![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Quadrate |
Configuration in which a planet around the moon is 90 degrees from the sun as seen from the earth. |
|
|
Conjunction |
Astronomical configuration in which the position of the planet and the sun lie in the same part of the sky as seen from the earth |
|
|
Sidereal Period |
Time a celestial body takes to revolve around it's orbit relative to the stars moon = 27 1/3 days |
|
|
Synodic Period |
time a celestial object takes to return to the same position in the sky moon 29 1/2 days |
|
|
Superior Planets |
Planets with orbits beyond the earth
Saturn, Mars, Jupiter, Neptune, Uranus |
|
|
Inferior Planet |
Plants with orbits that lie between the Sun + Earth
Mercury + Venus + Sun + Earth |
|
|
Aphelion |
Earth's farthest distance from the sun
Ex. July 4th |
|
|
Perihelion |
Earth's closet approach to the sun
Ex. Jan. 4th |
|
|
Ecliptic |
The apparent path of the sun around the sky |
|
|
Revolution |
Orbital motion about a point located outside the orbiting body |
|
|
Roatation |
Motion around an axis through its center |
|
|
Celestial Equator |
Imaginary line around the sky directly above Earth's equator |
|
|
North Celestial Pole |
Point directly above Earth's North Pole Polaris |
|
|
Photometer |
A device used to measure brightness of stars |
|
|
Apparent Visual
Magnitude |
Brightness of star as seen by human eyes on Earth |
|
|
Asterism |
Named group of stars that are part of a constellation Ex. Big Dipper/ Little Dipper |
|
|
Constellation |
One of the stellar patterns identified by name associated with mythological gods, people, animals, or objects |
|
|
Angular Separation |
Way of measuring the distance between objects (or size) in the sky |
|
|
Precession |
Slow change in direction of Earth's axis of rotation |
|
|
Right Ascension (RA) |
Distance measured eastward along the celestial equator in hours (Longitude) |
|
|
Brightness = Magnitude |
Hipparchus (100 B.C.) Greek six classes of stars catalog first class star is the brightest Some Issues: 1. Translating catalog from Greek to Latin 2. fainter the star, the higher # will be 3. Some stars are close in Magnitude 4.Some stars are dimmer than his "six" class
|
|
|
Declination (Dec) |
Angular distance above or below the celestial equator (latitude) |
|
|
Apagee |
Moon farthest from the Earth |
|
|
Perigee |
Moon closest to the Earth |
|
|
Opposition |
configuration in which the Earth lies directly between a superior planet and the sun |
|
|
Elongation |
Apparent angular separation between an astronomical object + the sun as seen from the Earth |
|
|
Lunar Eclipse |
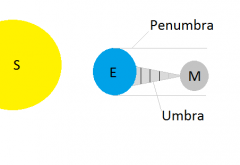
|
|
|
Solar Eclipse |
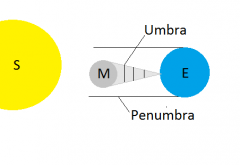
|

