 12,500 feet MSL, up to and including 14,000 feet MSL, must use supplemental oxygen ____________.
A. constantly B. after 1 hour of flight C. after 15 minutes of flight D. after 30 minutes of flight |
D. after 30 minutes of flight (LP 11, p. 48)
|
|
|
66. A pilot flying VFR must stay at least 2,000 feet laterally from the clouds in class ________ and ________ airspace.
A. B;C B. C;D C. B;E D. A;E |
B. C;D
(LP 11, p. 15) |
|
|
67. If takeoff minimums are not prescribed for a particular airport, the minimum visibility required for an air taxi aircraft having two engines or less is ________ statute mile(s).
A. 1/2 B. 1 C. 11/2 D. 2 |
B. 1
(LP, p. 31) |
|
|
68. Aircraft operating on an airway at the published MOCA are only guaranteed _________ within __________ of the VOR serving the airway.
A. terrain clearance; 22SM B. terrain clearance; 22NM C. NAVAID signal; 22SM D. NAVAID signal; 22NM |
D. NAVAID signal; 22NM
(LP 11, p. 32) |
|
|
69. Which of the following statements regarding “VFR on top” (OTP) is true?
A. Pilots must request clearance to maintain OTP B. Pilots maintaining OTP are required to obtain ATC approval prior to changing altitude C. Pilots maintaining OTP may, after advising ATC, deviate from their cleared route D. Traffic advisories will not be provided by ATC |
A. Pilots must request clearance to maintain OTP (LP 11, p. 25)
|
|
|
70. An aircraft on an IFR flight plan is in VFR conditions when a two-way radio failure occurs. The pilot shall ________.
A. proceed VFR and land as soon as practicable B. return IFR to point of departure C. squawk code 7500 D. proceed to nearest airport and execute an IFR approach |
A. proceed VFR and land as soon as practicable
(LP, p. 39) |
|
|
71. Which of the following would not be an assigned flight level?
A. FL360 B. FL320 C. FL240 D. FL160 |
D. FL160
(LP 11, p. 34) |
|
|
72. An inappropriate cruising altitude for an aircraft flying VFR on a magnetic course of 360 degrees is:
A. 2,000 MSL B. 2,500 MSL C. 3,500 MSL D. 4,500 MSL |
D. 4,500 MSL
(LP 11, p. 24) |
|
|
73. Which one of the following items is not required on a VFR flight plan?
A. Pilot’s name and address B. Fuel on board C. Name of each occupant D. Type of aircraft |
C. Name of each occupant
(LP, p. 10) |
|
|
74. A pilot shall file a DVFR flight plan if the flight will ________.
A. be in instrument flight conditions B. enter positive control airspace C. enter coastal ADIZ D. enter Class D airspace |
C. enter coastal ADIZ
(LP, p. 7) |
|
|
75. VFR aircraft in class E airspace at or above ________, must maintain ________ visibility. because there is no speed limit at that altitude.
A. 1200 feet AGL; 3SM B. 1200 feet AGL; 5SM C. 10,000 MSL; 3SM D. 10,000 MSL; 5SM |
D. 10,000 MSL; 5SM
(LP, p. 16) |
|
|
76. Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding SVFR clearances to fixed wing aircraft?
A. The pilot must request SVFR clearance B. A SVFR flight plan must be filed C. Flight visibility must be at least 1SM D. SVFR shall only be approved below 10,000 MSL |
B. A SVFR flight plan must be filed
(LP, p. 22) |
|
|
77. The definition of “wake turbulence” includes a number of phenomenon affecting flight safety. Which of the four choices are not included in the definition?
A. Mach buffet B. Rotorwash C. Propeller wash D. Jet blast |
A. Mach buffet
(LP, p.3) |
|
|
78. Vortices are generated at the moment an aircraft begins to ________.
A. taxi B. generate lift C. slow on approach D. touchdown on the runway |
B. generate lift
(LP, p. 11) |
|
|
79. _________ is jet engine exhaust.
A. Prop-wash B. Wake turbulence C. Jet blast D. Counter control |
C. Jet blast
(LP 13, p. 24) |
|
|
80. A _______ wing allows for a stronger vortex to be generated, because without flaps the wing has a smaller area and wing loading is greater per square foot.
A. delta B. clean configured C. high D. low |
B. clean configured
(LP 13, p. 6) |
|
|
81. With zero wind, vortices near the ground will travel laterally at a speed of ________ knots.
A. 10to20 B. 5to10 C. 2to3 D. 0 |
C. 2to3
(LP, p. 13) |
|
|
82. Counter control is most effective and roll is minimal when the wingspan and the ailerons extend beyond the ________ of the vortex.
A. vertical limits B. outer edges C. sink rate D. induced roll |
B. outer edges
(LP 13, p. 19) |
|
|
83. Downwash is created by ________.
A. Propeller driven aircraft B. Jet aircraft C. Helicopters D. Turboprop airplane |
C. Helicopters
(LP 13, p. 21) |
|
|
84. Circles parallel to the equator are called ________.
A. great circles B. parallels of longitude C. meridians D. parallels of latitude |
D. parallels of latitude
(LP, p. 5) |
|
|
85. The Prime Meridian is the ________.
A. great circle passing through the north and south poles B. line located at 0°latitude C. great circle running east and west around the earth D. line located at zero degrees (0°) longitude |
D. line located at zero degrees (0°) longitude
(LP, p. 6) |
|
|
86. Positions on the earth’s surface are described in terms of ________.
A. latitude and longitude B. latitude and parallels C. degrees and arcs D. longitude and meridians |
A. latitude and longitude
(LP, p. 7) |
|
|
87. A nautical mile equals ________ statute miles (SM).
A. .87 B. 1.15 C. 1.5 D. 1.87 |
B. 1.15
(LP, p. 14) |
|
|
88. Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is also referred to as ________ time.
A. Alfa B. Charlie C. X-ray D. Zulu |
D. Zulu
(LP, p. 17) |
|
|
89. Time zones are established for every ________.
A. 15’ of longitude B. 15°of latitude C. 15°of longitude |
C. 15°of longitude
(LP, p. 19) |
|
|
90. How do you convert local Daylight Savings Time to UTC?
A. Subtract the conversion factor. B. Add the conversion factor, then subtract 1 hour. C. Subtract the conversion factor, then add 1 hour. D. Add the conversion factor, then add 1 hour. |
B. Add the conversion factor, then subtract 1 hour.
(LP, p. 22) |
|
|
91. The angular difference between true and magnetic north at a given location is called ________.
A. correction B. variation C. compensation D. deviation |
B. variation
(LP, p. 41) |
|
|
92. King Air 2425K departed “A” at 2228 UTC. With a consistent 180-knot ground speed, N2425K arrived at destination “E” at 0258 UTC. How long did it take the aircraft to cover the distance from “B” to “C?”
A B C D E 160NM ? 105NM 185NM A. 1.5 HR B. 2HR C. 1.75 HR D. 2.25 HR |
B. 2HR
(LP 15, p. 25,26) |
|
|
93. Parallels and meridians are divided into ________, minutes and seconds.
A. circles B. days C. degrees D. hours |
C. degrees
(LP 15, p. 8) |
|
|
94. 100 nautical miles equals ____________ statute miles.
A. 130 B. 95 C. 87 D. 115 |
D. 115
(LP 15, p. 14) |
|
|
95. The basic form of navigation which uses visual reference to landmarks is ________.
A. pilotage B. dead reckoning C. rate, time, and distance D. radio navigation |
A. pilotage
(LP, p. 47) |
|
|
96. 2 PM on a 24-hour clock equals _________.
A. 1200 B. 0200 C. 2200 D. 1400 |
D. 1400
(LP 15, p. 19) |
|
|
97. An aircraft departs Denver at 9 P.M. (MST) and travels 3 hours, landing in Boston (EST). What was the aircrafts arrival time UTC? (conversion factor EST to UTC is +5)
A. 0700 B. 1700 C. 0200 D. 0600 |
A. 0700
(LP 15, p. 22) |
|
|
98. A line connecting points of zero variation is called a(n) ________.
A. isogonic line B. agonic line C. magnetic line D. meridian |
B. agonic line
(LP 15, p. 41) |
|
|
99. How long would it take an aircraft with a ground speed of 130 knots to fly 650 NM?
A. 4 hours, 30 minutes B. 5 hours C. 5 hours, 30 minutes D. 6 hours |
B. 5 hours
(LP, pp. 25 thru 27) |
|
|
100. The purpose of parallels of latitude is for measuring degrees of latitude ________.
A. east and west of the equator B. north and south of the equator C. north and south of the Prime Meridian D. east and west of the Prime Meridian |
B. north and south of the equator
(LP, p. 5) |
|
|
101. A pilot has determined the true heading from Oklahoma City to Kansas City is 020°. The magnetic variation is 7°E. What magnetic heading should be flown?
A. 013° B. 020° C. 027° D. 031° |
A. 013°
(LP 15, p. 42) |
|
|
102. The only line of latitude that is a great circle is the______________.
A. Prime Meridian B. Equator C. International Dateline D. Rhumb Line |
B. Equator
(LP, p. 4) |
|
|
103. An aircraft encounters a 20 KT crosswind and makes no heading correction. After 1 hour of flight, how far off course would the aircraft be?
A. 10NM B. 10SM C. 20NM D. 20SM |
C. 20NM
(LP 15, p. 35) |
|
|
104. At high altitudes, _______.
A. an aircraft’s IAS is significantly higher than it’s TAS B. an aircraft’s TAS is significantly higher than it’s IAS C. an aircraft’s groundspeed is always equal to it’s TAS D. an aircraft’s IAS is always equal to it’s TAS |
B. an aircraft’s TAS is significantly higher than it’s IAS
(LP 15, p. 37) |
|
|
105. In the airport data “18 L 100 122.8” on a Sectional Aeronautical Chart, the number “18” indicates the ________.
A. airport elevation B. length of the longest runway C. runway number of the primary runway D. height of the tallest obstruction within 5 nautical miles |
A. airport elevation
(LP 17, p. 12) |
|
|
106. VFR flyway planning charts are found on _________.
A. IFR/VFR planning charts B. VFR Terminal Area Charts C. Sectional Charts D. WAC Charts |
B. VFR Terminal Area Charts
(LP 17, p. 34) |
|
|
107. Frequencies placed just above a communication box on a Sectional Aeronautical Chart are used to contact which type of facility?
A. En Route Air Traffic Control Center B. Approach Control C. Tower D. Automated Flight Service Station |
D. Automated Flight Service Station
(LP, p. 15) |
|
|
108. The boundary of Class C airspace is depicted on a Sectional Aeronautical Chart by a solid ________ line.
A. blue B. magenta C. brown D. black |
B. magenta
(LP 17, p. 16) |
|
|
109. Which document would be most useful to a controller when recommending a suitable airport to a pilot in the event of an emergency?
A. JO 7110.65 B. Aeronautical Information Manual C. Airport/Facility Directory D. Letter of Agreement |
C. Airport/Facility Directory
(LP 17, p. 45) |
|
|
110. Information NOT found on sectional aeronautical charts are ________.
A. MEAs and MOCAs B. VOR, VORTAC’s, NDB’s, as well as their position, identification, and frequencies C. MOAs, Restricted, Prohibited, Alert and Warning Areas D. airports |
A. MEAs and MOCAs (LP 17, p. 3-20)
|
|
|
111. The Airport/Facility Directory is published every ________ days.
A. 28 B. 56 C. 112 D. 180 |
B. 56
(LP, p. 41) |
|
|
112. What chart(s) or publication would you use to find out if an airport has a control tower, and the tower frequency?
A. Sectional Aeronautical Chart B. Terminal Area Chart C. Airport/Facility Directory D. All of the above |
D. All of the above
(LP, pp. 9, 32, 42) |
|
|
113. The graphic depiction of a SID or STAR is found in the _______ section of the chart.
A. margin B. planview C. textual description D. legend |
B. planview
(LP 19, p. 21) |
|
|
114. SIDs are listed alphabetically in the U.S. Terminal Procedures Publication -first under ________ then under ________.
A. SIDs, STARs B. airport name, city C. Index, Legend D. city, airport name |
D. city, airport name
(LP, p. 14) |
|
|
115. Which statement is true regarding a SID?
A. A pilot may accept a SID when possessing only the textual description B. SIDs are normally assigned by En Route controllers.. C. If a SID exists for the departure airport, the pilot must be prepared to accept it as part of the clearance. D. Pilots are encouraged to include the phrase “No SID” in their flight plans if they do not want a SID. |
D. Pilots are encouraged to include the phrase “No SID” in their flight plans if they do not want a SID.
(LP, p. 24) |
|
|
116. Standard Instrument Departures (SIDs) are air traffic control procedures used at busier airports to do all of the following except ________.
A. simplify clearance delivery B. expedite traffic flow C. facilitate noise abatement procedures D. reduce pilot/controller workload |
C. facilitate noise abatement procedures
(LP 19, p. 3) |
|
|
117. A STAR is designed to simplify clearance delivery and facilitate transition between ________.
A. procedure turns and final approaches B. takeoffs and en route operations C. the airport departure and the destination airport D. en route and instrument approach operations |
D. en route and instrument approach operations
(LP 19, p. 3) |
|
|
118. To accept a clearance for the DANDD 5 arrival to Denver, the pilot must be in possession of the ________ for that STAR.
A. altitude restrictions B. approved chart C. pertinent frequencies D. Planview |
B. approved chart
(LP, p. 29) |
|
|
119. Which statement is true regarding a STAR?
A. A STAR is designed to provide a transition for departures from the airport into the en route environment. B. One STAR may serve several airports. C. Several STARs may be included on a single chart. D. STARs are located with the Instrument Approach Procedures in the U.S. Terminal Procedures Publication, while SIDs have their own section in the front of the book. |
B. One STAR may serve several airports.
LP, p. 29) |
|
|
120. To locate a SID or STAR, select the correct U.S. Terminal Procedures Volume, then before using it, ________.
A. look in the index under airport name. B. look in the index under city name. C. find the appropriate section. D. check for currency. |
D. check for currency.
(LP, p. 5) |
|

121. Match Symbol Open Triangle
|
E Non-Compulsory Reporting Point
|
|

122. Match Symbol Dashed Line with Arrow
|
B Lost Communication Track
|
|

123. Match Symbol Triangle With Blocked Corners
|
D. Vortac
|
|
|
124. Match Symbol 5500(underlined)
|
B Minimum Altitude
|
|

