![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
415 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Tetraethyl lead (TEL) is used principally as an additive that:
- absorbs moisture in gasoline - decreases viscosity of gasoline - has a low antiknock quality - increases gasoline antiknock quality - increases volatility of gasoline |
increases gasoline antiknock quality
|
|
|
Standard weights have been established for numerous items used in weight and balance computations. The standard weight for gasoline used in an airplane is:
- 6 lbs./US gal - 7.5 lbs./US gal - 8.35 lbs./US gal - 10 lbs./US gal - 15 lbs./US gal |
6 lbs./US gal
|
|
|
The pitot is an important component in measuring:
- airspeed - altitude - direction - fuel pressure - oil pressure |
airspeed
|
|
|
At a controlled airport, the light signal used by the tower to warn an aircraft in flight that the airport is unsafe and not to land is a(n):
- alternating red and green - flashing green - flashing red - steady green - steady red |
flashing red
|
|
|
Airport runway lights used to illuminate the runway are:
- blue - green - red - white - yellow |
white
|
|
|
Which type of rope is the strongest?
- cotton - hemp - manila - nylon - sisal |
nylon
|
|
|
An unlighted buoy, used to mark the LEFT side of a channel when facing inland, is called a:
- bell buoy - can buoy - nun buoy - spar buoy - whistle buoy |
can buoy
|
|
|
The International Date Line is located at:
- the 0 meridian - the 180th meridian - the celestial meridian - Greenwich, England - the prime meridian |
the 180th meridian
|
|
|
The Beaufort scale is generally used at sea in estimating:
- wind direction - wind speed - atmospheric pressure - relative humidity - water depth |
wind speed
|
|
|
When a person is reported overboard, the action to take first is to:
- bring the ship to a halt - track the person with a pair of binoculars - throw life buoys over at once - turn the ship around 180 degrees - reduce the ship's speed |
throw life buoys over at once
|
|
|
At sea, the time zones are generally bands of longitude:
- 7 1/2 degrees in width - 15 degrees in width - 24 degrees in width - 30 degrees in width - 45 degrees in width |
15 degrees in width
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT considered to be an "aid to navigation"?
- buoys - fog signals - lightships - loran - mountain peaks |
mountain peaks
|
|
|
Fog is generally formed when:
- cold air moves over cold water - cold air moves over hot water - colder air moves over warmer water - warm air moves over warm water - warmer air moves over colder water |
warmer air moves over colder water
|
|
|
An unlighted buoy, used to mark the RIGHT side of a channel when facing inland, is called a:
- bell buoy - can buoy - gong buoy - nun buoy - spar |
nun buoy
|
|
|
Ships or boats are steered by one or more rudders at the stern. The faster the vessel is moving:
- the GREATER the pressure against the rudder and the QUICKER the turning effect - the GREATER the pressure against the rudder and the SLOWER the turning effect - the LESS the pressure against the rudder and the QUICKER the turning effect - the LESS the pressure against the rudder and the SLOWER the turning effect - none of the above |
the GREATER the pressure against the rudder and the QUICKER the turning effect
|
|
|
What do the terms PORT, STARBOARD, FORE, and AFT mean?
- left, right, up, and down - right, left, above, and below - left, right, in front, and behind - right, left, behind, and in front - left, right, above, and beyond |
left, right, in front, and behind
|
|
|
On an aircraft carrier deck, what color shirt would a plane handler or tractor driver wear?
