![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
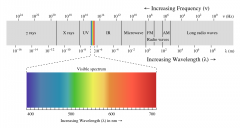
Electromagnetic Radiation |
Energy radiated in the form of a wave, resulting from the motion of electrical charges and the magnetic fields they produce. |
|
|
Electromagnetic Spectrum |
A continuum depicting the range of electromagnetic radiation, with the longest wave length at one end and the shortest at the other. |
|
|
Emission Spectrum |
A spectrum consisting of individual lines at characteristic wavelengths produced when light passes through an incandescent gas; a bright line spectrum. |
|
|
Continuous Spectrum |
A spectrum that contains all colors of wavelengths. |
|
|
Absorption Spectrum |
A continuous spectrum crossed by dark lines produced when light passes through a non-incandescent gas. |
|
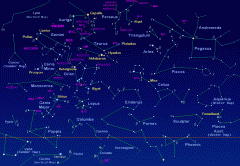
Constellation |
A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky. |
|
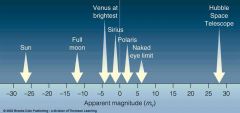
Apparent Magnitude |
The measure of how bright a star appears to be to an observer on earth. |
|

Astronomical Unit |
The average distance between Earth and the Sun, about 150 million kilometers. |
|

Light Year |
The distance that light travels in 1 year, about 9.5 trillion kilometers. |
|
|
Parsec |
A unit of measurement used to describe distances between celestial objects, equal to 3,258 light-years. |
|
Luminosity |
The brightness of a star. |
|
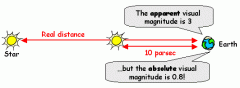
Absolute Magnitude |
The measure of how bright a star would be if it were located 10 parsecs from Earth. |
|

Cepheid Variable |
A variable star that brightens and dims regularly, or pulses and whose distance can be determined from its period of pulsation. |
|
Main Sequence |
A star that is at the point in its life cycle in which it is actively fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei; also, the band of the Hertzsprung-Russel diagram depicting stars. |
|

Giant Star |
A large star with great luminosity and a diameter 10 to 100 times greater than that of the Sun. |
|
Supergiants |
The most luminous massive stars, with diameters greater than 100 times the diameter of the Sun. |
|

White Dwarfs |
The remnant of a giant star that has lost its outer atmosphere; the glowing stellar core. |
|

Nebula |
A large cloud of gas and dust in space. |
|

Planetary Nebula |
A halo of gases that is formed by expelled layers of a star's atmosphere. |
|

Supernova |
The brilliant burst of light that follows the collapse of the iron core of a massive star. |
|

Neutron Star |
The super dense remains of a massive star that collapsed with enough force to push all of its electrons into the nuclei they orbit, resulting in a mass of neutrons. |
|

Pulsar |
A distant neutron star that emits rapid pulses of light and radio waves instead of steady radiation. |
|

Black Hole |
The final life stage of an extremely massive star, with a gravitational field so intense that not even light can escape. |
|
|
Galaxies |
A group of millions, or billions, of stars held together by gravity. |
|

Quasar |
A very distant, extremely luminous celestial object that scientists consider to be a type of active galactic nuclei. |
|

Big Bang Model |
The theory holding that the universe originated from the instant expansion of an extremely small agglomeration of matter of extremely high density and temperature. |