125. Match Symbol Solid Line with Arrow
|
C. Transition Route
|
|

126. Match Symbol Thick Line with Radial inside
|
B Departure-Arrival Route
|
|

127. 2 Jagged Lines
|
D. Distance Not to Scale
|
|

128. Open Retangle
|
E. Runway
|
|

129. Elongated Oval
|
C. Holding Pattern
|
|

130. Number inside circle with direction arrow
|
A. DME Mileage
|
|
|
131. Which of the following is assigned by ATC to a single aircraft and used for radar identification and flight tracking?
A. non-discrete code B. discrete code C. mode C D. aircraft identification |
B. discrete code (LP 21, p 33)
|
|
|
132. Which instrument is NOT connected to the pitot-static system?
A. Airspeed indicator B. Vertical speed indicator C. Attitude indicator D. Altimeter |
C. Attitude indicator (LP, p. 2)
|
|
|
133. What may be obtained from the attitude indicator?
A. Rate of turn B. Degrees of bank C. Height above sea level D. Rate of climb |
B. Degrees of bank
(LP, p. 20) |
|
|
134. The major components of the pitot-static system are the ________.
A. absolute and indicated altitude indicators B. vacuum pump and regulator C. attitude and heading indicators D. impact and static pressure chambers, and lines |
D. impact and static pressure chambers, and lines (LP 21, p. 2)
|
|
|
135. As a controller, when an aircraft under your control jurisdiction informs you that it is responding to a TCAS RA, you ________.
A. are responsible for maintaining separation from the intruder aircraft. B. shall not issue instructions contrary to the RA. C. may discontinue traffic advisories and safety alerts. D. shall immediately issue an amended clearance. |
B. shall not issue instructions contrary to the RA. (LP 21, p. 41)
|
|
|
136. Because of precession, the heading indicator is periodically set by the pilot to agree with the ________.
A. attitude indicator B. altimeter C. magnetic compass D. Directional Gyro (DG) |
C. magnetic compass (LP, p. 19)
|
|
|
137. In order to fly a desired course toward a VOR station, the pilot must ensure that the aircraft’s heading agrees with the course set on the VOR course selector, the instrument displays a “TO” indication, and the ________.
A. VOR needle is centered B. aircraft is not climbing or descending C. magnetic compass is not precessed D. airspeed is constant |
A. VOR needle is centered (LP, p. 25)
|
|
|
138. The altimeter depends on which of the following for its operation?
A. Pitot tube. B. Gyro. C. Static port. D. Rudder. |
C. Static port.
(LP 21, p. 4) |
|
|
139. A transponder code consists of four numbers from zero to seven with _________ possible codes.
A 4,006 B. 4,066 C. 4,086 D. 4,096 |
D. 4,096
(LP, p. 33) |
|
|
140. The FMS is __________.
A. a computer data base used for navigation B. a radio NAVAID receiver C. a gyroscopic instrument D. Inoperable with a clogged pitot |
A. a computer data base used for navigation
(LP, p. 34) |
|
|
141. In most small aircraft, if the vacuum pump fails, which instruments become inoperative?
A. Airspeed indicator and turn and bank B. Altimeter and directional gyro C. Heading indicator and attitude indicator D. Vertical speed indicator and attitude indicator |
C. Heading indicator and attitude indicator
(LP 21, p. 13) |
|
|
142. Hypoxia is a condition of the body that exists when there is ________.
A. a lack of oxygen in the body tissue B. a lack of oxygen in the air C. excessively fast breathing D. a lack of carbon dioxide in the body |
A. a lack of oxygen in the body tissue
(LP, p. 44) |
|
|
143. An interagency agreement that provides for the effective utilization of all available facilities during search and rescue missions is called a(an) ________.
A. Search and Rescue Mission B. Rescue Coordination Center C. National Search and Rescue Plan D. Alert Notice |
C. National Search and Rescue Plan
(LP, p. 2) |
|
|
144. When a VFR aircraft becomes overdue, who initiates the INREQ message?
A. ARTCC B. AFSS C. RCC D. ATCT |
B. AFSS
(LP, p. 10) |
|
|
145. The ALNOT search area is generally described as ________.
A. 100 miles either side of the route of flight from departure point to destination B. 50 miles either side of the route of flight from departure point to destination C. 100 miles either side of the route of flight from the last reported position to destination D. 50 miles either side of the route of flight from the last reported position to destination |
D. 50 miles either side of the route of flight from the last reported position to destination
(LP, p. 10) |
|
|
146. The transfer of search responsibility to RCC is done ________.
A. when the ALNOT search has been completed with negative results B. if the aircraft has not been located within 30 minutes after issuance of the ALNOT C. 1 hour past ETA D. at fuel exhaustion time plus 1 hour |
A. when the ALNOT search has been completed with negative results
(LP, p. 15) |
|
|
147. An aircraft on a VFR flight plan is considered overdue when it fails to arrive ________ minutes after its ETA and communications or location cannot be established.
A. 15 B. 30 C. 45 D. 60 |
B. 30
(LP, p. 9) |
|
|
148. A pilot requesting Lake Reporting Service will report every 10 minutes. Search and rescue must be initiated if no report is received in ________ minutes.
A. 10 B. 15 C. 30 D. 60 |
B. 15
(LP, p. 16) |
|
|
149. Consider an IFR aircraft overdue and take appropriate action when ________.
A. 30 minutes has passed since an ETA over a compulsory reporting point B. 30 minutes has passed since clearance void time C. you have reason to believe the aircraft is overdue D. any of the above |
D. any of the above
(LP, p. 11) |
|
|
150. Which of the following is a characteristic of a temperature inversion?
A. They cannot form along frontal zones B. Decreased temperatures with increased altitude C. Increased temperatures with increased altitude D. They never occur at or near the surface of the earth |
C. Increased temperatures with increased altitude
(LP 25, p. 27) |
|
|
151. When de-icing or anti-icing equipment fails to reduce or control the icing hazard, the icing is categorized as ________.
A. extreme B. severe C. moderate D. heavy |
B. severe
(LP 25, p. 39) |
|
|
152. A sudden wind shift, even at low speeds, can be hazardous on takeoff and landing because it can ________.
A. cause engine failure B. cause wing failure C. cause the plane to bounce on the runway D. quickly become a crosswind or tailwind |
D. quickly become a crosswind or tailwind
(LP, p. 9) |
|
|
153. Which airplane would be most at risk from a 25-knot crosswind on landing?
A. General aviation, single propeller B. Corporate business jet C. Commercial jetliner D. Military cargo transport |
A. General aviation, single propeller
(LP, p. 10) |
|
|
154. Water vapor, lift, and unstable air are necessary for the formation of _________.
A. a thunderstorm cell B. wind shear C. icing D. hail |
A. a thunderstorm cell
(LP 25, p. 46) |
|
|
155. Low-level wind shear is a change in windspeed of _______ knots or more within _______ feet AGL.
A. 25; 1,000 B. 10; 2,000 C. 25; 2,000 D. 10; 1,000 |
B. 10; 2,000
(LP 25, p. 54) |
|
|
156. Airplane performance gradually degrades as the wind ________.
A. turns perpendicular to the runway B. decreases suddenly C. passes over a mountain range D. is trapped in a valley |
A. turns perpendicular to the runway
(LP, p. 5) |
|
|
157. Severe damage can occur if ________ is ingested into an engine.
A. snow B. volcanic ash C. smoke D. mist |
B. volcanic ash
(LP, p. 18) |
|
|
158. An area as large as 10 miles or more of strong damaging winds reaching speeds as high as 120 knots, on or near the ground, is a ________.
A. wind shear B. microburst C. downburst D. funnel cloud |
C. downburst
(LP 25, p. 48) |
|
|
159. Which stage of a thunderstorm is characterized by updrafts exceeding 3,000 feet per minute?
A. Towering cumulus B. Mature C. Virga D. Dissipating |
A. Towering cumulus
(LP 25, p. 47) |
|
|
160. What type of turbulence is caused by any obstruction to the wind, such as buildings or mountains?
A. Physical B. Mechanical C. Convective D. Clear air |
B. Mechanical
(LP 25, p. 23) |
|
|
161. What type of turbulence causes occupants to be forced violently against seat belts or shoulder straps, unsecured objects to be tossed about, and makes food service and walking impossible?
A. Light B. Moderate C. Severe D. Trace |
C. Severe
(LP, p. 29) |
|
|
162. Which effect occurs to airplanes on departure during a high density altitude condition?
A. A slower rate of climb. B. A shorter takeoff roll is required. C. A higher rate of climb. D. An increase in thrust. |
A. A slower rate of climb.
(LP, p. 33) |
|
|
163. Which of the following is NOT true regarding fog?
A. Fog reduces horizontal visibility to less than 5/8 SM B. Fog forms slowly, allowing pilots to avoid this hazard C. Fog forms when the temperature and dewpoint spread is at or near zero D. Fog is a cloud with it’s base at the earth’s surface. |
B. Fog forms slowly, allowing pilots to avoid this hazard
(LP 25, p. 15) |
|
|
164. Light turboprop aircraft are more susceptible to icing than commercial jet aircraft because they typically fly ________.
A. during the daytime B. at higher speeds C. at higher altitudes D. at lower altitudes |
D. at lower altitudes
(LP, p. 41) |
|
|
165. The valid period of a routine TAF beginning at 0000Z on the 10th day of the month would be coded as ______.
A. 1000/1100 B. 1000/1104 C. 1000/1112 D. 1000/1024 |
D. 1000/1024
(LP 27, p. 7) |
|
|
166. A forecast of non-convective LLWS would be found in what NWS product?
A. SIGMET B. TAF C. Convective SIGMET D. SPECI |
B. TAF
(LP 27, p. 13) |
|
|
167. Which of the following NWS products is scheduled?
A. AIRMET ZULU B. SIGMET C. MIS D. CWA |
A. AIRMET ZULU
(LP 27, p. 35) |
|
|
168. A forecast of visibility less than one mile would be found in what NWS product?
A. SIGMET B. AIRMET SIERRA C. CWA D. METAR |
B. AIRMET SIERRA
(LP 27, p. 35) |
|
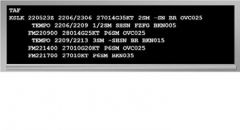
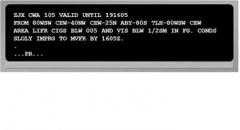
169. Based on the following TAF, what is the earliest time thunderstorms can be expected? KOKC 051130Z 0512/0612 14008KT 5SM BR BKN030
TEMPO 0513/0516 1 1/2SM BR FM051600 16010KT P6SM SKC FM051900 20013G25KT 4SM SHRA OVC020 FM060500 20010G20KT 2SM SHRA BKN010 PROB30 0507 2SM TSRA OVC008CB FM060800 21015KT P6SM SCT040 |
D. 6th day at 0500Z
(LP 27, p. 20) |
|
|
170. What will temporarily restrict the visibility on the 22nd at 0730Z?
A. Light snow B. Light snow, freezing mist C. Light snow showers, freezing mist D. (Moderate) snow showers, freezing fog |
D. (Moderate) snow showers, freezing fog
(LP, pp. 10, 18-19) |
|
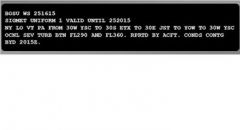
171. Which altitude is forecast to have occasional severe turbulence?
A. 8,500 feet B. Flight level 180 C. Flight level 320 D. Flight level 410 |
C. Flight level 320
(LP, p. 26) |
|
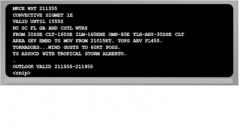
172. What is the forecast movement of the area of severe embedded thunderstorms?
A. From 150 degrees at 21 knots B. From 150 degrees at 55 mph C. From 210 degrees at 15 knots D. From 210 degrees at 60 mph 9. Which hazards are forecast for Kentucky (KY) at 1700Z? |
C. From 210 degrees at 15 knots
(LP, pp. 30, 31) |
|
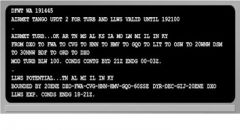
173. Which hazards are forecast for Kentucky (KY) at 1700Z?
A. IFR; strong surface winds greater than 30 knots B. IFR; moderate turbulence below 1,000 feet C. Moderate turbulence below 1,000 feet; low-level wind shear D. Moderate turbulence below 10,000 feet; low-level wind shear |
D. Moderate turbulence below 10,000 feet; low-level wind shear
(LP, pp. 35, 36) |
|
174. Which hazard is forecast in the Jacksonville ARTCC (ZJX) airspace?
A. Low-level wind shear below 500 feet B. Moderate turbulence below 500 feet C. IFR D. Low IFR (LOW IFR) |
D. Low IFR (LOW IFR)
(LP, p. 42) |
|