- green - blue - purple - yellow - red |
blue
|
|
|
The angle between the chord line of a wing or airfoil and the direction of the relative wind or airflow is called the:
- angle of pitch - degree of roll - angle of deflection - angle of attack - degree of yaw |
angle of attack
|
|
|
A wall or vertical surface within a ship is called a:
- bulkhead - bilgeway - gangway - keel - frame |
bulkhead
|
|
|
A conventional fixed-wing aircraft is controlled around its longitudinal axis by means of the:
- ailerons - elevators - rudder - trim tab - flaps |
ailerons
|
|
|
Two statute miles are equal to:
- 2.0 nautical miles - 1.74 nautical miles - 2.3 nautical miles - 2.3 knots - 2.0 knots |
1.74 nautical miles
|
|
|
The altimeter typically shows the height of the aircraft above a particular pressure level in:
- feet - hundreds of feet - thousands of feet - hundreds of meters - thousands of meters |
thousands of feet
|
|
|
The time of 7 PM would be expressed using the 24-hour clock as:
- 0700 - 1400 - 1700 - 1900 - none of the above |
1900
|
|
|
When a pilot pulls back on the control stick, the elevators will:
- extend - retract - move upward - move downward - assume a neutral position |
move upward
|
|
|
The order given to the helmsman to align the rudder with the keel of the ship is:
- "Ease the rudder." - "Rudder amidships." - "Steady as you go." - "Align your rudder." - "Steady the rudder." |
"Rudder amidships."
|
|
|
If one end of a runway was numbered 09, what number would designate the other end of the same runway?
- 90 - 27 - 18 - 10 - 36 |
27
|
|
|
The coordinates of latitude and longitude are used to express _______ in _______.
- direction, degrees - position, degrees - distance, time - location, meridians - heading, mils |
position, degrees
|
|
|
Which of the following engines could operate outside the earth's atmosphere?
- jet engine - turbofan engine - rocket engine - four-stroke diesel engine - two-stroke gasoline engine |
rocket engine
|
|
|
The bridge of a ship is where:
- all orders and commands affecting the ship originate - the lookout is assigned - the captain has his quarters - the ship's officers meet and consume their meals - the superstructure and the mast are joined together |
all orders and commands affecting the ship originate
|
|
|
Which of the following is a flight instrument?
- tachometer - fuel flow indicator - control column - trim tab - altimeter |
altimeter
|
|
|
The tailhook of a carrier-borne aircraft is used to:
- catch one of four arresting cables stretched across the deck - position the aircraft on the deck for launch - engage with the catapult T-bar before launch - stabilize the aircraft on the deck elevator - designate to the bridge when an aircraft is ready for launch |
catch one of four arresting cables stretched across the deck
|
|
|
VFR stands for:
- Velocity Flight Resistance - Venturi Flight Resonance - Vertical Flight Rules - Visual Flight Rules - Visual Front Resolution |
Visual Flight Rules
|
|
|
A nautical mile is approximately:
- 1760 yards - 5280 feet - 6076 feet - 7676 feet - 9082 feet |
6076 feet
|
|
|
The four aerodynamic forces acting on an aircraft in flight are:
- gravity, lift, thrust, and friction - lift, weight, thrust, and drag - velocity, drag, lift, and thrust - lift, weight, velocity, and drag - attitude, pitch, lift, and drag |
lift, weight, thrust, and drag
|
|
|
A flashing green air traffic control directed to an aircraft on the ground is a signal that the pilot:
- should radio the tower - should stop taxiing - should hold his position - has clearance to take off - has clearance to taxi |
has clearance to taxi
|
|
|
The Latin phrase "Semper Paratus" is the motto of the:
- U.S. Navy Submarine Service - U.S. Marine Corps - U.S. Marine Air Wing - U.S. Coast Guard - U.S. Air Force Air Combat Command |
U.S. Coast Guard
|
|
|
The empennage of an airplane is usually referred to as the:
- vertical stabilizer - horizontal stabilizer - main body - wing root - tail section |
tail section
|
|
|
On an aircraft carrier, the standard watch length for the Officer of the Deck is:
- two hours - four hours - six hours - eight hours - 12 hours |
four hours
|
|
|
________ are designed to help minimize a pilot's workload by aerodynamically assisting movement and position of the flight control surfaces to which they are attached.