175. Which statement is true concerning the product below?
A. The product is valid until the 3rd day of the month at 0200Z B. A warm front will reach the Cleveland control area by late Sunday afternoon C. Icing is forecast between the surface and 12,000 feet D. Pilots and dispatchers are the primary users of this product |
A. The product is valid until the 3rd day of the month at 0200Z (LP, p. 47)
|
|
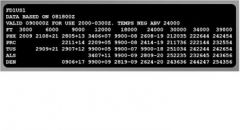
176. What is the forecast wind and temperature at Alamosa, CO (ALS) at FL340?
A. Wind two three two at two six, temperature four five B. Wind two three two at six , temperature minus four five C. Wind two three zero at two six gusts four five D. Wind two three zero at two six, temperature minus four five |
D. Wind two three zero at two six, temperature minus four five (LP, pp. 51-53)
|
|
|
177. AFSSs are identified by stating name of the facility followed by what?
A. Flight Service B. Flight Watch C. Radio D. Broadcast |
C. Radio (LP 29, p. 24)
|
|
|
178. What is the call sign for a civil aircraft with the President aboard?
A. “AIR FORCE ONE” B. “EXECUTIVE ONE PRESIDENT” C. “PRESIDENT ONE” D. “EXECUTIVE ONE” |
D. “EXECUTIVE ONE” (LP, p. 35)
|
|
|
179. Jet route 35 would be spoken as ________.
A. “J THIRTY-FIFE” B. “JET ROUTE THREE FIFE” C. “Q - THIRTY-FIFE” D. “J THREE FIFE” |
A. “J THIRTY-FIFE”
(LP, p. 41) |
|
|
180. Which of the following is the correct way to state an assigned altitude of 16,000 feet?
A. One six zero hundred B. One six zero zero zero C. One six thousand D. One six zero thousand |
C. One six thousand (7110.65; LP 29, p. 10)
|
|
|
181. An action to transfer radar identification of an aircraft from one controller to another when the aircraft will enter the receiving controller’s airspace and radio communication is transferred is a ________.
A. point out B. handover C. handoff D. transfer |
C. handoff
(LP, p. 50) |
|
|
182. What is the action whereby the responsibility for separation of an aircraft is transferred from one controller to another?
A. Transfer of control B. Transfer of communications C. Point out D. Handoff |
A. Transfer of control
(LP, p. 54) |
|
|
183. How is a time of 6:42 a.m. stated as UTC time?
A. ”Zero six four two zulu” B. ”Zero six four two local” C. ”Zero six four two alpha mike” D. ”Oh six four two zulu” |
A. ”Zero six four two zulu”
(LP 29, p. 12) |
|
|
184. According to the ICAO alphabet pronunciation table, in radiotelephony “C-H-A-P” should be pronounced ________.
A. CHARLIE HONEY ALFA PETER B. CHARLIE HOTEL ALFA PAPA C. CHARLIE HECTOR ALFA PAPA D. CHARLIE HOTEL ALFA PETER |
B. CHARLIE HOTEL ALFA PAPA
(LP 29, p. 6) |
|
|
185. The terminology for stating an altimeter of 28.72 is ________.
A. “Altimeter two eight point seven two” B. “Altimeter two eight decimal seven two” C. “Altimeter two eight seven two” D. “Altimeter twenty-eight seventy-two” |
C. “Altimeter two eight seven two”
(LP, p. 14) |
|
|
186. The surface wind is from 170 degrees at 20 knots. This would be stated as ________.
A. “Wind one seventy at twenty knots” B. “Wind south at twenty knots” C. “Wind one seven zero at zero two zero” D. “Wind one seven zero at two zero” |
D. “Wind one seven zero at two zero”
(LP, p. 16) |
|
|
187. When can a pilot interrupt their communications guard?
A. When requested B. When requested and an agreeable time off frequency is established C. When requested and in VFR conditions D. At any time |
B. When requested and an agreeable time off frequency is established
(LP 29, p. 4) |
|
|
188. How often are interphones and assigned frequencies to be monitored?
A. According to the level of traffic in the area B. At half-hour intervals C. Continuously D. Hourly |
C. Continuously
(LP 29, p. 3) |
|
|
189. During which step in the relief process does the relieving specialist check, verify, and update the position information obtained?
A. Preview the position B. Verbal briefing C. Assumption of position responsibility D. Review the position |
D. Review the position
(LP, p. 64) |
|
|
190. When stating flight levels, an aircraft at 28,000 feet would be said to be at an altitude of __________.
|
ANSWER: “Flight level two eight zero”
(LP, p. 11) |
|
|
191. Runway 31C would be spoken as __________.
|
“Runway tree one center”
(LP, p. 17) |
|
|
192. The phraseology for contacting Columbia Automated Flight Service Station would be __________.
|
“COLUMBIA RADIO”
(LP, p. 24) |
|
|
193. The first priority during coordination or during the transfer of information is __________.
|
emergencies (LP, p. 47)
|
|
|
194. List, in order, the four steps in the position relief process.
1.) Preview position 2.) Verbal briefing 3.) Assumption of position responsibility 4.) Position review |
List, in order, the four steps in the position relief process.
1.) Preview position 2.) Verbal briefing 3.) Assumption of position responsibility 4.) Position review (LP, p. 61) |
|
|
195. Which item is always included in a clearance?
A. Aircraft identification B. Departure procedure C. Holding instructions D. Altitude |
A. Aircraft identification (LP, p. 6)
|
|
|
196. The purpose of an ATC clearance is to ________.
A. relieves controller stress. B. provides classified instructions to pilots. C. prevent collision between known aircraft. D. provide for emergency situations. |
C. prevent collision between known aircraft. (LP, p. 3)
|
|
|
197. The pilot-in-command of an aircraft shall comply with all provisions of an ATC clearance unless an amended clearance has been obtained, an emergency exists or _______.
A. conducting military operations B. participating in a speed run C. operating aircraft in IFR conditions D. responding to a TCAS resolution advisory |
D. responding to a TCAS resolution advisory (LP, p. 5)
|
|
|
198. Select the correct sequence of the following clearance items:
1. Route of flight 2. Holding instructions 3. Aircraft identification 4. Clearance limit 5. Mach number, if applicable 6. Altitude data in order flown 7. Frequency and beacon code information 8. Departure procedure or DP/FMSP 9. Any special instructions A. 3,4,8,1,6,5,2,9,7 B. 3,8,1,2,4,5,9,6,7 C. 3,9,8,7,4,1,6,2,5 D. 3,1,6,4,8,5,2,7,9 |
A. 3,4,8,1,6,5,2,9,7
(LP, p. 6) |
|
|
199. Use prefixes when relaying ________, ________, or ________ through non-ATC facilities.
A. clearances, instructions, reports B. information, instructions, requests C. clearances, information, requests D. instructions, reports, requests |
C. clearances, information, requests (LP 31, p.8)
|
|
|
200. The type of clearance that provides for intermediate stops while en route is a/an ________ Clearance.
A. Approach B. Through C. Composite D. Cruise |
B. Through (LP, p. 18)
|
|
|
201. An authorization for a pilot to conduct flight at any altitude from the minimum IFR altitude up to and including the altitude specified in the IFR clearance is a/an ________ Clearance.
A. Cruise B. Landing C. Approach D. Composite |
A. Cruise
(LP, p. 21) |
|
|
202. Considering the prescribed order of clearance items, which of the following clearances is correct?
A. “United seventy seven, descend and maintain one zero thousand, fly heading two four zero for spacing.” B. “Lifeguard tree echo foxtrot, cleared to the Tulsa VORTAC, hold west, descend and maintain one zero thousand.” C. “Continental twenty tree, cleared to the Little Rock airport, climb and maintain flight level two three zero via J twenty, squawk four four two seven.” D. “November six seven x-ray, cleared direct Bartlesville V-O-R, climb and maintain one two thousand.” |
D. “November six seven x-ray, cleared direct Bartlesville V-O-R, climb and maintain one two thousand.”
(LP, p. 6) |
|
|
203. Holding an aircraft is NOT used for ________.
A. en route traffic B. position relief C. flow control D. spacing |
B. position relief
(LP 4, p. 41) |
|
|
204. The minimum vertical separation required for aircraft above FL600 is _______ feet.
A. 10,000 B. 5,000 C. 2,000 D. 1,000 |
B. 5,000
(LP 4, p. 7) |
|
|
205. The minimum vertical separation for IFR flight at and below FL410 is _______ feet.
A. 5,000 B. 2,000 C. 1,000 D. 4,000 |
C. 1,000
(LP 4, p. 7) |
|
|
206. Minimum vertical separation below an aircraft which is dumping fuel is ______ feet.
A. 4,000 B. 2,000 C. 1,000 D. 500 |
B. 2,000
(LP 4, p. 11) |
|
|
207. To clear aircraft to hold over different fixes at the same altitude, you must ensure that all
A. aircraft are cleared to make right turns. B. holding pattern airspace areas do not overlap. C. leg lengths are specified in minutes. D. aircraft are using the same NAVAID to hold from. |
B. holding pattern airspace areas do not overlap.
(LP 4, p. 45) |
|
|
208. What type of separation is defined as the spacing of aircraft at the same altitude by a minimum distance expressed in units of time or miles?
A. Lateral B. Longitudinal C. Vertical D. Visual |
B. Longitudinal
( LP 4, p. 15) |
|
|
209. Standard radar separation provided by an en route facility between two aircraft at FL270 is ______ miles.
A. 3 B. 5 C. 10 D. 20 |
B. 5 (LP 4, pp. 29, 30)
|
|
|
210. Terminal radar separation minima require that when two aircraft are less than 40 miles from the antenna, ________ separation is required; when two aircraft are 40 miles or more from the antenna, ________ separation is required.
A. 3 miles; 5 miles B. 3 miles; 6 miles C. 5 miles; 3 miles D. 5 miles; 10 miles |
A. 3 miles; 5 miles
(LP 4, p. 28) |
|
|
211. Controllers may use visual separation ________.
A. up to, but not including, FL180 B. at FL180 and below C. up to and including 18,000 feet MSL D. up to but not including 18,000 feet AGL |
A. up to, but not including, FL180
(LP 4, p. 35) |
|
|
212. Runway separation is applied by ________ controllers.
A. Air Route Traffic Control Center (ARTCC) B. Air Traffic Control Tower (ATCT) C. Terminal Radar Approach Control (TRACON) D. Automated Flight Service Station (AFSS) |
B. Air Traffic Control Tower (ATCT)
(LP 4, p. 37) |
|
|
213. Which radar system uses both a ground-based interrogator and an aircraft-based transponder?
A. Primary radar B. Airport radar C. Secondary radar D. Global position radar |
C. Secondary radar
(LP, p. 22) |
|
|
214. What is a radio detection device which provides information on the range, azimuth, and/or elevation of objects?
A. Transponder B. Radar C. Nondirectional beacon D. VORTAC |
B. Radar
(LP, p. 3) |
|
|
215. The primary radar display depicts the ________ and ________ of objects that reflect radio energy.
A. position; altitude B. position; movement C. altitude; speed D. movement; speed |
B. position; movement
(LP 6, p. 8) |
|
|
216. What are two types of radar jamming?
A. Position and passive B. Action and active C. Precise and passive D. Passive and active |
D. Passive and active
(LP, p. 19) |
|
|
217. Which is not a component of a primary radar system?
A. Transmitter B. Interrogator C. Antenna D. Receiver |
B. Interrogator
(LP 6, p. 6) |
|
|
218. Which radar feature reduces or eliminates echoes from precipitation?
A. Circular Polarization B. Linear Polarization C. Passive radar D. Inversion |
A. Circular Polarization
(LP, p. 13) |
|
|
219. What causes Anomalous Propagation clutter on primary radar systems?
A. Particles in the air slowing the radar signal B. Moisture in the air bending the radar signal C. Warm air over cool air deflecting the radar signal D. Cool air over warm air reflecting the radar signal |
B. Moisture in the air bending the radar signal
(LP, p. 16) |
|
|
220. What causes temperature inversion clutter on primary radar systems?
A. Particles in the air slowing the radar signal B. Moisture in the air bending the radar signal C. Warm air over cool air deflecting the radar signal D. Cool air over warm air reflecting the radar signal |
C. Warm air over cool air deflecting the radar signal
(LP, p. 17) |
|
|
221. Secondary radar interference caused by a transponder replying excessively is called _______.
A. Ring around B. Anomalous Propagation C. Range interference D. Inversion |
A. Ring around
(LP, p. 29) |
|
|
222.. Which of the following is an advantage of a secondary radar system?
A. It displays weather echoes. B. It only displays aircraft with transponders. C. Radar responses are not degraded by weather or ground clutter. D. Signal strength is affected by aircraft orientation. |
C. Radar responses are not degraded by weather or ground clutter.
(LP, p. 30) |
|
|
223. Broadcasts interrogator transmission
|
E. Antenna
(LP, p. 24) |
|
|
224. Processes transponder replies and forwards data to the radar
|
C. Decoder
(LP, p. 27) |
|
|
225. Ground-based transmitter
|
D. Interrogator
(LP, p. 24) |
|
|
226. Airborne receiver/transmitter
|
A. Transponder
(LP, p. 26) |
|
|
227. Depicts an electronic presentation of radar-derived information.
|
B. Radar display
(LP, p. 27) |
|
|
228. The purpose of an LOA is to supplement established operational procedures for ________ use.
A. regional B. intrafacility C. interfacility D. military |
C. interfacility
(LP, p. 2) |
|
|
229. Which of the following is NOT an example of typical SOP content?
A. External Coordination B. Position relief briefing C. Equipment usage D. Local stripmarking procedures |
A. External Coordination
(LP 8, p. 10) |
|
|
identify the content/procedures that would require the implementation of an LOA/SOP. Write A for LOA or B for SOP in the blanks provided.
230. Define coordination procedures between two air traffic facilities |
A
(LP, p. 2) |
|
|
identify the content/procedures that would require the implementation of an LOA/SOP. Write A for LOA or B for SOP in the blanks provided.
231. Define coordination procedures between internal operational positions |
B
(LP, p. 11) |
|
|
identify the content/procedures that would require the implementation of an LOA/SOP. Write A for LOA or B for SOP in the blanks provided.
232. Define coordination procedures between AFSS Inflight and ARTCC Radar Associate positions |
A
(LP, p. 3) |
|
|
identify the content/procedures that would require the implementation of an LOA/SOP. Write A for LOA or B for SOP in the blanks provided.
233. Define responsibilities between an air traffic control facility and the Airport Manager |
A
(LP, p. 2) |
|
|
identify the content/procedures that would require the implementation of an LOA/SOP. Write A for LOA or B for SOP in the blanks provided.
234. Describe operating position/sector |
B
(LP, p. 11) |
|
|
identify the content/procedures that would require the implementation of an LOA/SOP. Write A for LOA or B for SOP in the blanks provided.
235. Define coordination procedures between two control towers within the same approach control airspace |
A (
LP, p. 3) |
|
|
identify the content/procedures that would require the implementation of an LOA/SOP. Write A for LOA or B for SOP in the blanks provided.
236. Establish local stripmarking procedures |
B
(LP, p. 10) |
|
|
identify the content/procedures that would require the implementation of an LOA/SOP. Write A for LOA or B for SOP in the blanks provided.
237. Delegate the responsibility for ATC services to the tower, approach control, and the ARTCC |
A
(LP, p. 5) |
|
|
238. A device that is used or intended to be used for flight in the air.
|
Aircraft
(LP, p. 5) |
|
|
239. An area of land or water that is used or intended to be used for the landing and takeoff of aircraft
|
Airport
(LP, p. 6) |
|
|
240. A service operated by appropriate authority to promote the safe,
orderly, expeditious flow of air traffic |
Air Traffic Control
(LP, p. 6) |
|
|
241. An authorization by air traffic control for the purpose of preventing collision between known aircraft, and for an aircraft to proceed under specified traffic conditions within controlled airspace.
|
Air Traffic Clearance
(LP, p. 4) |
|
|
242. Specified information relating to the intended flight of an aircraft, that is filed orally, in writing, or by
|
Flight Plan
(LP, p. 7) |
|
|
243. A level of constant atmospheric pressure related to a reference datum of 29.92 inches of mercury.
|
Flight Level
(LP, p. 7) |
|
|
244. Separation of all air traffic within designated airspace by air traffic
control. |
Positive Control
(LP, p. 7) |
|
|
245. Separation in accordance with the applicable minima in FAA Order JO 7110.65.
|
Approved Separation
(LP, p. 8) |
|
|
246. A geographical location in relation to which the position of an aircraft is reported.
|
Reporting Point
(LP, p. 7) |
|
|
247. A pilot in command may deviate from FAR 91 if ________.
A. the aircraft is within Class G airspace B. there is an emergency requiring immediate action C. the aircraft is in visual conditions D. an ATC clearance is requested |
B. there is an emergency requiring immediate action
(LP, p. 27) |
|
|
248. Which of the following Right-of-Way rules is not correct?
A. Converging aircraft, aircraft on the left has right-of-way B. Overtaking, aircraft being overtaken has right-of-way C. Head-on, both aircraft give way to the right D. Landing, aircraft on final approach has right-of-way |
A. Converging aircraft, aircraft on the left has right-of-way
(LP 10, p. 16) |
|
|
249. Pilots of two aircraft may operate as a formation flight when ________.
A. authorization is obtained from ATC B. flight visibility is at least 3 miles C. prior arrangements are made and no paying passengers are aboard D. flight is conducted at or above 1,500 feet MSL |
C. prior arrangements are made and no paying passengers are aboard
(LP, p. 14) |
|
|
250. ATC specialists who are age 40 and above shall be scheduled by facility managers for medical examinations every __________ if in the terminal/center environment.
A. 3 years B. year C. 2 years D. 6 months |
B. year
(LP 10, p. 41) |
|
|
251. The maximum speed authorized by FAR for aircraft below 10,000 feet MSL is ________ knots.
A. 250 B. 200 C. 180 D. 150 |
A. 250
(FAR, 91.117; LP, p. 19) |
|
|
252. Airspeed in a VFR corridor through Class B airspace shall not be more than ________ knots.
A. 150 B. 180 C. 200 D. 250 |
C. 200
(LP, p. 21) |
|
|
253. A pilot operating below 18,000 feet MSL shall set the altimeter to ________.
A. current altimeter setting of a station along the route and within 100 NM of the aircraft B. current altimeter setting of a station along the route and within 200 NM of the aircraft C. 29.29 in/hg D. 29.92 in/hg |
A. current altimeter setting of a station along the route and within 100 NM of the aircraft (LP, p. 25)
|
|
|
254. When operating an aircraft at an airport in Class G Airspace that has an operating control tower, unless otherwise authorized, the pilot must have ________.
A. a transponder with Mode C B. a transponder only C. radar contact and two-way communications D. two-way radio communications with the tower |
D. two-way radio communications with the tower
(LP, p. 28) |
|
|
255. The minimum age required to obtain an ATC control tower operator certificate is: ________.
A. 18 B. 21 C. 30 D. No age requirement |
A. 18
(LP, p. 38) |
|
|
256. Bernoulli’s Principle states: “The internal pressure of a fluid ________ at points where the speed of the fluid ________.”
A. increases; increases B. decreases; increases C. increases; decreases D. decreases; decreases |
B. decreases; increases
(LP, p. 3) |
|
|
257. Regarding helicopters, the cyclic controls the _______ of the rotor blades and the collective controls the _________.
A. pitch; tilt B. speed; pitch C. tilt; pitch D. angle; speed |
C. tilt; pitch
(LP 12, pp. 40 and 42) |
|
|
258. Which of the following does NOT affect aircraft performance?
A. Temperature B. Moisture C. Pressure D. Relative wind |
257. D. Relative wind
(LP 12, p. 15) |
|
|
259. A secondary form of lift is a(n) __________ generated by air striking the underside of the airfoil and being deflected __________.
A. upward force; downward B. downward force, upward C. pressure differential; over the wing D. upward force; over the wing |
258. A. upward force; downward
(LP 12, p. 5) |
|
|
260. An imaginary straight line drawn from the leading edge to the trailing edge of a cross section of an airfoil is called the _______.
A. chord line B. camber C. relative wind D. angle of attack |
A. chord line
(LP, p. 8) |
|
|
261. When ________ and ________ are in equilibrium, the aircraft neither gains nor loses airspeed.
A. thrust; drag B. lift; thrust C. lift; weight D. weight; drag |
A. thrust; drag
(LP 12, p. 14) |
|
|
262. What force in flight counteracts lift?
A. Pressure B. Thrust C. Weight D. Relative wind |
C. Weight
(LP, p. 13) |
|
|
263. What is used to determine the angle of attack?
A. Chord line and the ground B. Relative wind and chord line C. Flight path and relative wind D. Flight path and upper camber |
B. Relative wind and chord line
(LP, p. 9) |
|
|
264. If a pilot adjusts the pitch and yaw, the aircraft is moving along the ________ and __________ axes.
A. longitudinal; vertical B. lateral; vertical C. longitudinal; lateral D. lateral; horizontal |
B. lateral; vertical
(LP 12, p. 25) |
|
|
265. Relative wind flows in a direction __________ and __________ the direction of flight.
A. parallel with; opposite to B. parallel with; perpendicular to C. opposite to; perpendicular to D. opposite to; divergent from |
A. parallel with; opposite to (LP 12, p. 6)
|
|
|
266. The blades of a helicopter are shaped like ________ and act as ________.
A. airfoils; ailerons B. ailerons; elevators C. airfoils; wings D. ailerons; wings |
C. airfoils; wings
(LP 12, p. 39) |
|
|
267. Which of the following is a principal airfoil?
A. Rudder B. Propeller C. Fuselage D. Trim tabs |
B. Propeller
(LP 12, p. 7) |
|
|
268. When air density decreases what occurs?
A. Rate of climb is faster and landing speed will be faster B. Landing speed is faster and engine power output will be decreased C. Takeoff run is longer and the engine produces more power D. Rate of climb is slower and takeoff run is shorter |
B. Landing speed is faster and engine power output will be decreased
(LP 1 2, p. 21) |
|
|
269. An aircrafts movement around the longitudinal axis is controlled by the __________ and is called _________.
A. rudder; yaw B. ailerons; roll C. elevator; pitch D. ailerons; yaw |
B. ailerons; roll
(LP 12, p. 24) |
|
|
270. At approximately what angle of attack will air no longer flow smoothly over the wing’s upper surface?
A. 5-10 B. 10-15 C. 13-18 D. 15-20 |
D. 15-20
(LP, p. 45) |
|
|
271. What type of icing is an aircraft likely to encounter when flying in temperatures above freezing?
A. Pitot tube icing B. Wing icing C. Carburetor icing D. Windshield icing |
C. Carburetor icing
(LP, p. 51) |
|
|
272. What is the basic purpose of the autorotation maneuver in a helicopter?
A. Provide a controlled landing when the engine is no longer supplying power B. Conserve fuel during cruise flight C. Maintain a constant altitude D. Allow hovering flight in a strong wind |
A. Provide a controlled landing when the engine is no longer supplying power
(LP, p. 44) |
|
|
273. An aircraft with a certificated takeoff weight of more than 41,000 lbs. up to but not including 300,000 lbs. is classified as ________.
A. heavy B. large C. small D. medium |
B. large
(LP 14, p. 9) |
|
|
274. A small business jet aircraft will fall into which aircraft category?
A. Small B. Category I C. Category II D. Category III |
D. Category III
(LP, p. 4) |
|
|
275. A C17 is what type of aircraft?
A. Cessna B. Cargo C. Caravan D. Commercial |
B. Cargo
(LP 14, p. 12) |
|
|
276. Three (3) of the 6 basic tail configurations are ________.
A. conventional, forward slant and “T” B. swept, delta and straight C. horizontal stabilizer above fuselage, empennage and modified “V” D. twin boom, conventional and delta |
A. conventional, forward slant and “T”
(LP 14, p. 22) |
|
|
277. Most CAT I aircraft will generally operate within which speed range?
A. Zero–90 Knots B. 100-160 Knots C. 160-250 Knots D. 300-550 Knots |
B. 100-160 Knots
(LP, p. 5) |
|
|
278. Recognition features of the B737 are ___________.
A. One jet engine under each wing, low wing B. Two jet engines under each wing, low wing C. One jet engine under each wing, T-tail D. One jet engine under each wing, one jet in tail |
A. One jet engine under each wing, low wing
(LP 14, p. 58) |
|
|
279. Which of the following is not one of the three basic wing placements found on aircraft?
A. Tandem-wing B. High-wing C. Low-wing D. Mid-wing |
A. Tandem-wing
(LP, p. 18) |
|

280 . The following graphic depicts a/an
A. L1011. B. MD11. C. DC10. |
B. MD11.
(LP, p. 64) |
|

281 The aircraft pictured is a ________.
A. A320 B. B737 C. A306 D. B757 |
C. A306
(LP 14, p. 60) |
|
|
282. What is the prominent identification feature of the C172?
A. High-wing B. Conventional gear C. Mid-tail D. Turboprop |
A. High-wing
(LP, p. 35) |
|