- Labor-saving devices - Secondary flight controls - Trim systems - Spoilers - Adverse yaw deflectors |
Trim systems
|
|
|
The Carrier Strike Group could be employed in a variety of roles, such as:
- protection of commercial and/or military shipping - protection of a Marine amphibious force - establishing a naval presence in support of national interests - all of the above - none of the above |
all of the above
(i.e. protection of commercial and/or military shipping, protection of a Marine amphibious force, establishing a naval presence in support of national interests) |
|
|
Ailerons:
- extend from the midpoint of the wing outward toward the tip - create aerodynamic forces that cause the airplane to roll - move in opposite directions - all of the above - none of the above |
all of the above
(i.e. extend from the midpoint of the wing outward toward the tip, create aerodynamic forces that cause the airplane to roll, move in opposite directions) |
|
|
"Pri-Fly" is:
- the facility where US military aircraft are designed - the control tower for flight operations on an aircraft carrier - the two-aircraft section that has priority for launch from a carrier - where carrier aircraft get refueled and serviced - the prime runwar for takeoff from an airport |
the control tower for flight operations on an aircraft carrier
|
|
|
The two types of turn indicators used in an aircraft are:
- turn-and-slip indicator and attitude indicator - attitude indicator and automatic gyroscope - turn-and-slip indicator and turn coordinator - left and right indicators - turn coordinator and vertical speed indicator |
turn-and-slip indicator and turn coordinator
|
|
|
In the Navy, the term "Bravo Zulu" has come to traditionally mean:
- well done - two hours later than Greenwich Mean (Zulu) time - two hours earlier than Greenwich Mean (Zulu) time - beyond the zone - below the zone |
well done
|
|
|
When an airplane banks into a turn:
- the horizontal lift component acts PARALLEL to the earth's surface and opposes INERTIA - the horizontal lift component acts PARALLEL to the earth's surface and opposes GRAVITY - the horizontal lift component acts PERPENDICULAR to the earth's surface and opposes INERTIA - the horizontal lift component acts PERPENDICULAR to the earth's surface and opposes GRAVITY - none of the above |
the horizontal lift component acts PARALLEL to the earth's surface and opposes INERTIA
|
|
|
Which aircraft generally climbs at a steeper angle?
- Apache AH-64 - C-130 - Cessna 310 - F-4 Phantom |
F-4 Phantom
|
|
|
The first Digital-Fly-By-Wire (DFBW) was first tested in 1992 on a:
- F-4 - F-8 - A-10 - X-15 |
F-8
|
|
|
A rating of "AQ" means:
- Aviation Bombsight & Fire Control Mechanic - Aviation Quartermaster - Aviation Fire Control Technician - Aviation Support Equipment Technician |
Aviation Fire Control Technician
|
|
|
Pressure altitude is an altitude measured from the standard sea level pressure of:
- 29.89 - 29.92 - 29.97 - 29.99 |
29.92
|
|
|
What are the four cycles of an internal combustion aircraft engine?
- exhaust, compression, ignition, detonation - intake, compression, power, exhaust - intake, P-lead, power, ignition - ignition, compression, power, detonation |
intake, compression, power, exhaust
|
|
|
Which aircraft would always have the right of way?
- A Boeing 747 declaring an emergency - A hot air balloon - An experimental aircraft - The Goodyear Blimp |
A Boeing 747 declaring an emergency
|
|
|
Which navy built the first ships called "aviation vessels" solely for launching aerial vehicles?