283. Which of the following aircraft is depicted in this graphic?
A. Citation 550 B. Citation 10 C. Beechjet D. Golden Eagle |
A. Citation 550
(LP 14, p. 48) |
|
|
284. An aircraft weighing 300,000 pounds will fall into the ________ weight class.
A. Small B. Medium C. Large D. Heavy |
D. Heavy
(LP 14, p. 9) |
|
|
285. Name four aircraft identification features.
_____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ |
Size, engine location and number, engine type, wing placement, wing configuration, tail configuration, windows, fuselage shape, and landing gear.
(LP, p. 16) |
|
|
286. Low altitude RNAV route 12 is spoken:
A. “Q twelve” B. “Quebec twelve” C. “T twelve” D . “Tango twelve” |
D . “Tango twelve”
(LP 16, p. 37) |
|
|
287. The different classes of VORs are ________.
A. High, Low, Terminal B. High, Medium, Low C. High, Low, Compass Locator D. High, Medium, Terminal |
A. High, Low, Terminal
(LP, p. 7) |
|
|
288. The bearing and DME frequencies of a TACAN are paired and assigned by ________ numbers.
A. course B. radial C. channel D. heading |
C. channel
(LP 16, p. 11) |
|
|
289. Generally, the vertical dimensions of a low altitude VOR airway are from ________.
A. the surface up to but not including 18,000 feet AGL B. the surface up to but not including 18,000 feet MSL C. 12,000 feet AGL up to, but not including 18,000 feet MSL D. 1,200 feet AGL up to, but not including, 18,000 feet MSL |
D. 1,200 feet AGL up to, but not including, 18,000 feet MSL (LP, p. 33)
|
|
|
290. The non-radar lateral protected airspace of a victor airway within 51NM of the NAVAID is ________.
A. 8 NM either side of centerline B. 4 NM either side of centerline C. 10 NM either side of centerline D. 20 NM either side of centerline |
B. 4 NM either side of centerline
(LP, p. 34) |
|
|
291. The component of the ILS which gives lateral course guidance to the runway is the ________.
A. localizer B. marker beacon C. glide slope D. DME |
A. localizer
(LP, p. 17) |
|
|
292. Which is not a characteristic of a Nondirectional Radio Beacon (NDB)?
A. More accurate than a VOR B. Provides a bearing to be flown during an approach C. Adversely affected by lightning D. Used to establish nonprecision approaches |
A. More accurate than a VOR (LP 16, p.4)
|
|
|
293. The GPS receiver needs at least ________ satellites to yield three-dimensional information, including position, velocity, time, and altitude.
A. 3 B. 4 C. 5 D. 6 |
B. 4
(LP, p. 26) |
|
|
294. The difference between DME slant-range and actual horizontal distance is greatest ________.
A. at low altitude close to the NAVAID B. at high altitude far from the NAVAID C. at low altitude far from the NAVAID D. at high altitude close to the NAVAID |
D. at high altitude close to the NAVAID
(LP, p. 12) |
|
|
295. An Non Directional Beacon (NDB) used in conjunction with the Instrument Landing System (ILS) is called a(n) ________.
A. compass locator B. marker beacon C. Outer Marker (OM) D. Automatic Direction Finder (ADF) |
A. compass locator
(LP, p. 4) |
|
|
296. When NO MEA is depicted, the MEA on a jet route is _______ feet MSL.
A. 14,500 B. 18,000 C. 24,000 D. 45,000 |
B. 18,000
(LP, p. 40) |
|
|
297. Which chart furnishes terminal data for IFR flight in congested areas?
A. IFR Area Charts B. Terminal Area Charts C. Airport/Facility Directory D. En Route Low Altitude Charts |
A. IFR Area Charts
(LP 18, p. 45) |
|
|
298. Which chart(s) depict ATIS frequencies where ATIS is available?
A. En Route Low Altitude Chart B. En Route High Altitude Chart C. IFR Area Chart D. Both A and C |
D. Both A and C
(LP, pp. 12, 45) |
|
|
299. Which of the following is a requirement for an airport to be published on the IFR EnRoute High Altitude Chart?
A. Has a published instrument approach. B. Has a 5000’ or greater hard surfaced runway. C. Has an operational ATCT D. Is public use. |
B. Has a 5000’ or greater hard surfaced runway.
(LP 18, p. 40) |
|
|
300. If NO changeover point is depicted along an airway, it means that ________.
A. the airway segment crosses through uncontrolled airspace B. either NAVAID can be used for the entire length of the route segment C. there is a gap in NAVAID signal coverage along the airway D. the changeover is to be made at the halfway point between the two NAVAIDs |
D. the changeover is to be made at the halfway point between the two NAVAIDs (LP, p. 19)
|
|
|
301. How is Class A airspace depicted on an En Route High Altitude Chart?
A. As a shaded brown area B. In blue, with a solid blue border C. With a hatched blue line around the boundary D. Open white area |
D. Open white area
(LP, p. 43) |
|
|
302. On an En Route Low Altitude chart, prohibited, restricted, and warning areas are shown within ________ boundaries.
A. solid grey B. blue hatched C. light brown D. solid magenta |
B. blue hatched
(LP 18, p. 27) |
|
|
303. Chart(s) that are specifically designed to provide aeronautical information used during instrument flight
A. En Route Low Charts B. En Route High Charts C. IFR Area Charts D. All of the above |
D. All of the above
(LP) |
|
|
304. En Route Low Altitude Charts are published every ________.
A. 56 days B. 112 days C. 3 months D. 6 months |
A. 56 days
(LP 18, p. 3) |
|
|
305. _______ approaches utilize WAAS and/or LAAS for course guidance.
A. RNAV B. ILS C. Localizer D. TACAN |
A. RNAV
(LP 20, p. 11) |
|
|
306. A Nonprecision approach does not provide ________.
A. electronic glide slope information B. azimuth guidance to Category D aircraft C. height and visibility minima D. missed approach instructions |
A. electronic glide slope information
(LP, p. 8) |
|
|
307. The basic marker beacons normally associated with an ILS approach are ________.
A. outer and locator B. inner and outer C. middle and inner D. outer and middle |
D. outer and middle
(LP 20, p. 9) |
|
|
308. The four segments of an IAP, in the order flown, are: Initial, Intermediate, _______, and ______.
A. Missed; Final B. Final; Outbound C. Inbound; Final D. Final; Missed |
D. Final; Missed
(LP 20, p. 5) |
|
309. In the chart, the number 6600 depicts the ________ altitude.
A. decision height B. minimum glideslope intercept C. minimum descent D. procedure turn |
B. minimum glideslope intercept
(LP 20, p. 26) |
|
|
310. Which of the following items is not found on the planview section of the IAP Chart?
A. Airport Lat./Long. Coordinates B. Initial Approach Fix C. Transition Routes D. Obstructions |
A. Airport Lat./Long. Coordinates
(LP 20, p. 20) |
|
|
311. Height of obstructions depicted on Instrument Approach Procedure Charts are _______.
A. always AGL B. found only in the Planview section C. sometimes AGL D. always MSL |
D. always MSL
(LP, p. 20, 24) |
|
|
312. A Localizer approach differs from an ILS approach because ________.
A. a localizer’s decision height is always higher than that of an ILS B. lateral course guidance is provided by a VOR signal C. localizer approaches can not provide straight-in minimums D. no electronic altitude guidance is provided |
D. no electronic altitude guidance is provided
(LP, p. 9) |
|
|
313. Which statement is true regarding Minimum Safe Altitudes (MSAs)?
A. MSAs provide obstacle clearance within 22 nautical miles of the primary approach NAVAID. B. NAVAID frequency reception is ensured at the MSA. C. Individual MSAs are depicted along each segment of the approach procedure. D. MSAs provide 1,000-foot obstacle clearance. |
D. MSAs provide 1,000-foot obstacle clearance.
(LP, p. 22) |
|
314. The intermediate segment of an approach procedure ends at the _________.
A. final approach fix B. initial approach fix C. missed approach point D. runway |
A. final approach fix
(LP, p. 6) |
|
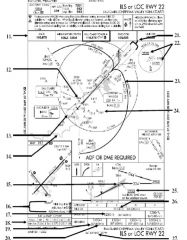
315. 11.
|
Frequency Information
|
|
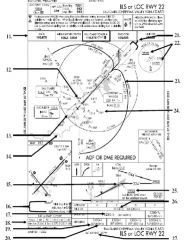
316. 12.
|
EAU VORTAC
|
|
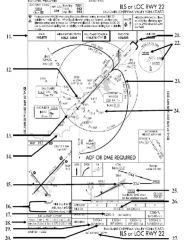
317. 13.
|
Missed Approach Track
|
|
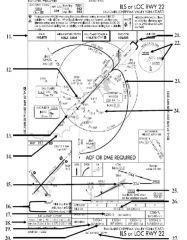
318. 14.
|
River
|
|
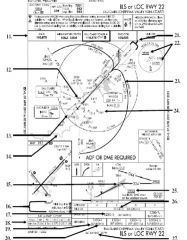
319. 15.
|
Nonprecision (Localizer) Final Approach Fix
|
|
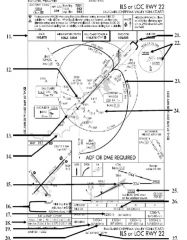
320.16.
|
Runway Lighting Aids
|
|
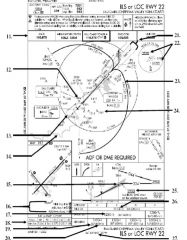
321. 17.
|
Minimum Descent Altitude
|
|
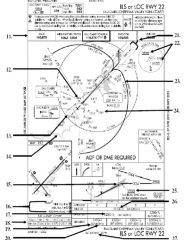
322. 18.
|
Time/Speed Table
|
|
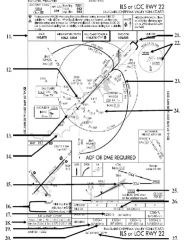
323. 19.
|
Height Above Airport
|
|
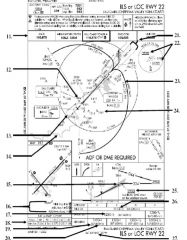
324. 20
|
Military Minimums
|
|
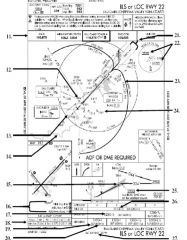
325. 21.
|
Localizer
|
|
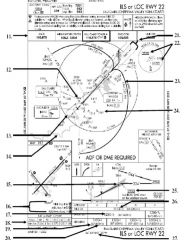
326. 22.
|
Minimum Safe Altitudes
|
|
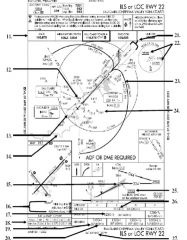
327. 23.
|
DME Arc
|
|
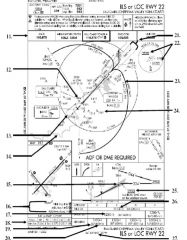
328. 24.
|
Obstruction
|
|
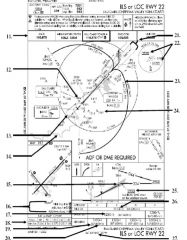
329. 25.
|
Minimum Glide slope Intercept Altitude
|
|
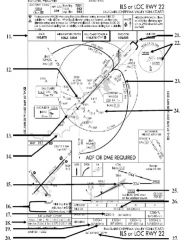
330. 26.
|
Decision Altitude
|
|
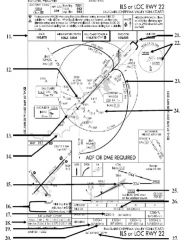
331. 27.
|
Airport Coordinates
|
|
|
332. An aircraft threatened by serious and/or imminent danger which requires immediate assistance is considered as a/an ________ condition.
A. urgent B. distress C. concerned D. lost |
B. distress
(LP, p. 4) |
|
|
333. If you are in contact with an aircraft with a suspected bomb threat, what action should you not take?
A. Comply with the pilots requests B. Handle the aircraft as an emergency C. Suggest actions for the pilot to take D. Provide the most expeditious handling possible |
C. Suggest actions for the pilot to take
(LP 22, p. 18) |
|
|
334. A pilot of an aircraft experiencing radio failure can be expected to squawk ________.
A. 7300 B. 7500 C. 7600 D. 7700 |
C. 7600
(LP 22, p. 16) |
|
|
335. Fuel remaining is expressed in _________.
A. time B. pounds C. gallons D. nautical miles |
A. time
(LP 22, p. 9) |
|
|
336. Because specific procedures are not prescribed for every emergency situation, air traffic control personnel must ________.
A. pursue a course of action which appears to be most appropriate under the circumstances B. receive the supervisor’s approval before decisive action is taken C. make an entry in the facility log D. notify the pilot’s point of departure as soon as an emergency is declared |
A. pursue a course of action which appears to be most appropriate under the circumstances
(LP 22, p. 3) |
|
|
337. Which facility is responsible for receiving and relaying all pertinent ELT signal information to the appropriate authorities?
A. AFSS B. ARTCC C. RCC D. ATCT |
B. ARTCC
(LP, p. 14) |
|
|
338. Which of the following refers to a condition of being concerned about safety and of requiring timely, but not immediate assistance?
A. Flight assistance B. Distress C. Routine emergency D. Urgency |
D. Urgency
(LP 22, p. 5) |
|
|
339. What National Weather Service office provides meteorological forecasts, and advice to ARTCCs and other FAA facilities regarding weather impact on their missions?
A. Center Weather Service Unit (CWSU) B. Weather Forecast Office (WFO) C. Meteorological Watch Office (MWO) D. Aviation Weather Center (AWC) |
A. Center Weather Service Unit (CWSU)
(LP 24, p. 41) |
|
|
340. Within which layer of the atmosphere does temperature increase with altitude, making it a stable layer, generally devoid of significant weather?
A. Tropopause B. Troposphere C. Stratosphere D. Mesosphere |
C. Stratosphere
(LP, p. 5) |
|
|
341. Precipitation formation requires water vapor, lift, and ________.
A. a growth process B. frontal pressure C. a stable temperature D. a steep pressure gradient |
A. a growth process
(LP 24, p. 31) |
|
|
342. What type of air mass produces stable air that is associated with smooth air, poor visibility, and stratiform clouds?
A. A warm air mass moving over a cold surface B. A cold air mass moving over a warm surface C. Any warm air mass D. Any cold air mass |
A. A warm air mass moving over a cold surface
(LP 24, p. 23) |
|
|
343. Which gas constitutes only a small percentage of the earth’s atmosphere and varies widely in both time and space, ranging from trace amounts to 4 percent by volume?
A. Oxygen B. Carbon Monoxide C. Carbon Dioxide D. Water vapor |
D. Water vapor
(LP, p. 9) If asked, Oxygen is appx. 20%, CO .00001%, CO2 .039% |
|
|
344. Virtually all aircraft fly in which two layers of the atmosphere?
A. Mesosphere and stratosphere B. Troposphere and mesosphere C. Thermosphere and stratosphere D. Troposphere and stratosphere |
D. Troposphere and stratosphere
(LP 24, p. 4) |
|
|
345. When the ________ is greater than zero, the air is unsaturated.
A. condensation point B. temperature-dew point spread C. temperature D. dew point |
B. temperature-dew point spread
(LP, p. 11) |
|
|
346. A sinking parcel of air compresses and ________ as it encounters increasing pressure; this causes a cloud to quickly ________.
A. warms, form B. warms, dissipate C. cools, form D. cools, dissipate |
B. warms, dissipate
(LP, p. 16) |
|
|
347. What type of clouds look like fluffy cotton balls or heaps, indicate upward vertical motion or thermal uplift of air, and can produce severe turbulence, icing, and other hazards?
A. Cirriform B. Nimboform C. Cumuliform D. Stratiform |
Cumuliform
|
|
|
348. Air flow around a high diverges in a ________ motion and ________, causing the air to compress and warm, which tends to dissipate clouds.
A. clockwise, rises B. clockwise, sinks C. counterclockwise, rises D. counterclockwise, sinks |
B. clockwise, sinks
(LP, p. 19) |
|
|
349. Standard atmosphere is NOT used for ________.
A. pressure altimeter calibrations B. aircraft performance calculations C. weather observations D. aircraft design |
C. weather observations
(LP 24, p. 6) |
|
|
350. The ratio of water vapor in the air compared to the amount of water vapor the air can hold at a particular temperature and pressure is the definition of _________.
A. barometric surface pressure B. relative humidity C. dew point D. saturated air |
B. relative humidity
(LP 24, p. 10) |
|
|
351. Which front is associated with poor visibility, smooth air, and steady precipitation?
A. Warm B. Occluded C. Cold D. Stationary |
A. Warm
|
|
|
352. What type of precipitation occurs when there is a shallow layer aloft with above freezing temperatures, with a deep layer of below freezing air based at the surface?
A. Rain B. Snow C. Ice pellets D. Freezing rain |
C. Ice pellets
|
|
|
353. Gusty wind is coded as a ________ in the wind group of a METAR.
A. GW B. W C. WG D. G |
D. G
|
|
|
354. In the contiguous United States of America region, the ICAO Station Identifier prefix is ________.
A. PA B. P C. KA D. K |
D. K
|
|
|
355. “A scheduled report transmitted at fixed intervals” describes a ________.
A. METAR B. SPECI C. TAF D. UUA |
A. METAR
|
|
|
356. In the date/time field of a METAR, ________.
A. the first two digits are the date, the second two digits are the hour, and the last two digits are the minutes in UTC B. the six digits represent the hour, minutes, and seconds of the observation in UTC C. the first two digits are the date, the second two digits are the hour, and the last two digits are the minutes in local time D. the six digits represent the hour, minutes, and seconds of the observation in local time |
A. the first two digits are the date, the second two digits are the hour, and the last two digits are the minutes in UTC
|
|
|
357. A sky coverage of six-eighths is reported as ________.
A. BKN B. FEW C. SCT D. SKC |
A. BKN
|
|
|
358. What term refers to the greatest distance that can be seen throughout at least half the horizon circle (180 degrees), not necessarily continuous?
A. Runway Visual Range (RVR) B. Sector visibility C. Tower visibility D. Prevailing visibility |
D. Prevailing visibility
|
|
|
359. What is an instrumentally derived value that represents the horizontal distance a pilot may see down the runway from the approach end?
A. Runway Visual Range (RVR) B. Sector visibility C. Tower visibility D. Prevailing Visibility |
A. Runway Visual Range (RVR)
|
|
|
360. In the METAR/SPECI Sky Condition Group, heights are reported in ________.
A. hundreds of feet AGL B. thousands of feet AGL C. hundreds of feet MSL D. thousands of feet MSL |
A. hundreds of feet AGL
|
|
|
361. In a METAR/SPECI report, what do temperatures and dew points prefixed with an “M” signify?
A. Missing B. Below zero C. ”more than” D. Degrees Fahrenheit |
B. Below zero
|
|
|
362. SPECI KHYS 092338Z AUTO…
A. “Hays, automated, special report, three eight observation…” B. “Hays, special report, automated, two three three eight observation…” C. “Hays, special report, automated two three three eight zulu observation…” D. “Special report, Hays, two three three eight zulu observation, automated…” |
A. “Hays, automated, special report, three eight observation…”
|
|
|
363. Based on the following METAR, the visibility is ________. KOKC 181456Z 01010KT 10SM FEW055 BKN100 04/M02 A2992 RMK AO2 SLP070
A. 4 statute miles B. 10 nautical miles C. 10 statute miles D. missing |
C. 10 statute miles
|
|
|
364. R17/M0600FT
A. “Runway one seven R-V-R less than six hundred” B. “Runway one seven visual range more than six hundred feet” C. “R-V-R runway one seven below six hundred” D. “R-V-R runway one seven less than six hundred feet” |
A. “Runway one seven R-V-R less than six hundred”
|
|
|
365. SCT00 BKN080 OVC120
A. “Scattered three thousand, ceiling broken eight hundred, overcast one two thousand” B. “Scattered three thousand, broken eight hundred, ceiling one two thousand overcast” C. “Three thousand scattered, ceiling eight thousand broken, one two thousand overcast” D. “Three thousand scattered, eight thousand broken, ceiling one thousand two hundred overcast” |
C. “Three thousand scattered, ceiling eight thousand broken, one two thousand overcast”
|
|
|
366. PK WND 23034/43
A. “Peak wind two three zero at three four happened at four three zulu” B. “Peak wind two three zero at three four occurred at four three past the hour” C. “Peak wind two three zero degrees at three four knots occurred at four three zulu” D. “Peak wind two hundred thirty degrees at thirty-four knots occurred at forty-three zulu” |
B. “Peak wind two three zero at three four occurred at four three past the hour”
|
|
|
367. CIG 005V008
A. “Ceiling five hundred variable eight hundred” B. “Ceiling five hundred feet variable eight hundred feet“ C. Ceiling variable between five hundred and eight hundred” D. “Ceiling variable between five hundred feet and eight hundred feet” |
C. Ceiling variable between five hundred and eight hundred”
|
|
|
368. The purpose of a Pilot Weather Report (PIREP) is ________.
A. to report a pilot’s position B. to report meteorological conditions in flight C. to report a pilot incident D. a pilot’s report of an accident |
B. to report meteorological conditions in flight
|
|
|
369. PIREPs are used by ________ to expedite the traffic flow in the vicinity of an airport.
A. the National Weather Service B. Flight Service Stations C. centers D. towers and TRACONs |
D. towers and TRACONs
|
|
|
370. Air traffic facilities must solicit PIREPs when ________ is reported.
A. light turbulence B. visibility of 5 miles or less C. a ceiling at or below 10,000 feet D. icing of trace or greater intensity |
B. visibility of 5 miles or less
|
|
|
371. Each PIREP must include the type of aircraft, altitude, location, and ________.
A. coordinated universal time B. the temperature in degrees Celsius C. remarks D. local time |
A. coordinated universal time
|
|
|
372. When preparing PIREPs involving turbulence or icing, ________ shall always be included.
A. Sky condition B. Visibility C. Intensity D. Wind |
C. Intensity
|
|
|
373. The following PIREP indicates the base of the second cloud layer is ________.
UA/OV MKC-JOT/TM 1100/FL080/TP C182/SK BKN025-TOP045/OVC050-TOP075/WX FV99/TA08 A. 5,000 feet AGL B. 4,500 feet MSL C. 7,500 feet AGL D. 5,000 feet MSL |
D. 5,000 feet MSL
|
|
|
OKC UA /OV OKC180010/TM 1516/FL120/TP TA20/SK 035 BKN 075/OVC095-TOPUNKN/WX FV01SM SN/TA M04/TB MOD 050-070/RM TCU W DURC
374. At what altitude(s) did the aircraft first encounter turbulence? A. unknown B. 3,500-7,500 feet C. 5,000 feet D. 12,000 feet |
C. 5,000 feet
|
|
|
OKC UA /OV OKC180010/TM 1516/FL120/TP TA20/SK 035 BKN 075/OVC095-TOPUNKN/WX FV01SM SN/TA M04/TB MOD 050-070/RM TCU W DURC
375. What is the type of aircraft that made this report? A. FV01 B. TA20 C. TA04 D. TM1516 |
B. TA20
|
|
|
OKC UA /OV OKC180010/TM 1516/FL120/TP TA20/SK 035 BKN 075/OVC095-TOPUNKN/WX FV01SM SN/TA M04/TB MOD 050-070/RM TCU W DURC
376. What is the height of the base of the second layer? A. Not reported B. 3,500 feet C. 7,500 feet D. 9,500 feet |
D. 9,500 feet
|
|
|
OKC UA /OV OKC180010/TM 1516/FL120/TP TA20/SK 035 BKN 075/OVC095-TOPUNKN/WX FV01SM SN/TA M04/TB MOD 050-070/RM TCU W DURC
377. What was the weather element that caused the reduction in visibility? A. RN B. SHRA C. SN D. GR |
C. SN
|
|
|
378. After departing OKC at 0455Z, SWA5325, B737-700, 20 miles northwest of OKC climbing through 15,300 feet, reported bases 2,700, still IMC. Light turbulence was reported during the climb from 1,500 to 3,000, negative ice, wind 310 at 28
Record the intensity of the turbulence and the altitude at which it was first encountered? A. LGT/15 B. LGT 1.5 C. LGT 150 D. LGT 015 |
D. LGT 015
|
|
|
379. After departing OKC at 0455Z, SWA5325, B737-700, 20 miles northwest of OKC climbing through 15,300 feet, reported bases 2,700, still IMC. Light turbulence was reported during the climb from 1,500 to 3,000, negative ice, wind 310 at 28 377. What should be recorded in the remarks?
A. WND 31028KT B. NEG ICE C. DURC D. OKC315020 |
C. DURC
|
|
|
380. Authorized symbols and abbreviations must be used for recording ________.
A. TCAS RAs when voice recorders are operational B. relief briefings C. clearances, requests and advisories D. clearances, reports and instructions |
D. clearances, reports and instructions
|
|
|
381. The letters “OTP” on a strip stand for _______.
A. VFR conditions-on-top B. oceanic transfer point C. procedure turn D. out of control area |
A. VFR conditions-on-top
|
|
|
382. What symbol indicates that an aircraft’s clearance is void if not airborne by a specific time?
A. V= B. ~V C. V < D. V |
C. V <
|
|
|
383. What symbol should be used to delete any unwanted or unused altitude information?
A. X B. − C. + D. / |
A. X
|
|
|
384. Flight progress strips are used for _______.
A. traffic count only B. traffic sequencing only C. posting current data on air traffic D. traffic metering |
C. posting current data on air traffic
|
|
|
385. Flight progress strips are considered ________ documents.
A. outdated B. necessary C. legal D. current |
C. legal
|
|
|
386. When used on a strip, “VA” indicates which of the following?
A. Volcanic Ash B. Variable Altitude C. Visual Approach D. Virginia |
C. Visual Approach
|
|
|
387. Which of the following is the correct format to record a block altitude?
A. 100B120 B. 210/230 C. 230B210 D. B150/170 |
A. 100B120
|
|
|
388. Flight progress strips that are hand printed must ________.
A. use standard characters B. be legible C. conform to the machine printed format D. all the above |
D. all the above
|
|