- the Swedish Navy - the English Navy - the German Navy - the French Navy |
the Swedish Navy
|
|
|
On an aircraft carrier, what color shirts are the aviation fuels?
|
purple
(aka "Grapes") |
|
|
On an aircraft carrier, what color shirts are the plane handlers and tractor drivers?
|
blue
(also: aircraft elevator operators and messenger/phone talkers) |
|
|
On an aircraft carrier, what color shirts are air wing maintenance personnel and cargo-handling personnel?
|
green
(also: catapult and arresting gear crews, Ground Support Equipment (GSE) troubleshooters, hook runners, Photographer's Mates, helicopter landing signal enlisted personnel (LSE)) |
|
|
On an aircraft carrier, what color shirts are aircraft handling officers and plane directors?
|
yellow
(also: catapult/arresting gear officers) |
|
|
On an aircraft carrier, what color shirts are ordnancemen?
|
red
(also: Explosive Ordinance Disposal (EOD), crash and salvage crew) |
|
|
On an aircraft carrier, what color shirts are air wing plane captains and air wing line leading petty officers?
|
brown
|
|
|
On an aircraft carrier, what color shirts are medical personnel?
|
white
(also: air wing quality control personnel, squadron plane inspectors, Landing Signal Officer (LSO), Air Transfer Officers (ATO), Liquid Oxygen (LOX) crews, safety observers) |
|
|
All motions of an aircraft take place around:
- the landing gear - the longitudinal axis - the vertical axis - the center of gravity - the empennage |
the center of gravity
|
|
|
The term "abeam" refers to:
- anything aft of amidships - anything forward of amidships - 90 degrees or 270 degrees relative to one's own ship - directly ahead of or behind one's own ship - the depth of the water under the keel |
90 degrees or 270 degrees relative to one's own ship
|
|
|
A ________ would be an example of a deck fitting.
- bulkhead - marlinespike - cleat - watertight hatch - quarterdeck |
cleat
|
|
|
What three components make up the structure of an aircraft?
- nose, wings, and tail - cockpit, passenger compartment, and empennage - wings, fuselage, and empennage - bow, keel, and stern - flaps, stabilizer, and landing gear |
wings, fuselage, and empennage
|
|
|
A _______ is a horizontal cylinder usually turned by a motor upon which cable, rope, or chain is wound.
- windlass - forecastle - hand crank - jumbo sheet - half-stitch |
windlass
|
|
|
When discussing aircraft movement, what is yaw?
- side-to-side movement of the nose - up-and-down movement of the nose - rotational movement of the fuselage - using main-gear steering to move the aircraft while on the ground - oscillation during high-speed flight |
side-to-side movement of the nose
|
|
|
The term _______ refers to that part of the ship or island that is sheltered or away from the relative wind.
- downwind - windward - leeward - starboard - port |
leeward
|
|
|
When discussing aircraft movement, what is pitch?
- the side-to-side movement of the nose - an up or down movement of the nose - the rotational movement of the fuselage - the roll about the vertical axis - using differential braking to move the aircraft while on the ground |
an up or down movement of the nose
|
|
|
The term _______ refers to the direction from which the wind blows.
- downwind - windward - leeward - port - starboard |
windward
|
|
|
An aircraft engine cowling provides what advantages?
- it allows for cooling air to reach the power plant - it protects the engine from external objects - it provides aerodynamic union between the engine and the aircraft fuselage or wing - all the above - none of the above |
all the above
|
|
|
Any position on a nautical chart can be located or expressed in terms of _______ and ________.
- fathoms and depth - reefs and shoals - miles and kilometers - latitude and longitude - X and Y axes |
latitude and longitude
|
|
|
In aeronautics, the term "chord" refers to:
- the straight-line distance between the leading edge and the trailing edge of a wing - the overall length of the fuselage - the effective wing area - the straight-line distance between either wingtip and the nose of the aircraft - the speed at which air compression is at its maximum |
the straight-line distance between the leading edge and the trailing edge of a wing
|
|
|
The Beaufort Scale is used to describe:
- wind speed - cloud cover - amount of precipitation - the depth of the water - the length of a ship |
wind speed
|
|
|
What happens to atmospheric pressure with an increase in altitude?
- atmospheric pressure is not affected by an altitude increase - atmospheric pressure INCREASES as altitude increases - atmospheric pressure DECREASES as altitude increases - atmospheric pressure is affected only by aircraft speed - atmospheric pressure does not affect aircraft |
atmospheric pressure DECREASES as altitude increases
|
|
|
If a ship is secured by a single anchor, it is said to be "anchored". If a ship is secured by two anchors, it is said to be:
- double anchored - moored - held fast - hove to - quartered |
moored
|
|
|
What happens to temperature as altitude increases?