En Route Strip
389. On all en route strips, Block 5 is used for what purpose? A. Aircraft ID B. Equipment suffix C. Aircraft type D. Filed true airspeed |
D. Filed true airspeed
This card is incomplete |
|

390. For en route strips, altitude information is found in which block?
A. 8 B. 27 C. 16 D. 20 |
D. 20
|
|

391. On an en route strip, in which block is the aircraft identification located?
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 |
C. 3
|
|

392. On an en route strip, which block contains the center-estimated time over the fix?
A. 11 B. 15 C. 19 D. 25 |
B. 15
|
|
|
393. Which control symbol(s) indicates that an ARTCC has forwarded flight plan information?
A. Slash B. Horizontal line C. Check mark D. Red circle |
D. Red circle
|
|
Terminal Strip
394. On all terminal strips, Block 5 is used for what purpose? A. Aircraft ID B. Aircraft type C. Computer ID D. Beacon code |
D. Beacon code
This question is incomplete |
|
395. For terminal arrival strips, altitude information is found in which block?
A. 6 B. 7 C. 8 D. 9 |
D. 9
This question is incomplete |
|
396. On a terminal strip, in which block is the aircraft identification located?
A. 10 B. 7 C. 1 D. 2 |
C. 1
This question is incomplete |
|
397. On a terminal strip, which block contains the estimated time of arrival over a coordination fix?
A.3 B. 8 C. 18 D. 10 |
B. 8
|
|
|
398. How is a terminal strip marked to indicate that the aircraft has an emergency?
A. Black “E” B. ”EMRG” C. Red check mark D. Red ‘E” |
D. Red ‘E”
|
|
|
399. When used in FAA Orders JO 7110.10, JO 7110.65, and JO 7210.3, the word “should” means that the procedure is ________.
A. recommended B. optional C. approved D. mandatory . |
A. recommended
|
|
|
400. Letters of Agreement (LOA) are for ________ use and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are for ________ use.
A. intrafacility; extrafacility B. interfacility; intrafacility C. extrafacility; jurisdictional D. intrafacility; interfacility |
B. interfacility; intrafacility
|
|
|
401. Which of the following statements about the NAS is FALSE ?
A. NextGen is the NAS modernization program. B. The NAS is entirely owned and operated by the FAA ( C. The NAS is continuously evolving. D. The NAS includes ATCS, NAVAIDS, and FARs |
B. The NAS is entirely owned and operated by the FAA
|
|
|
402. What information is contained in the FAA Order JO 7340.2?
A. Prescribes air traffic procedures and phraseology used by Flight Service specialists B. Prescribes air traffic procedures and phraseology used by air traffic controllers C. Provides direction and guidance for operating and managing Air Traffic facilities D. Contains approved words and phrase contractions used by the FAA |
D. Contains approved words and phrase contractions used by the FAA
|
|
|
403. Positive control is the ________ of all air traffic within designated airspace by ATC.
A. separation B. observation C. deviation D. sequencing |
A. separation
|
|
|
404. An ARTCC/TRACON is divided into areas of control jurisdiction called ________.
A. positions B. regions C. sectors D. sections |
C. sectors
|
|
|
405. In an ATCT, which 3 positions communicate directly with the pilots?
A. Flight Data, Local and Ground B. Local, Clearance Delivery, and Tower Coordinator C. Ground, Local and Clearance Delivery D. Local, Tower Coordinator, and Flight Data |
C. Ground, Local and Clearance Delivery
|
|
|
406. Traffic management programs are one of several processes administered by the Air Traffic Control System Command Center (ATCSCC) to achieve optimum use of the ________ and minimize ________ without increasing controller workload.
A. airspace, accidents B. NAS, delays C. ATC System, accidents D. airports, delays |
B. NAS, delays
|
|
|
407. Which document lists location identifiers authorized by the FAA?
A. FAA Order JO 7340.2 B. FAA Order JO 7110.65 C. Aeronautical Information Manual D. FAA Order JO 7350.8 |
D. FAA Order JO 7350.8
|
|
|
408. Considering the operational priorities of an air traffic controller, ________ have priority over ________ aircraft.
A. VFR/IFR B. aircraft in distress/lifeguard C. presidential/lifeguard D. diverted/aircraft in distress |
B. aircraft in distress/lifeguard
|
|
|
409. “Automation procedures are used in preference to non-automation procedures” is an example of ATC:
A. Duty Priority B. Procedural Preference C. Operational Priority D. Primary Purpose |
B. Procedural Preference
|
|
|
410. The correct designation for a runway with a magnetic heading of 009 degrees is runway ________.
A. 9 B. 1 C. 01 D. 10 |
B. 1
|
|
|
411. Which of the following is not one of the uses of a movement area?
A. Air taxiing B. Hover taxiing C. Loading passengers D. Takeoff and landing of aircraft |
C. Loading passengers
|
|
|
412. Which of the following statements about airport beacons is FALSE?
A. They are turned on at night B. They are turned on during restricted weather C. They are turned on whenever the tower is operational D. They identify the type of airport |
C. They are turned on whenever the tower is operational
|
|
|
413. At an airport with no precision approach procedures, which of the following runway markings will NOT be present?
A. Touchdown zone B. Runway designator C. Runway centerline D. Aiming point |
A. Touchdown zone
|
|
|
414. “Separating aircraft and issuing safety alerts” represents an air traffic controller’s first ________.
A. Duty Priority B. Procedural Preference C. Operational Priority D. Primary Purpose |
A. Duty Priority
|
|
|
415. The addition, deletion, or modification of information or instructions within an order are made through a(n) ________.
A. change B. notice C. supplement D. amendment |
A. change
|
|
|
416. RVSM stands for ________
A. Required Visual Separation Minima B. Reduced Vertical Separation Minima C. Requested Visual Separation Minima D. Required Vertical Separation Minima |
B. Reduced Vertical Separation Minima
|
|
|
417. Minimum vertical separation between RVSM equipped IFR aircraft up to and including FL410 is ________ feet.
A. 1,000 B. 5,000 C. 4,000 D. 2,000 |
A. 1,000
|
|
|
418. Which of the following is not a method for establishing non-radar longitudinal separation?
A. Depart at a specified time B. Arrive at a fix at a specified time C. Clear aircraft to fly on airways which do not overlap D. Hold at a fix until a specified time |
C. Clear aircraft to fly on airways which do not overlap
|
|
|
419. When using non-radar departure divergence ___________.
A. the airport must have at least 2 runways that intersect B. the ATCS must wait 10 minutes between successive departures C. the ATCS must ensure visual separation exists D. the ATCS must assign courses that diverge by at least 45 degrees |
D. the ATCS must assign courses that diverge by at least 45 degrees
|
|
|
420. When using visual separation, what are the separation minima?
A. 5NM B. 1,000 feet C. 10 minutes D. There are no specified minima. |
D. There are no specified minima.
|
|
|
421. The minimum terminal radar separation for two IFR aircraft less than 40 miles from the antenna is ________ miles.
A. 3 B. 10 C. 5 D. 20 |
A. 3
|
|
|
422. A nonstandard holding pattern ________.
A. has leg lengths which must be measured in minutes B. is one that is located at a navigational aid C. uses left turns D. uses right turns |
C. uses left turns
|
|
|
423. Runway separation is applied by ________ controllers.
A. Air Route Traffic Control Center (ARTCC) B. Air Traffic Control Tower (ATCT) C. Terminal Radar Approach Control (TRACON) D. Automated Flight Service Station (AFSS) |
B. Air Traffic Control Tower (ATCT)
|
|
|
424. Who is responsible for observing and reporting the conditions of the landing area of an airport?
A. Airport manager/operator B. Tower controller C. Pilot D. Flight service specialist |
A. Airport manager/operator
|
|
|
425. What type of NOTAM consists of information that is regulatory in nature, pertaining to flight, including but not limited to changes to IFR charts, procedures, and airspace usage?
A. NOTAM D B. FDC NOTAM C. Military NOTAM D. Pointer NOTAM |
B. FDC NOTAM
|
|
|
426. A feature which improves a primary radar display is:
A. Moving target indicator B. Anomalous propagation C. Temperature inversion D. Ring around |
A. Moving target indicator
|
|
|
427. Which radar system relies on reflected radio signals and does NOT require equipment in aircraft?
A. Primary radar B. Secondary radar C. Airport radar D. Positive radar |
A. Primary radar
|
|
|
428. Which of the following is a component of a secondary radar system?
A. Moving Target Indicator B. Circular polarization C. Receiver D. Transponder |
D. Transponder
|
|
|
429. An advantage of secondary radar over primary radar is it's ______.
A. longer range B. ability to switch from linear polarization to circular polarization C. improved weather display D. display of any object which reflects radio energy |
A. longer range
|
|
|
430. Which document provides direction and guidance for operating and managing Air Traffic facilities?
A. FAA Order JO 7110.10 B. FAA Order JO 7210.3 C. Aeronautical Information Manual D. Terminal Phraseology Guide |
B. FAA Order JO 7210.3
|
|
|
431. Which document prescribes air traffic procedures and phraseology used by Flight Service specialists?
A. FAA Order JO 7210.3 B. FAA Order JO 7110.10 C. Aeronautical Information Manual D. FAA Order JO 7110.65 |
B. FAA Order JO 7110.10
|
|
|
432. Advising the En Route Radar and Radar Associate positions of sector actions required to accomplish the safe and efficient operation of the sector is a responsibility of the En Route ________ position.
A. radar coordinator/handoff B. radar flight data C. clearance delivery D. traffic management |
A. radar coordinator/handoff
|
|
|
433. Which AFSS position uses the radio call sign "Flight Watch"
A. EFAS B. Inflight C. Broadcast D. Preflight |
A. EFAS
|
|
|
434. Airmen’s information can be disseminated via Aeronautical Charts and _______.
A. satellite communications B. facility directives C. flight information publications D. FAA orders |
C. flight information publications
|
|
|
435. Which document contains items concerning pilot’s health and medical facts, factors affecting flight safety, and accident reporting?
A. FAA Order JO 7110.10 B. FAA Order JO 7210.3 C. Aeronautical Information Manual D. Terminal Phraseology Guide |
C. Aeronautical Information Manual
|
|
|
436. The purpose of a “Supplement” is ________.
A. temporary direction for a situation requiring immediate action B. to add, delete, or modify information or instructions within an order C. to make one-time announcements D. to consolidate instructions from different levels into a single directive |
D. to consolidate instructions from different levels into a single directive
|
|
|
437. Which of the following is an example of a temporary directive?
A. Supplements B. LOA C. GENOT D. Orders |
C. GENOT
|
|
|
438. Taxiway centerline lights emit ______.
A. steady green lights B. flashing green lights C. alternating green and blue lights D. steady blue lights |
A. steady green lights (LP 3, p. 33)
|
|

439. What aircraft is pictured above?
A. B737 B. B757 C. A300 D. B777 |
D. B777
(LP 14, p. 62) |
|

440. What aircraft is pictured above?
A. BE58 B. PAY1 C. PA34 D. P28A |
C. PA34
(LP 14, p. 44) |
|
|
441. Generally, what are the two basic types of landing gear?
A. Bicycle and tricycle B. Tricycle and conventional C. Bicycle and conventional D. Tricycle and nose dragger |
B. Tricycle and conventional (LP 14, p. 29)
|
|
|
442. An aircraft with a certified takeoff weight of ________ pounds or less will fall into the small weight class.
A. 12,500 B. 41,000 C. 50,000 D. 155,000 |
B. 41,000
(LP 14, p. 9) |
|
|
443. A helicopter generates wingtip vortices when ________.
A. lift is first generated B. in stationary hover C. in vertical ascent D. in forward flight |
D. in forward flight
(LP 13, p. 22) |
|
|
444. Which three aircraft characteristics represent the greatest generated wake turbulence?
A. Heavy, dirty, slow B. Small, clean, fast C. Large, dirty, slow D. Heavy, clean, slow |
D. Heavy, clean, slow
(LP 13, p. 4) |
|
|
445. The pitch (angle of attack) of a helicopter rotor blade is controlled by the ________.
A. cyclic B. throttle C. collective D. antitorque pedal |
C. collective
(LP 12, p. 40) |
|
|
446. Actual atmospheric pressure at a given time and place does not depend on which of the following?
A. Temperature B. Wind C. Density of the air D. Altitude |
B. Wind
(LP 12, p. 17) |
|
|
447. A term for the air flow which is parallel with, and opposite to, the direction of flight is called a/an ____________.
A. angle of attack B. relative wind C. flight path D. headwind |
B. relative wind
(LP 12, p. 6) |
|
|
448. When an IFR flight loses two-way communications with ATC, controllers should consider the pilot’s actions with regard to their:
A. route, speed and altitude B. route, time to leave their clearance limit and speed C. altitude, route and time to leave their clearance limit D. altitude, time to leave their clearance limit and speed |
C. altitude, route and time to leave their clearance limit
(LP 11, p. 40) |
|
|
449. FAR Part ___________ covers General Operating and Flight Rules.
A. 67 B. 121 C. 91 D. 135 |
C. 91
(LP 11, p. 3) |
|
|
450. Which of the following statements concerning special VFR (SVFR) is true?
A. ATC clearance is required. B. SVFR operations may be conducted at any altitude below FL180. C. Pilot need not request SVFR clearance. D. 3SM visibility is required. |
A. ATC clearance is required. (LP 11, p. 22)
|
|
|
451. A pilot in command operating in VFR conditions shall not cancel an IFR flight plan while operating in Class ________ Airspace.
A. D B. C C. B D. A |
D. A
(LP 10, p.27) |
|
|
452. What pre-flight action does FAR 91 require pilots to take before beginning a flight?
A. File a flight plan B. Receive ATC authorization for the flight C. Advise ATC of intentions D. Familiarize themselves with all available information concerning the flight |
D. Familiarize themselves with all available information concerning the flight
(LP 10, p. 13) |
|
|
453. Which special use airspace is always located offshore?
A. Warning Area B. Alert Area C. Controlled Firing Area D. National Security Area |
A. Warning Area
(LP 9, p. 19) |
|

454. What aircraft is pictured above?
A. Citation 550 B. Citation 10 C. Beechjet D. Golden Eagle |
A. Citation 550
(LP 14, p. 52) |
|

455. Which of the following aircraft is depicted in this graphic?
A. C172 B. C208 C. C210 D. C130 |
C. C210
(LP 14, p. 38) |
|
|
456. Which statement is NOT true regarding the general characteristics of Category II aircraft?
A. Large weight class B. They operate at FL240 and below C. Speed is 160-250 knots D. Climb rate is 1,000 to 2,000 feet per minute |
A. Large weight class
(LP 14, p. 6) |
|
|
457. A C17 is included in aircraft Category ___________.
A. I B. II C. III D. IV |
C. III
(LP 14, p. 4) |
|
|
458. Counter control to a wake turbulence induced roll is most effective when _______.
A. there is no more than a 5 knot crosswind B. a large aircraft follows a heavy aircraft C. a rapid descent is made D. the ailerons extend beyond the edge of the vortex |
D. the ailerons extend beyond the edge of the vortex
(LP 13, p.19) |
|
|
459. The effect of the rotating air masses generated behind the wing tips of aircraft or behind the rotor tips of helicopters in forward motion is __________.
A. updrafts and downdrafts B. wake turbulence C. low-level wind shear D. attitude variations |
B. wake turbulence
(LP 13, p. 3) |
|
|
460. The forces that are acting on a helicopter in flight are lift, thrust, _______, and _______.
A. torque, drag B. weight, gravity C. angle of attack, drag D. weight, drag |
D. weight, drag
(LP 12, p. 39) |
|
|
461. With a(n) ________ in airspeed, drag ________.
A. increase; increases rapidly B. increase; decreases rapidly C. decrease; increases rapidly D. decrease; remains the same |
A. increase; increases rapidly (LP 12, p. 14)
|
|
|
462. When air is forced to travel at a faster speed across the top of a wing versus the bottom, this will result in ________ the wing.
A. lower pressure above B. lower pressure below C. higher pressure above D. atmospheric pressure above |
A. lower pressure above
(LP 12, p. 4) |
|
|
463. A pilot flying VFR must maintain at least 5 miles visibility in all or part of class ________ and ________ airspace.
A. E;A B. E;G C. G;D D. C;D |
B. E;G
(LP 11, pp. 16 and 18) |
|
|
464. No person may operate an aircraft under VFR in Class C airspace with a flight visibility of less than ________.
A. 1NM B. 1SM C. 3NM D. 3SM |
D. 3SM
(LP 11, p. 15) |
|
|
465. An ATC specialist who is 41 years of age and works in the Terminal option is required to have a medical examination every ________.
A. year B. 2 years C. 3 years D. 5 years |
A. year
(LP 10, p. 41) |
|
|
466. Which of the following statements is true concerning FAR Part 91 aircraft speed restrictions?
A. Above 10,000 MSL, no aircraft may exceed 250 knots. B. No aircraft may exceed 200 knots in any Class C airspace. C. No aircraft may exceed 200 knots when operating below Class B airspace. D. Under no circumstances may an aircraft exceed 250 knots in Class B airspace. |
C. No aircraft may exceed 200 knots when operating below Class B airspace.
(LP 10, p. 21) |
|
|
467. A(n) ________is specified information, relating to the intended flight of an aircraft.
A. ATC Clearance B. Flight Plan C. Supplement D. Notice |
B. Flight Plan
(LP 10, p. 7) |
|
|
468. ATC does not have the authority or the responsibility to issue clearances in class _____ airspace.
A. C B. D C. E D. G |
D. G
(LP 9, p. 12) |
|
|
469. Recognition features of the B737 are ___________.
A. One jet engine under each wing, low wing B. Two jet engines under each wing, low wing C. One jet engine under each wing, T-tail D. One jet engine under each wing, one jet in tail |
A. One jet engine under each wing, low wing
(LP 14, p. 58) |
|
|
470. What is a prominent identification feature of the BE35?
A. Tricycle gear B. Low-wing C. Propeller-driven D. “V”-tail |
D. “V”-tail
(LP 14, p. 40) |
|
|
471. A civilian aircraft designator __________.
A. is always 4 alpha-numerics B. indicates the mission C. generally indicates the manufacturer D. may be 1 to 4 characters |
C. generally indicates the manufacturer
(LP 14, p. 11) |
|
|
472. _________ is jet engine exhaust.
A. Prop-wash B. Wake turbulence C. Jet blast D. Counter control |
C. Jet blast
(LP 13, p. 24) |
|
|
473. Which of the following statements regarding wingtip vortices is true?
A. They drift inward and sink. B. They drift outward and sink. C. They drift inward and rise. D. They drift outward and rise. |
B. They drift outward and sink. (LP 13, p. 12)
|
|
|
474. The most hazardous aspect of structural icing is _______.
A. decreases weight B. increased drag C. reduced thrust D. airfoil distortion |
D. airfoil distortion
(LP 12, p. 49) |
|
|
475. Which are the primary control surfaces on an airplane?
A. Ailerons, elevator, and flaps B. Elevator, flaps, and trim tabs C. Rudder, ailerons, and elevator D. Flaps, ailerons, and propeller |
C. Rudder, ailerons, and elevator
(LP 12, p. 26) |
|
|
476. Which of the following is NOT a principal airfoil?
A. Wing B. Propeller C. Horizontal tail surface D. Fuselage |
D. Fuselage
(LP 12, p. 7) |
|
|
477. What is the requirement for supplemental oxygen above 15,000 MSL?
A. Only the pilot is provided supplemental oxygen B. None C. Each occupant of aircraft is provided with supplemental oxygen D. Pilot and co-pilot are provided supplemental oxygen |
C. Each occupant of aircraft is provided with supplemental oxygen
(LP 11, p. 48) |
|
|
478. A pilot flying under IFR conditions experiences a radio failure. If a route has not been assigned and/or ATC has not advised a route to be expected, what action should the pilot take?
A. Proceed by the route filed in the flight plan. B. Land at nearest available airport. C. Climb to VFR-on-top and continue flight. D. Proceed to alternate airport. |
A. Proceed by the route filed in the flight plan.
(LP 11, p. 42) |
|
|
479. An appropriate magnetic course for an aircraft flying VFR at 6,500 feet MSL and more than 3,000 feet AGL would be ________ degrees.
A. 190 B. 100 C. 360 D. 010 |
A. 190
(LP 11, p. 24) |
|
|
480. To be eligible for an ATC tower operator's certificate, you must hold a _________ medical certificate.
A. First Class B. Second Class C. Third Class D. No medical is required. |
B. Second Class
(LP 10, p. 38) |
|
|
481. An aircraft has the right-of-way over all other aircraft when it is in ________.
A. VFR conditions B. distress C. IFR conditions D. controlled airspace |
B. distress
(LP 10, p. 15) |
|
|
482. Which type of special use airspace may contain a high volume of pilot training activities or unusual types of aerial activities, neither of which is hazardous to aircraft?
A. Alert areas B. Prohibited areas C. Restricted areas D. Warning areas |
A. Alert areas
(LP 9, p. 20) |
|
|
483. What is generally the vertical limit of Class D airspace?
A. 2,500 feet MSL B. Up to, but not including, 18,000 MSL C. 2,500 feet above airport elevation D. 3,500 AGL |
C. 2,500 feet above airport elevation
(LP 9, p. 10) |
|
|
484. Which of the following transponder codes is invalid?
A. 2345 B. 3456 C. 4567 D. 5678 |
D. 5678
(LP 21, p. 33) |
|
|
485. Which of the following is an optional component of an ILS?
A. Inner marker beacon B. Visual information C. Glide slope D. Localizer |
A. Inner marker beacon
(LP 20, p. 9) |
|
|
486. Standard Instrument Departure charts are published every ________.
A. 3 months B. 6 months C. 112 days D. 56 days |
D. 56 days
(LP 19, p. 5) |
|
|
487. Standard Instrument Departures (SIDs) have been established at certain airports to ________.
A. simplify clearance delivery, expedite traffic flow, and reduce pilot/controller workload. B. eliminate the need for clearance delivery procedures. C. ensure all aircraft depart on exactly the same route. D. relieve airport congestion and increase pilot/controller workload. |
A. simplify clearance delivery, expedite traffic flow, and reduce pilot/controller workload. (LP 19, p. 3)
|
|
|
488. Solid triangles indicate ________.
A. VOR changeover points B. DME fixes C. compulsory reporting points D. substitute route structure |
C. compulsory reporting points
(LP 18, p. 22) |
|
|
489. Class D airspace on a sectional aeronautical chart is depicted by a ________ line.
A. dashed blue B. solid blue C. solid magenta D. dashed magenta |
A. dashed blue
(LP 17, p. 16) |
|
|
490. The maximum usable range of an “H” class VOR is _______.
A. 25 NM B. 130 NM C. 40NM D. 100 NM |
B. 130 NM
(LP 16 p. 8) |
|
|
491. True course corrected for the effects of wind is ________.
A. magnetic heading B. magnetic track C. true heading D. true track |
C. true heading
(LP 15, p. 36) |
|
|
492. A nautical mile equals ________ statute miles (SM).
A. .87 B. 1.15 C. 1.5 D. 1.87 |
B. 1.15
(LP 15, p. 14) |
|
|
493. Which of the following is a gyroscopic instrument?
A. Heading indicator B. Altimeter C. Airspeed indicator D. Vertical speed indicator |
A. Heading indicator
(LP 21, p. 13) |
|
|
494. Instrument Approach Procedures (IAPs) are designed to ________.
A. be used only by aircraft in IFR conditions B. transition an aircraft to a point where the aircraft may be vectored to the final approach course C. expedite air traffic in terminal areas D. provide an IFR descent from an en route environment to a point where a safe landing can be made |
D. provide an IFR descent from an en route environment to a point where a safe landing can be made
(LP 20, p. 3) |
|
|
495. Of the types of instrument approaches listed, which one is a precision approach?
A. VOR B. NDB C. ILS D. TACAN |
C. ILS
(LP 20, p. 8) |
|
|
496. The primary purpose of an IFR Area Chart is to furnish ________.
A. VFR reporting points B. visual landmarks for use in congested areas C. terminal data for VFR flights in congested areas D. terminal data for IFR flights in congested areas |
D. terminal data for IFR flights in congested areas
(LP 18, p. 45) |
|
|
497. The En Route Low Altitude charts are for use below ________.
A. 18,000 feet MSL B. 18,000 feet AGL C. 12,500 feet MSL D. 14,000 feet MSL |
A. 18,000 feet MSL
(LP 18, p. 3) |
|
|
498. Basic terrain contour lines on a Sectional Aeronautical Chart are generally spaced at ________ foot intervals.
A. 100 B. 500 C. 1,000 D. 2,000 |
B. 500
(LP 17, p. 8) |
|
|
499. The primary use for Sectional Aeronautical Charts is ________ navigation by ________ speed aircraft.
A. IFR; slow and medium B. VFR; high C. IFR; high D. VFR; slow and medium |
D. VFR; slow and medium
(LP 17, p. 3) |
|
|
500. An aircraft travels 300 nautical miles over the ground in three hours while experiencing a tailwind of 25 knots. The aircraft’s ground speed is ________ knots.
A. 150 B. 125 C. 100 D. 90 |
C. 100
(LP 15, p. 25) |
|
|
501. The navigational method based solely on computing air speed, course, wind, ground speed, and elapsed time is ________.
A. dead reckoning B. VFR navigation C. pilotage D. radio navigation |
A. dead reckoning
(LP 15, p. 45) |
|
|
502. Circles parallel to the equator are called ________.
A. great circles B. parallels of longitude C. meridians D. parallels of latitude |
D. parallels of latitude
(LP 15, p. 5) |
|
|
503. A lack of oxygen in the body tissue results in ________.
A. Hyperventilation B. Vertigo C. Hyperextension D. Hypoxia |
D. Hypoxia
(LP 21, p. 44) |
|
|
504. In which section of the Instrument Approach Chart are the DME arcs depicted?
A. Profile View B. Airport Diagram C. Planview D. Circling section |
C. Planview
(LP 20, p. 21) |
|
|
505. The STAR is not designed to ________.
A. expedite ATC arrival procedures. B. funnel arrival traffic into one-way corridors and reduce coordination between ATC facilities. C. provide guidance to a fix in the terminal area. D. ensure appropriate separation minima between aircraft. |
D. ensure appropriate separation minima between aircraft.
(LP 19, p. 3, 29) |
|
|
506. Chart(s) that are specifically designed to provide aeronautical information used during instrument flight
A. En Route Low Charts B. En Route High Charts C. IFR Area Charts D. All of the above |
D. All of the above
(LP 18) |
|
|
507. An asterisk (∗) before an altitude along a low altitude airway indicates a(n) ________.
A. MOCA B. MCA C. MEA D. MRA |
A. MOCA
(LP 18, p. 19) |
|
|
508. Where are Class B airspace operating rules found?
A. On the Terminal Area Chart B. On the inside flap of a Sectional Aeronautical Chart C. In the World Aeronautical Chart Legend D. Only in the Airport/Facility Directory |
A. On the Terminal Area Chart (LP 17, p. 34)
|
|
|
509. The component of the ILS which provides the descent angle is the ________.
A. marker beacon B. localizer C. glide slope D. back course marker |
C. glide slope
(LP 16, p. 17) |
|
|
510. What condition will cause an aircraft’s indicated airspeed to decrease?
A. A decrease in altitude or temperature B. A decrease in altitude or an increase in temperature C. An increase in altitude or a decrease in temperature D. An increase in altitude or temperature |
D. An increase in altitude or temperature
(LP 15, p. 38) |
|
|
511. Time zones are established for every ________.
A. 15’ of longitude B. 15°of latitude C. 15°of longitude D. 15’ of latitude |
C. 15°of longitude
(LP 15, p. 19) |
|
|
512. A pilot would most likely be issued a STAR from a/an ________ controller.
A. tower B. approach C. ground D. en route |
D. en route
(LP 19, p. 32) |
|
|
513. On an En Route High Altitude Chart, all NAVAIDs shown are ________ class, unless otherwise identified.
A. Low B. High C. Terminal D. Regional |
B. High
(LP 18, p. 40) |
|
|
514. Airports are listed in the A/FD in which order?
A. largest to smallest B. state, airport, city C. city, airport, state D. state, city, airport |
D. state, city, airport
(LP 17, p. 42) |
|
|
515. A VHF Omni-Directional Range (VOR) has how many usable magnetic radials?
A. 90 B. 180 C. 360 D. 350 |
C. 360
(LP 16, p. 6) |
|
|
516. Which formula is correct when D = distance, S = speed, and T = time?
A. S=DxT B. D=S÷T C. D=SxT D. T=S x D |
C. D=SxT
(LP 15, p. 26) |
|
|
517. One minute of latitude is equal to ___________ any place on the Earth’s surface.
A. 60 nautical miles (NM) B. 60 statute miles (SM) C. 1 nautical mile (NM) D. 1 statute mile (SM) |
C. 1 nautical mile (NM)
(LP 15, p. 9) |
|
|
518. Which instrument would be affected if the pitot tube became clogged?
A. Altimeter B. Vertical speed indicator C. Heading indicator D. Airspeed indicator |
D. Airspeed indicator
(LP 21, p. 3) |
|
|
519. Runway Visual Range (RVR) is ________.
A. the horizontal distance a pilot will see down the runway from the approach end B. given in nautical miles C. located in the Airport Diagram section of the IAP D. used only for military aircraft |
A. the horizontal distance a pilot will see down the runway from the approach end
(LP 20, p. 31) |
|
|
520. World Aeronautical Charts are used primarily for which type of navigation?
A. RNAV B. Pilotage C. IFR D. Satellite |
B. Pilotage
(LP 17, p. 38) |
|
|
521. Generally, ATS routes defined from 1,200 feet AGL to, but not including 18,000 feet MSL describe ________.
A. victor routes B. jet routes C. Q routes D. MTRs |
A. victor routes
(LP 16, p. 33) |
|
|
522. An aircraft travels at 450 knots for 2 hours, 30 minutes. How many nautical miles has the aircraft traveled?
A. 1,050 miles B. 1,075 miles C. 1,100 miles D. 1,125 miles |
D. 1,125 miles
(LP 15, pp. 25 thru 27) |
|
|
523. Lines connecting points of equal difference between true and magnetic north are called ________ lines.
A. agonic B. isochronous C. isogonic D. isobaric |
C. isogonic
(LP 15, p. 41) |
|
|
524. The phrase “MAYDAY” describes a/an ________ situation.
A. potential B. composed C. distress D. urgency |
C. distress (LP 22, p. 4)
|
|
|
525. The pilot of an aircraft which has been hijacked can be expected to squawk Code ________.
A. 7300 B. 7500 C. 7600 D. 7700 |
7500
(LP 22, p. 17) |
|
|
526. An aircraft on a VFR flight plan is first considered ________ 30 minutes after its ETA.
|
overdue
(LP 23, p. 9) |
|
|
527. When a parcel of air has all the water vapor it can hold, it is ________.
|
saturated
(LP 24, p. 10) |
|
|
528. A warm, moist air mass moving over a ________ surface often produces ________, poor visibility, stratiform clouds, fog, and drizzle.
|
cold, smooth air
(LP 24, p. 24) |
|
|
529. What type of precipitation occurs when the temperature remains below freezing throughout the entire depth of the atmosphere?
|
Snow
(LP 24, p. 32) |
|
|
530. Which effect will an airplane experience when taking off with a tailwind?
|
A longer take off roll is required.
(LP 25, p. 8) |
|
|
531. Ice becomes perceptible. Rate of accumulation is slightly greater than sublimation. Deicing/anti-icing equipment is NOT utilized unless encountered for an extended period of time (over 1 hour). What type of ice is being described?
|
Trace
(LP 25, p. 39) |
|
|
532. In a METAR/SPECI Wind Group, wind speed is referenced to which unit of measure?
|
Knots
(LP 26, p. 19) |
|
|
533. +TSRAGR
|
“Thunderstorm, heavy rain, hail”
(LP 26, pp. 30, 31) |
|
|
534. Which in-flight advisory would provide a forecast of occasionally severe turbulence over Colorado?
|
SIGMET
(LP 27, p. 26) |
|
|
535. What product is for ATC use to alert pilots of existing or anticipated adverse weather conditions within the next two hours?
|
CWA
(LP 27, p. 41) |
|
|
536. A report of meteorological conditions encountered by aircraft in flight is known as a/an ________.
|
PIREP
(LP 28, p. 3) |
|
|
537. Which is not a reportable intensity of icing?
|
Heavy
(LP 28, p. 17) |
|
|
538. Who has the final responsibility for the course of action to be followed in an emergency?
|
Pilot
(LP 22, p. 14) |
|
|
539. The effective utilization of all available search and rescue facilities, including Federal, state, and local efforts, is described by the ________.
|
National Search and Rescue Plan
(LP 23, p. 2) |
|
|
540. The average vertical depth of this layer of the atmosphere is 36,000 feet, but varies from about 65,000 feet at the equator to 20,000 feet at the poles.
|
Troposphere
(LP 24, p. 5) |
|
|
541. What cloud type indicates thermal lift of air, and whose tops can reach over 60,000 feet?
|
Cumuliform
(LP 24, p. 17) |
|
|
542. Which front moves in such a way that colder air replaces warmer air?
|
Cold front
(LP 24, p. 25) |
|
|
543. What National Weather Service office provides meteorological forecasts, and advice to ARTCCs and other FAA facilities regarding weather impact on their missions?
|
Center Weather Service Unit (CWSU)
(LP 24, p. 41) |
|
|
544. IFR weather is primarily a hazard ________.
|
during takeoff and landing
(LP 25, p. 13) |
|
|
545. What can produce almost every weather hazard?
|
Thunderstorm
(LP 25, p. 45) |
|
|
546. Which of the following METAR code groups designate a ceiling?
|
VV006
(LP 26, p. 37) |
|
|
547. Based on the following METAR, the temperature is _________. KOKC 181456Z 23015G28KT 10SM FEW025 SCT040 BKN150 OVC200 01/M01 A2981 RMK AO2 SLP096
|
1°C
(LP 26, p. 45) |
|
|
548. Convective SIGMETs are valid for ________ hours and are used to report convective weather significant to the safety of all aircraft.
|
two
(LP 27, p. 30-31) |
|
|
549. A Meteorological Impact Statement (MIS) is ________.
|
A. an unscheduled discussion product that summarizes anticipated weather conditions with potential impact on air traffic flow control and flight operations in an ARTCC’s area of responsibility
(LP 27, p. 45) |
|
|
550. Air Traffic Facilities are required to solicit PIREPs when ________ is reported or forecasted.
|
Light icing
(LP 28, p. 6) |
|
|
551. Which of the following is not one of the minimum information requirements for handling an emergency?
|
Aircraft color
(LP 22, p. 9) |
|
|
552. The Rescue Coordination Center is operated by the ________.
|
military
(LP 23, p. 6) |
|
|
553. At what rate does temperature decrease with height (lapse rate) in the standard atmosphere?
|
2°c/1,000 feet
(LP 24, p. 6) |
|
|
554. Which statement about a pressure system and cloud creation is TRUE?
|
Air in a low pressure system will rise, cool, and create clouds
(LP 24, p. 19) |
|
|
555. The three necessary ingredients for precipitation formation are ________, ________, and ________.
|
water vapor, lift, a growth process
(LP 24, p. 31) |
|
|
556. Which condition is responsible for the most weather-related aviation accidents?
|
Adverse wind
(LP 25, p. 4) |
|
|
557. Turbulence that causes large, abrupt changes in altitude and/or attitude describes ________ turbulence.
|
severe
(LP 25, p. 29) |
|
|
558. What is an unscheduled report that is taken when certain criteria have been observed?
|
SPECI
(LP 26, p. 5) |
|
|
559. M1/4SM FG
|
“Visibility less than one-quarter, fog”
(LP 26, p. 23) |
|
|
560. TAFs are used by air traffic controllers to anticipate weather changes that will affect aircraft operations ________.
|
at specified terminals
(LP 27, p. 3) |
|
|
561. Which in-flight advisory would provide a forecast of moderate icing over New York and Pennsylvania?
|
AIRMET Zulu
(LP 27, p. 35) |
|
|
562. A computer generated forecast of wind direction, wind speed, and temperature at selected times, altitudes, and locations is a(n) _________ forecast.
|
wind and temperature aloft
(LP 27, p. 50) |
|
|
563. Each PIREP reporting turbulence must include the ________.
|
turbulence intensity
(LP 28, p. 7) |
|
|
564. Positive control is the ________ of all air traffic within designated airspace by ATC.
|
separation
(7110.65; LP 1, p. 15) |
|
|
565. The first duty priority of an air traffic controller is ________.
|
separating traffic and issuing safety alerts
(7110.65; LP 1, p. 16) |
|
|
566. Rotating airport beacons flashing white and green at regular intervals identifies what type of airport?
|
Lighted land airport
(AIM; LP 3, p. 29) |
|
|
567. What type of separation is defined as the spacing of aircraft at the same altitude by a minimum distance expressed in units of time or miles?
|
Longitudinal
(7110.65; LP 4, p. 15) |
|
|
568. Assigning departing aircraft headings which diverge by at least 45 degrees is an example of ________ separation.
|
lateral
(7110.65; LP 4, p. 14) |
|
|
569. This NOTAM consists of information that requires wide dissemination and pertains to En route navigational aids, airports listed in the Airport Facility Directory (AFD), facilities and services.
|
NOTAM D
(7930.2; LP 5, p. 6) |
|
|
570. Which of the following is not a component of a secondary radar system?
|
Receiver
(ETM 12-0-1; LP 6, p. 23) |
|
|
571. Which of the following is a disadvantage of a secondary radar system?
|
Only displays aircraft with transponders
(ETM 12-0-1; LP 6, p. 30) |
|
|
572. This document provides the aviation community with basic flight information and ATC procedures for use in the United States National Airspace System (NAS).
|
Aeronautical Information Manual
(AIM) (AIM; LP 7, p. 18) |
|
|
573. Which airspace extends from the surface to 10,000 feet MSL surrounding the nation’s busiest airports?
|
Class B
(AIM; LP 9, p. 6) |
|
|
574. ATC specialists in Terminal/Center, age 39 and below, shall be scheduled for medical examinations by facility managers _________.
|
every two years
(FAR 67; LP 10, p. 41) |
|
|
575. A pilot flying VFR must stay at least 2,000 feet laterally from the clouds in classes ________ and ________ airspace.
|
C;D
(FAR 91; LP 11, p. 15) |
|
|
576. A pilot must use supplemental oxygen for the entire flight when flying at altitudes ________.
|
above 14,000 MSL
(FAR 91; LP 11, p. 48) |
|
|
577. Relative wind flows in a direction __________ and __________ the direction of flight.
|
parallel with; opposite to
(8083-25; LP 12, p. 6) |
|
|
578. When ________ and ________ are in equilibrium, the aircraft neither gains nor loses altitude.
|
lift; weight
(8083-25; LP 12, p. 14) |
|
|
579. What type of icing is an aircraft likely to encounter when flying in temperatures above freezing?
|
Carburetor icing
(8083-25; LP 12, p. 51) |
|
|
580. The definition of “wake turbulence” includes a number of phenomenon affecting flight safety. Which of the following choices is not included in the definition?
|
Mach buffet
(7110.65; LP 13, p. 3) |
|
|
581. A hovering helicopter will generate a high speed outward vortex to a distance of approximately ________ times the diameter of the rotor.
|
3
(8083-21; LP 13, p. 21) |
|
|
582. An aircraft with a certificated takeoff weight of more than 41,000 lbs. up to but not including 300,000 lbs. is classified as ________.
|
large
(7110.65; LP 14, p. 9) |
|
|
583. All helicopters are classified as ________.
|
category I
(ATG-2; LP 14, p. 4) |
|