- temperature is not affected by an altitude increase - temperature decreases as altitude increases - temperature increases as altitude increases - temperature is affected only by aircraft speed - temperature does not affect aircraft |
temperature DECREASES as altitude increases
|
|
|
Slanted lettering on a nautical chart indicates:
- updated data since the previous chart was issued - information more than six months old - all names and designations for restricted areas - all information about objects that are affected by tidal changes and currents - nothing (slanted lettering is only for emphasis) |
all information about objects that are affected by tidal changes and currents
|
|
|
The initials VFR stand for:
- velocity of flight restrictions - variable flight regime - visual flight requirements - visual flight rules - VHF flight radio |
visual flight rules
|
|
|
A "port quartering sea" would describe:
- seas that are arriving at an angle on the right side of the stern - seas that are arriving at an angle on the left side of the stern - seas that are arriving at an angle from the left side of the bow - seas that are arriving as the ship enters port - waves between 4 and 6 feet |
seas that are arriving at an angle on the left side of the stern
|
|
|
Adding corrections for temperature and pressure to calibrated airspeed (CAS) gives you:
- ground speed - true airspeed - equivalent airspeed - mach number - aircraft never-exceed speed |
true airspeed
|
|
|
The program that issues information and updates by the U.S. Coast Guard to aid in updating nautical charts and other publications is called:
- Seamanship Weekly - The Coast Guard Monthly - Notice to Mariners - The Sailor's Report - The Maritime Daily Report |
Notice to Mariners
|
|
|
The United Nations-based organization that organizes aeronautical standards and recommended practices concerning international air navigation and operations is:
- the Civil Aviation Safety Authority - the International Civil Aviation Organization - the Federal Aviation Administration - the Airline Pilots Organization - none of the above |
the International Civil Aviation Organization
|
|
|
You have just been ordered to "take the helm". You would be expected to:
- set the anchor detail - make an entry into the deck log - assume the watch - steer the ship - empty the ballast tanks |
steer the ship
|
|
|
The aerodynamic force that acts perpendicular to the direction of relative motion is:
- weight - thrust - drag - lift - pressure |
lift
|
|
|
To determine the swinging radius of a ship at anchor to avoid hitting other ships in your anchorage, what is one of the important factors to know?
- the overall length of your own ship - the amount of anchor line out - the depth of the water you are anchored in - all the above - none of the above |
all the above
|
|
|
With regard to landing distance, what happens at a high-altitude airport?
- landing distance is not affected by altitude - landing distance decreases - landing distance increases - landing distance is only a factor of aircraft speed - the aircraft landing gear is less limited by landing speed |
landing distance increases
|
|
|
The ______ is that part of a ship that is reserved for official and ceremonial functions.
- orlop deck - poop deck - quarterdeck - forecastle - bilge |
quarterdeck
|
|
|
With regard to takeoff distance, what happens in conditions of high temperature?
- takeoff distance increases - takeoff distance decreases - takeoff distance does not change - takeoff distance is only a factor of aircraft speed - standard takeoff distance is halved |
takeoff distance increases
|
|
|
A _______ is a pier or dock providing shipside access for passengers and cargo.
- quay - davit - brow - gunwale - bollard |
quay
|
|
|
One mechanism that is used to increase aircraft lift in a slow-speed environment would be:
- a horizontal stabilizer - a vertical stabilizer - wing flaps - a pitot static system - a landing gear extension |
wing flaps
|
|
|
At 0 degrees angle of attack, a symmetrical airfoil will produce:
- lift, but less than a positively cambered airfoil - no form drag - no induced drag - no net aerodynamic force |
lift, but less than a positively cambered airfoil
|
|
|
Airport runways are numbered according to:
- length and width - wind direction - the first two digits of compass direction - order of construction |
the first two digits of compass direction
|
|
|
Which of the following, when doubled, will cause the greatest change in lift?