584. The aircraft pictured above is a ________.
|
MD11
(ATG-2; LP 14, p. 65) |
|
|
585. 2 PM on a 24-hour clock equals _________.
|
1400
(FAA-H-8083-25; LP 15, p. 19) |
|
|
586. An aircrafts TAS is significantly higher than its IAS ________.
|
at high altitudes
(FAA-H-8083-25, LP 15, p. 38) |
|
|
587. VORs are classed according to operational use. There are three classes. Which one of the selections below is not one of those classes?
|
UH (Ultra high altitude)
(FAA-H-8083-25; LP 16 p. 5) |
|
|
588. Class B operating rules can be found on the back of _______.
|
VFR Terminal Area Charts (TAC legend; LP 17, p. 34)
|
|
|
589. The primary purpose of an IFR Area Chart is to furnish ________.
|
terminal data for IFR flights in congested areas
(AIM; LP 18, p. 45) |
|
|
590. Which DP is always printed graphically and must be assigned by ATC?
|
SID
(7110.65; LP 19, p. 12) |
|
|
591. On the profile view of a non-precision instrument approach, the Maltese Cross depicts the __________.
|
Final Approach Fix (FAF) (8083-15; LP 20, p. 27)
|
|
|
592. The height of obstructions shown on the planview and airport diagram section of an IAP are always given in ________.
|
MSL
(AIM; LP 20, p. 8) |
|
|
593. Symptoms of hypoxia include all of the following except ___________.
|
increased alertness
(FAA-H-8083-25; LP 21, p. 45) |
|
|
594. Which of the following refers to a condition of being threatened by serious and/or imminent danger and requiring immediate assistance?
|
Distress
(7110.65; LP 22, p. 4) |
|
|
595. A pilot of an aircraft experiencing radio failure can be expected to squawk ________.
|
7600
(7100.65; LP 22, p. 16) |
|
|
596. What cloud type indicates thermal lift of air, and whose tops can reach over 60,000 feet?
|
Cumuliform
(NWS Jetstream -Online School for Weather; LP 24) |
|
|
597. What National Weather Service office provides meteorological forecasts, and advice to ARTCCs and other FAA facilities regarding weather impact on their missions?
|
Center Weather Service Unit (CWSU)
(NWS Jetstream -Online School for Weather; LP 24, p. 41) |
|
|
598. Which of the following is NOT true regarding fog?
|
Fog forms slowly, allowing pilots to avoid this hazard (FMH1, p. A-4; LP 25, p. 15)
|
|
|
599. Which of the following METAR code groups does NOT designate a ceiling?
|
SKC
(AC 00-45; LP 26, p. 35) |
|
|
600. “A scheduled report transmitted at fixed intervals” describes a ________.
|
METAR
(FMH1; LP 26, p. 4) |
|
|
601. What type of forecast is issued when specific conditions are affecting or are expected to affect an area of 602. At least 3,000 square miles or an area judged to have a significant impact on the safety of aircraft operations?
|
SIGMET
(AC 00-45; LP 27, p. 26) |
|
|
602. The message type “UUA” indicates that the PIREP falls under what classification?
|
Urgent PIREP
(7110.10; LP 28, p. 3) |
|
|
603. Each PIREP must include the altitude, location, time, and ________.
|
aircraft type
(7110.10; LP 28, p. 7) |
|
|
604. An action taken to transfer radar identification of an aircraft from one controller to another controller when the aircraft will enter the receiving controller’s airspace and radio communications will be transferred is called a(n) ________.
|
handoff
(7110.66; LP 29, p. 51) |
|
|
605. How is a time of 6:42 a.m. stated as UTC time?
|
ZERO SIX FOUR TWO ZULU (7110.65; LP 29, p. 12)
|
|
|
606. Which of the following represents, in order, the steps of the position relief briefing?
|
Preview position, verbal briefing, assumption of position responsibility, position review
(7110.65; LP 29 p. 61) |
|
|
607. What is the proper procedure for deleting any umwanted or unused altitudes?
|
Write an X through it
(7110.65; LP 30, p. 9) |
|
|
608. On terminal flight progress strips, blocks 10 -18 are ________.
|
specified by facility directive (7110.65; LP 30, p. 18)
|
|
|
609. The pilot-in-command of an aircraft may only deviate from the provisions of an air traffic clearance when a(n) ________ occurs, or a(n) ________ is obtained.
|
emergency; amended clearance
(7110.65; LP 31, p. 5) |
|
|
610. The terminal flight progress strip has ________ use(s) in the terminal option.
|
three
(7110.65; LP 30, p. 17) |
|
|
611. Use prefixes when relaying ________, ________, or ________ through non-ATC facilities.
|
clearances, information, requests
(7110.65; LP 31, p. 10) |
|
|
612. Taxi clearances are instructions provided by ATC for the route aircraft/vehicles are to follow while on the ________ of an airport.
A. apron areas B. movement and non-movement areas C. movement areas D. non-movement areas |
C. movement areas
(7110.65; LP 31, p. 17) |
|
|
613. The ________ position in the ATC terminal option is normally responsible for issuing control instructions to aircraft and vehicles operating in the airport movement area.
A. Local Control B. Ground Control C. Clearance Delivery D. Flight Data |
B. Ground Control
(7110.65; LP 1, p. 34) |
|
|
614. Which is not a function of the Radar position in the ARTCC?
A. Maintain direct communication with aircraft B. Scan radar display C. Make weather observations D. Ensure separation |
C. Make weather observations
(7110.65; LP 1, p. 44) |
|
|
615. An Automated Flight Service Station has the primary function of providing ________.
A. pilot briefings and receiving and processing flight plans B. air traffic control services to aircraft operating in the vicinity of an airport or on the movement area C. advisory service to VFR aircraft and control service to IFR aircraft D. control service to aircraft on an IFR flight plan operating outside of controlled airspace |
A. pilot briefings and receiving and processing flight plans (7110.10; LP 1, p.24)
|
|
|
616. The correct designation for a runway with a magnetic heading of 009 degrees is runway ________.
A. 36 B. 1 C. 01 D. 10 |
B. 1
(AIM; LP 3, p. 5) |
|
|
617. Minimum radar separation between two aircraft at FL 200 in ARTCC airspace is ________ miles.
A. 3 B. 5 C. 10 D. 20 |
B. 5
(7110.65; LP 4, p. 29) |
|
|
618. When applying vertical separation, RVSM status of an aircraft is a consideration between which altitudes?
A. FL 180, up to and including FL 450 B. FL 450, up to and including FL 600 C. FL 290, up to and including FL 410 D. FL 180, up to and including FL 290 |
C. FL 290, up to and including FL 410
(7110.65; LP 4, p. 11) |
|
|
619. A/An _______ is a predetermined maneuver which keeps an aircraft within a specified airspace while awaiting further clearance from air traffic control.
A. holding procedure B. approach procedure C. procedure turn D. auto-rotation |
A. holding procedure (7110.65; LP 4, p. 42)
|
|
|
620. The two subsystems for disseminating aeronautical information are ________.
A. AIS and NOTAMs B. NFDC and NOTAMs C. NAS and NFDC D. AIS and AFSS |
A. AIS and NOTAMs
(7930.2; LP 5, p. 3) |
|
|
621. The primary radar display depicts the ________ and ________ of objects that reflect radio energy.
A. position; altitude B. position; movement C. altitude; speed D. movement; speed |
B. position; movement
(ETM 12-0-1; LP 6, p. 8) |
|
|
622. Which of the following is an example of a temporary directive, e.g., a notice that needs to be distributed immediately?
A. Supplements B. LOA C. GENOT D. GETS |
C. GENOT
(1320.1; LP 7, p. 16) |
|
|
623. Letters of Agreement (LOA) are for ________ use and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are for ________ use.
A. intrafacility; extrafacility B. interfacility; intrafacility C. extrafacility; jurisdictional D. intrafacility; interfacility |
B. interfacility; intrafacility (7210.3; LP 8, p. 2 and 9)
|
|
|
624. To be eligible for an _________, an individual must be at least 18 years of age, of good moral character, able to read, write, and understand the English language, speak English without an accent or impediment, and hold a valid second class medical certificate.
A. ATC airspace operator license B. ATC airspace specialist certificate C. ATC tower operator certificate D. ATC tower specialist license |
C. ATC tower operator certificate
(FAR, 65; LP 10, p. 38) |
|
|
625. Which of the following Right-of-Way rules is not correct?
A. Converging aircraft, aircraft on the left has right-of-way B. Overtaking, aircraft being overtaken has right-of-way C. Head-on, both aircraft give way to the right D. Landing, aircraft on final approach has right-of-way |
A. Converging aircraft, aircraft on the left has right-of-way (FAR 91; LP 10, p. 16)
|
|
|
626. Filing a VFR flight plan is ________.
A. optional, but strongly encouraged B. mandatory when penetrating a Military Operations Area C. only necessary when weather conditions are below VFR minimums D. only necessary for search and rescue missions |
A. optional, but strongly encouraged
(AIM; LP 11, p. 6) |
|
|
627. At an airport where takeoff minimums are not prescribed (revenue flights only), an aircraft with two engines or less may depart when there is at least ___________ statute mile(s) visibility.
A. 3 B. 2 C. 1 D. ½ |
C. 1
(FAR 91; LP 11, p. 31, 28) |
|
|
628. If a pilot adjusts the pitch and yaw, the aircraft is moving along the ________ and __________ axes.
A. longitudinal; vertical B. lateral; vertical C. longitudinal; lateral D. lateral; horizontal |
B. lateral; vertical
(8083-25; LP 12, p. 24) |
|
|
629. According to Bernoulli’s principle, lift is a result of ___________ differential.
A. airspeed B. pressure C. temperature D. reaction |
B. pressure
(8083-25; LP 12, p. 4) |
|
|
630. The blades of a helicopter are shaped like ________ and act as ________.
A. airfoils; ailerons B. ailerons; elevators C. airfoils; wings D. ailerons; wings |
C. airfoils; wings
(8083-21; LP 12, p. 39) |
|
|
631. The _______ of the aircraft is the greatest factor that affects the intensity of wake turbulence.
A. speed B. shape of the wing C. vortex strength D. weight |
D. weight
(AIM; LP 13, p. 5) |
|
|
632. Vortices are generated at the moment an aircraft begins to ________.
A. taxi B. leave the ground C. slow on approach D. touchdown on the runway |
B. leave the ground
(8083-25; LP 13, p. 11) |
|
|
633. Another name for thrust stream turbulence is ________.
A. turbine wash B. burner blast C. jet fuel burn D. jet blast |
D. jet blast
(AIM; LP 13, p. 24) |
|
|
634. For a military aircraft, the first letter(s) of the designator identifies the aircraft’s ________.
A. manufacturer B. model C. service branch D. mission |
D. mission
(7110.65; LP 14, p. 12) |
|
|
635. Category III aircraft generally climb at what rate?
A. 500’ – 1000’ per minute B. 1000’ – 2000’ per minute C. 2000’ – 4000’ per minute D. Greater than 4000’ per minute. |
C. 2000’ – 4000’ per minute (7110.65; LP 14, p. 6)
|
|
|
636. 100 nautical miles equals ____________ statute miles.
A. 130 B. 95 C. 87 D. 115 |
D. 115
(FAA-H-8083-25; LP 15, p. 15) |
|
|
637. An aircraft travels 300 nautical miles over the ground in three hours while experiencing a tailwind of 25 knots. The aircraft’s ground speed is ________ knots.
A. 150 B. 125 C. 100 D. 75 |
C. 100
(FAA-H-8083-25; LP 15, p. 29) |
|
|
638. The navigational method based solely on computing air speed, course, wind, ground speed, and elapsed time is ________.
A. radio navigation B. RNAV navigation C. FMS D. dead reckoning |
D. dead reckoning
(FAA-H-8083-25; LP 15; p. 46) |
|
|
639. Generally, ATS routes defined from 1,200 feet AGL to 18,000 feet MSL describe ________.
A. victor routes B. jet routes C. Q routes D. MTRs |
A. victor routes
(7110.65 & AIM; LP 16, p. 33) |
|
|
640. How often is the World Aeronautical Chart published?
A. every 56 days B. every 6 months C. every 12 months D. every 24 months |
C. every 12 months
(7110.65 & AIM; LP 17, p. 38) |
|
|
641. En Route Low Altitude Charts are published every ________.
A. 56 days B. 112 days C. 3 months D. 6 months |
A. 56 days
(AIM; LP 18, p. 3) |
|
|
642. STAR is not designed to ________.
A. expedite ATC arrival procedures. B. funnel arrival traffic into one-way corridors and reduce coordination between ATC facilities. C. provide guidance to a fix in the terminal area. D. ensure appropriate separation minima between aircraft. |
D. ensure appropriate separation minima between aircraft.
(FAA-H-8261-1; LP 19, p. 30) |
|
|
643. Of the types of instrument approaches listed, which one is a precision approach?
A. VOR B. NDB C. ILS D. TACAN |
C. ILS
(AIM; LP 20, p. 8) |
|
|
644. Which instrument does not depend on 'rigidity in space' for its operation?
A. heading indicator B. attitude indicator C. magnetic compass D. turn coordinator |
C. magnetic compass
(FAA-H-8083-25; LP 21, p. 16) |
|
|
645. Which of the following is assigned by ATC to a single aircraft and used for radar identification and flight tracking?
A. non-discrete codes B. discrete codes C. mode C D. aircraft identification |
B. discrete codes
(7110.65; LP 21, p 34) |
|
|
646. Which of the following is not one of the minimum information requirements for handling an emergency?
A. Nature of the emergency B. Aircraft identification and type C. Aircraft color D. Pilot’s desires |
C. Aircraft color
(7110.65; LP 22, p. 9) |
|
|
647. Which of the following is an interagency agreement which provides for the effective use of all available facilities in all types of search and rescue missions?
A. Letter of Understanding (LOU) B. National Search and Rescue Plan C. Letters of Agreement (LOA) D. Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) |
B. National Search and Rescue Plan
(7110.65; LP 23, p. 3) |
|
|
648. The temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure and constant water vapor content in order for saturation to occur is ________.
A. Relative humidity B. dew point C. lapse rate D. inversion |
B. dew point
(AC 00-6; LP 24, p. 10) |
|
|
649. What type of precipitation occurs when the temperature remains below freezing throughout the entire depth of the atmosphere?
A. Ice B. Snow C. Ice pellets D. Freezing rain |
B. Snow
(NWS Jetstream -Online School for Weather; LP 24, p. 32) |
|
|
650. The dissipating stage of a thunderstorm begins when ___________ are predominant.
A. downdrafts B. updrafts C. hail stones D. icing |
A. downdrafts
(AC 00-6; LP 25, p. 47) |
|
|
651. “Any wind more than 90 degrees to the longitudinal axis of the runway” defines a ________.
A. tailwind B. crosswind C. variable wind D. sudden wind shift |
A. tailwind
(AMS Glossary of Meteorology; LP 25, p. 8) |
|
|
652. The following METAR observation was taken at _______. KOKC 181456Z 23015G28KT 10SM FEW025 01/M01 A2981 RMK AO2 SLP096
A. 1815 local time B. 1456 UTC C. 1815 UTC D. 1456 local time |
B. 1456 UTC
(AC 00-6; LP 26, p. 14) |
|
|
653. Based on the following TAF, what is the earliest time thunderstorms and rain can be expected?
KOKC 051130Z 0512/0612 14008KT 5SM BR BKN030 TEMPO 0513/0516 1 1/2SM BR FM051600 16010KT P6SM SKC FM051900 20013G25KT 4SM SHRA OVC020 FM060500 20010G20KT 2SM SHRA BKN010 PROB30 0507 2SM TSRA OVC008CB FM060800 21015KT P6SM SCT040= A. 5th day at 1200Z B. 5th day at 1900Z C. 6th day at 1600Z D. 6th day at 0500Z |
D. 6th day at 0500Z
(AC 00-45; LP 27, p. 18) |
|
|
654. Which type of bulletin uses the alphabetic designators Sierra, Tango, or Zulu to indicate the type of condition being reported?
A. AIRMET B. MIS C. SIGMET D. WST |
A. AIRMET
(AC 00-45; LP 27, p. 35) |
|
|
655. Based on the following PIREP, the base of the second cloud layer is ________.
UA/OV KMRB-KPIT/TM 1600/FL100/TP BE55/SK BKN024-TOP032/BKN-OVC043-TOPUNKN/TA M12/IC LGT-MOD RIME 055-080 A. 4,300 feet MSL B. 3,200 feel AGL C. 4,300 feet AGL D. 2,400 feet MSL |
A. 4,300 feet MSL
(AC 00-45; LP 28. p. 12) |
|
|
656. How often are interphones and assigned frequencies to be monitored?
A. According to the level of traffic in the area B. At half-hour intervals C. Continuously D. Hourly |
C. Continuously
(7110.65; LP 29, p. 3) |
|
|
657. The correct ICAO phonetic spelling of the word “UNIT” is ________.
A. UNIFORM-NINER-INDIA-TANGO B. UNO-NOVEMBER-INDIGO-TANGO C. UNIFORM-NINER-INDIGO-TANGO D. UNIFORM-NOVEMBER-INDIA-TANGO |
D. UNIFORM-NOVEMBER-INDIA-TANGO
(7110.65; LP 29, p. 6) |
|
|
658. RNAV route 24 would be spoken as ________.
A. “QUEBEC TWO FOUR” B. “ROMEO TWENTY FOUR” C. “Q TWENTY FOUR” D. “RNAV TWO FOUR” |
C. “Q TWENTY FOUR” (7110.65; LP 29, p. 42)
|
|
|
659. What does the clearance abbreviation “PD” represent?
A. Cleared to depart from the fix B. Cleared to the airport C. Cleared to hold and instructions issued D. Cleared to climb/descend at pilot’s discretion |
D. Cleared to climb/descend at pilot’s discretion
(7110.65; LP 30, p. 4) |
|
|
660. Which of the following statements is not true of flight progress strips?
A. They are considered legal documents. B. They are either handwritten or printed on special printers. C. They are used to post clearances required for ATC control. D. They are formatted the same for each air traffic option. |
D. They are formatted the same for each air traffic option.
(7110.65; LP 30, p. 13) |
|
|
661. An authorization by air traffic control for aircraft to proceed under specified traffic conditions within controlled airspace for the purpose of preventing collisions between known aircraft is called an ________.
A. ATC clearance B. ATC coordination C. ATC instruction D. ATC separation |
A. ATC clearance
(7110.65; LP 31, p. 3) |
|
|
662. There can be as many as________ air traffic clearance items; the ________ is issued first, and is always included in a clearance.
A. 6; clearance limit B. 9; route of flight C. 6; altitude data in order flown D. 9; aircraft identification |
D. 9; aircraft identification (7110.65; LP 31, p. 6)
|
|
|
663. There are ________ types of ATC prefixes used when relaying through a non-ATC facility.
A. two B. three C. four D. five |
B. three
(7110.65; LP 31, p. 10) |
|
|
664. Traffic management programs are one of several processes administered by the Air Traffic Control System Command Center (ATCSCC) to achieve optimum use of the ________ and minimize ________ without increasing controller workload.
A. airspace, accidents B. NAS, delays C. ATC System, accidents D. airports, delays |
B. NAS, delays
(7210.3 and 7110.65; LP 1, p. 52) |
|
|
665. The facility that provides radar approach and departure control services to aircraft operating in the vicinity of one of more airports in a terminal area is a ________.
A. TRACON B. ATCT C. ARTCC D. AFSS |
A. TRACON
(7110.65; LP 1, p. 37) |
|
|
666. Which of the following is not one of the uses of a movement area?
A. Air taxiing B. Hover taxiing C. Loading passengers D. Takeoff and landing of aircraft |
C. Loading passengers (7110.65; LP 3, p. 2)
|
|
|
667. Runway separation is applied by ________ controllers.
A. Air Route Traffic Control Center (ARTCC) B. Air Traffic Control Tower (ATCT) C. Terminal Radar Approach Control (TRACON) D. Automated Flight Service Station (AFSS) |
B. Air Traffic Control Tower (ATCT)
(7110.65; LP 4, p. 37) |
|
|
668. Controllers may use visual separation ________.
A. up to, but not including, FL180 B. at FL180 and below C. up to and including 18,000 feet MSL D. up to but not including 18,000 feet AGL |
A. up to, but not including, FL180
(7110.65; LP 4, p. 35) |
|
|
669. The office/person responsible for reporting the conditions of the landing area of an airport is the ______.
A. Air Traffic Manager B. airport manager/operator C. tie-in AFSS D. local controller |
B. airport manager/operator (7930.2; LP 5, p. 15)
|
|
|
670. In FAA Order 7110.65, the word used to specify that a procedure is mandatory is ________.
A. shall B. may C. should D. will |
A. shall
(7110.65; LP 7, p. 21) |
|
|
671. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a Prohibited Area?
A. Established around residential areas for noise abatement B. Begins at the surface of the earth and extends upward to a defined altitude C. Established for security or other reasons associated with the national welfare D. Identified by the letter “P” plus a number |
A. Established around residential areas for noise abatement
(FAR 73; LP 9, p.17) |
|
|
672. A ________is specified information, relating to the intended flight of an aircraft.
A. ATC Clearance B. Flight Plan C. Supplement D. Notice |
B. Flight Plan
(FAR 1, LP 10, p. 7) |
|
|
673. When air density decreases what occurs?
A. Rate of climb is faster and landing speed will be faster B. Landing speed is faster and engine power output will be decreased C. Takeoff run is longer and the engine produces more power D. Rate of climb is slower and takeoff run is shorter |
B. Landing speed is faster and engine power output will be decreased
(8083-25; LP 12, p. 21) |
|
|
674. Which of the following is not a principal airfoil?
A. Wing B. Fuselage C. Propeller D. Horizontal tail surfaces |
B. Fuselage
(8083-25; LP 12, p. 7) |
|
|
675. Regarding helicopters, the cyclic controls the _______ of the rotor blades and the collective controls the _________.
A. pitch; tilt B. speed; pitch C. tilt; pitch D. angle; speed |
C. tilt; pitch
(8083-21; LP 12, p. 40) |
|
|
676. Counter control is most effective and roll is minimal when the wingspan and the ailerons extend beyond the ________ of the vortex.
A. vertical limits B. outer edges C. sink rate D. induced roll |
B. outer edges
(AIM; LP 13, p. 19) |
|
|
677. What are the three basic types of landing gear?
A. straight; swept; delta B. tandem; fixed; conventional C. tricycle; conventional; tandem D. forward; mid; conventional |
C. tricycle; conventional; tandem
(ATG-2; LP 14, p. 29) |
|
|
678. One minute of latitude is equal to ___________ any place on the Earth’s surface.
A. 5000 feet B. ½ nautical mile C. 1 nautical mile (NM) D. 1 statute mile (SM) |
C. 1 nautical mile (NM)
(FAA-H-8083-25; LP 15, p. 7) |
|
|
679. A line of equal magnetic variation is called a/an __________ line.
A. isogonic B. agonic C. magnetic D. longitude |
A. isogonic
(FAA-H-8083-25; LP 15, p. 42) |
|
|
680. Which of the following is not a characteristic of the Global Positioning System (GPS)?
A. The system is affected by weather.) B. The system provides satellite-based radio navigation. C. The system provides highly accurate position information. D. The system provides velocity information. |
A. The system is affected by weather.
(AIM; LP 16, p. 26) |
|
|
681. Sectional Aeronautical Charts are designed to be used for ________ navigation of ________ speed aircraft.
A. instrument; slow/medium B. visual; slow/medium C. required prior to entering controlled airspace D. required prior to departure from within controlled airspace. |
B. visual; slow/medium
(AIM; LP 17, p. 3) |
|
|
682. Which document would you use to determine type of fuel available at an airport?
A. US Terminal Procedures Charts B. Airport/Facility Directory C. Sectional Chart D. IFR Area Chart |
B. Airport/Facility Directory (7110.65 & AIM; LP 17, p. 42)
|
|
|
683. On an En Route High Altitude Chart, all NAVAIDs shown are ________ class, unless otherwise identified.
A. L B. H C. T D. R |
B. H
(En Route Charts; LP 18, p. 40) |
|
|
684. A localizer, a glide slope, and marker beacons are basic components of a/an ________ approach.
A. ILS B. nonprecision C. no gyro D. TACAN |
A. ILS
(7110.65; LP 20, p. 9) |
|
|
685. The purpose of TCAS is to _______.
A. provide standard separation B. prevent a collision C. replace ATC D. ensure terrain avoidance |
B. prevent a collision
(FAR Part 1, 91, 121 and 135; LP 21, p. 40) |
|
|
686. The universal emergency frequencies are ________.
A. VHF 121.0; VHF 243.5 B. VHF 122.5, UHF 245.0 C. VHF 121.5, UHF 243.0 D. VHF 245.0, UHF 122.5 |
C. VHF 121.5, UHF 243.0 (7110.65; LP 22, p. 5)
|
|
|
687. The Coast Guard and Air Force conduct ________ operations through the Rescue Coordination Center.
A. airborne search and rescue B. sheriffs department search and rescue C. telephonic search and rescue D. physical search and rescue |
D. physical search and rescue
(7110.65; LP 23, p. 7) |
|
|
688. Precipitation formation requires water vapor, lift, and ________.
A. a growth process B. frontal pressure C. a stable temperature D. a steep slope |
A. a growth process
(NWS Jetstream -Online School for Weather; LP 24, p. 31) |
|
|
689. Which of the following is a characteristic of a temperature inversion?
A. High winds B. Decreased temperatures with increased altitude C. Increased temperatures with increased altitude p. 27) D. Clear air turbulence |
C. Increased temperatures with increased altitude
(AC 00-6; LP 25, p. 27) |
|
|
690. Turbulence that causes large, abrupt changes in altitude and/or attitude describes ________ turbulence.
A. moderate B. severe C. intense D. extreme |
B. severe
(AC 00-45; LP 25, p. 29) |
|
|
691. What can produce almost every weather hazard?
A. Hurricane B. Thunderstorm C. Tornado D. Turbulence |
B. Thunderstorm
(AMS Glossary of Meteorology; LP 25, p. 45) |
|
|
692. Gusty wind is coded as a ________ in the wind group of a METAR.
A. B B. W C. T D. G |
D. G
(AC 00-45; LP 26, p. 19) |
|
|
693. What forecast product provides a plain language, non-technical description of weather expected to occur over an extended period ranging from several hours to two days?
A. AIRMET B. MIS C. SIGMET D. WST |
B. MIS
(AC 00-45; LP 27, p. 45) |
|
|
694. Air Traffic Facilities are required to solicit PIREPs when ________ is reported or forecasted.
A. Ceiling at or below 7,000 feet B. Light icing C. Light turbulence D. Visibility at or below 10 miles |
B. Light icing
(7110.10; LP 28, p. 6) |
|
|
695. According to the ICAO alphabet pronunciation table, in radiotelephony “C-H-A-P” should be pronounced ________.
A. CHARLIE HONEY ALFA PETER B. CHARLIE HOTEL ALFA PAPA C. CHARLIE HECTOR ALFA PAPA D. CHARLIE HOTEL ALFA PETER |
B. CHARLIE HOTEL ALFA PAPA
(7110.66; LP 29, p. 6) |
|
|
696. Which of the following is the correct way to state an altitude of 16,000 feet?
A. SIXTEEN COMMA THOUSAND B. ONE SIX ZERO ZERO ZERO C. ONE SIX THOUSAND D. SIXTEEN ZERO HUNDRED |
C. ONE SIX THOUSAND (7110.65; LP 29, p. 10)
|
|
|
697. What does the abbreviation “RA” mean when used on a flight progress strip?
A. Radar Advisories (flight following) B. Resolution Advisory (pilot reported TCAS event) C. Runway Approach D. Radar Approach |
B. Resolution Advisory (pilot reported TCAS event) (7110.65; LP 30, p. 5)
|
|
|
698. Air traffic facilities, airports, NAVAIDS, FARs, and personnel are all components of the ________.
A. Traffic Management System B. National Airspace System C. Airway Facilities Service D. Federal Aviation Administration |
B. National Airspace System (7110.65; LP 1, p. 55)
|