- coefficient of lift - velocity - density - area |
velocity
|
|
|
All motion or changes in aircraft attitude occur about which position?
- aerodynamic center (AC) - center of pressure (CP) - center of gravity (CG) - the cockpit |
center of gravity
|
|
|
What are the colors of the port and starboard running lights?
- white/white - red/green - green/red - red/white |
red/green
|
|
|
A pilot is flying under standard day conditions at sea level. His true airspeed will:
- equal indicated airspeed - be greater than indicated airspeed - be less than indicated airspeed |
equal indicated airspeed
|
|
|
The transponder codes for loss of communication and for emergency are:
- 7600 and 7500 - 7700 and 7600 - 7600 and 7700 - 7500 and 7700 |
7600 and 7700
|
|
|
What are the five major components of an airplane?
- wings, fuselage, empennage, landing gear, and engine - wings, cockpit, empennage, flaps, and engine - fuselage, rudder, empennage, airlerons, and engine - fuselage, empennage, engine/transmission assembly, vertical stabilizer, and tail rudder |
wings, fuselage, empennage, landing gear, and engine
|
|
|
Yaw is defined as the motion of the longitudinal axis about which axis?
- the lateral axis - the longitudinal axis - the vertical axis - the horizon |
the vertical axis
|
|
|
Vertigo can be described as:
- the sensation of spinning while stationary - too little oxygen in the bloodstream - the sensation of feeling no movement - a form of blackout |
the sensation of spinning while stationary
|
|
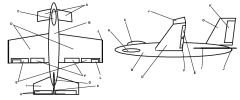
Identify part A
|
Canard
|
|
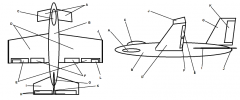
Identify part B
|
Fuselage
|
|
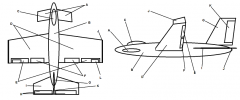
Identify part C
|
Cockpit
|
|
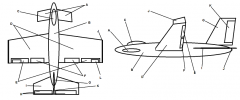
Identify part D
|
Wing(s)
|
|
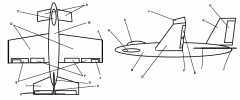
Identify part E
|
Ailerons
|
|
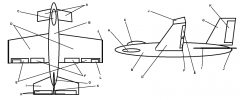
Identify part F
|
Flaps
|
|
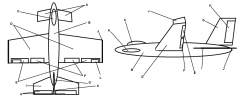
Identify part G
|
Vertical Stabilizer
|
|
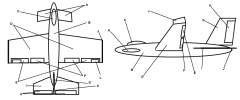
Identify part H
|
Elevator
|
|
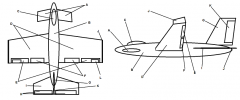
Identify part I
|
Horizontal Stabilizer
|
|
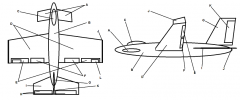
Identify part J
|
Winglets
|
|
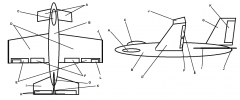
Identify part K
|
Rudder
|
|
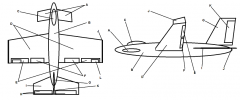
Identify part L
|
Trim Tab
|
|
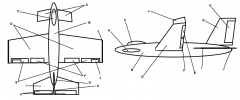
Which of the control surfaces is the primary surface for turning an airplane?
|
E, ailerons
|
|
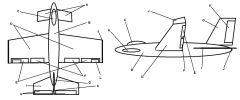
Which of the control surfaces is the primary control for altitude?
|
H, elevator
|
|
|
The primary purpose of winglets are:
- provide better control - improve stability - decrease drag |
decrease drag
|
|
|
The wings of an airplane are angled upward? What is the purpose of this angle?
|
Dihedral
The dihedral angle serves to improve stability and prevent unexpected roll. |
|
|
What causes the sonic boom when a supersonic jet breaks the sound barrier?
|
An abrupt pressure change across the shock wave
|
|
|
Who is the Father of the Navy?
("I have not yet begun to fight.") |
John Paul Jones
|
|
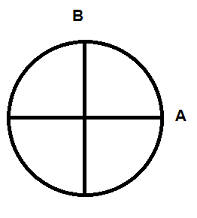
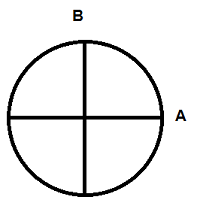
In the diagram of the earth, what does line A represent?
|
latitude
|
|
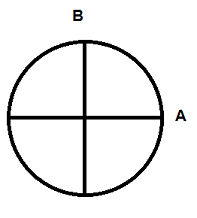
From where is latitude measured?
- Prime Meridian - Equator - International Date Line |
Equator
|
|
In the diagram of the earth, what does line B represent?
|
longitude
|
|
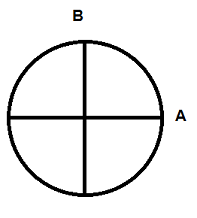
From where is longitude measured?
- Prime Meridian - Equator - International Date Line |
Prime Meridian
|
|
|
Where is the Prime Meridian located?
|
Greenwich, England
|
|
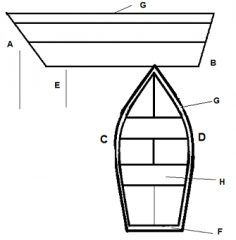
Identify part A
|
Bow
|
|
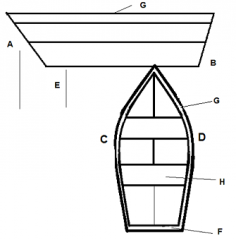
Identify part B
|
Stern
|
|
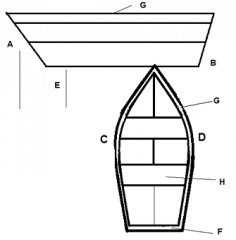
Identify part C
|
Port
|
|
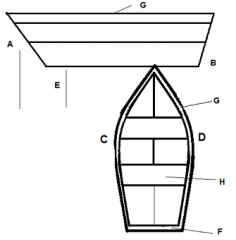
Identify part D
|
Starboard
|
|
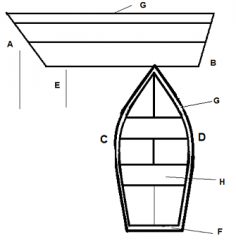
Identify part E
|
Stem
|
|
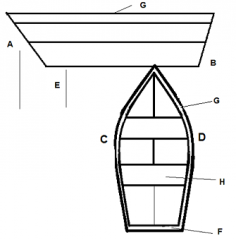
Identify part F
|
Transom
|
|
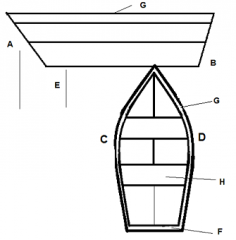
Identify part G
|
Gunwale
|
|
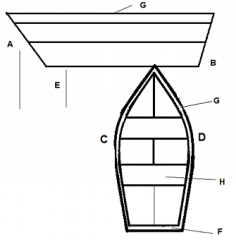
Identify part H
|
Thwart
|
|
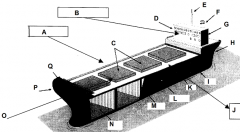
Identify part A
|
Starboard side (green nav light)
|
|
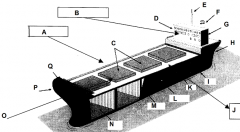
Identify part B
|
Conn-ships controls
|
|
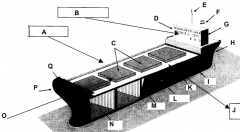
Identify part C
|
Hatches
|
|
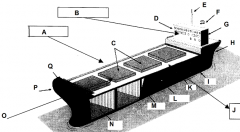
Identify part D
|
Bridge
|
|
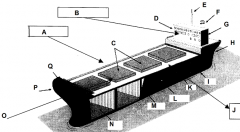
Identify part E
|
Mast
|
|
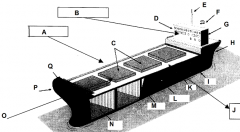
Identify part F
|
Funnel
|
|
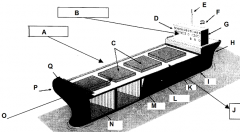
Identify part G
|
Accomodations
|
|
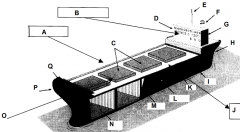
Identify part H
|
Stern
|
|
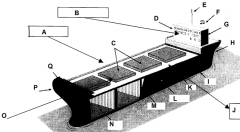
Identify part I
|
Keel
|
|
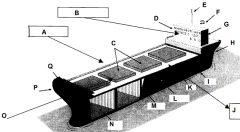
Identify part J
|
Port side (red nav light)
|
|
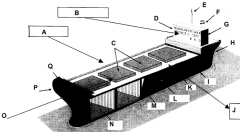
Identify part K
|
Deck
|
|
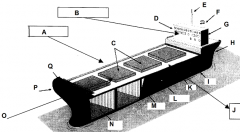
Identify part L
|
Load line
|
|
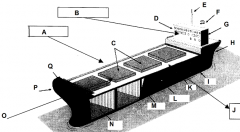
Identify part M
|
Bulkhead
|
|
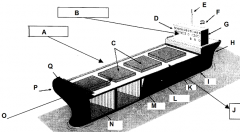
Identify part N
|
Cargo hold
|
|
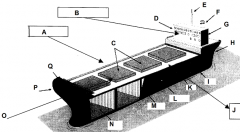
Identify part O
|
Front of the ship
(sorry...nothing fancy here) |
|
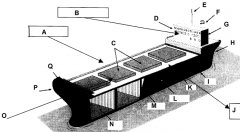
Identify part P
|
Bow
|
|
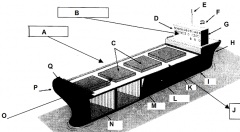
Identify part Q
|
Forecastle
|
|
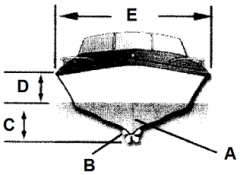
Identify part A
|
Keel
|
|
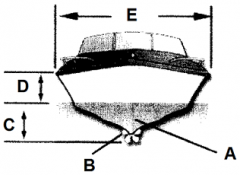
Identify part B
|
Propeller
|
|
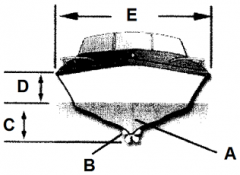
Identify part C
|
Draft
|
|
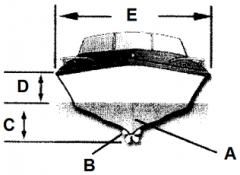
Identify part D
|
Freeboard
|
|
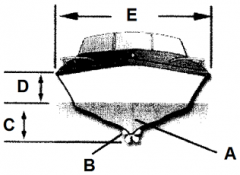
Identify part E
|
Beam
|
|
|
What kind of officers are Navy ensigns, lieutenants, and captains?
|
Company grade officers
|
|
|
What kind of officers are commodores and admirals?
|
Flag officers
|
|
|
Is an F-14 Tomcat's wings fixed or variable sweep?
|
Variable sweep
|
|
|
For variable sweep wings, what are the two positions called and what purpose do they serve?
|
Swept position = decrease drag in high speeds
Extended position = decrease ground speed, increase lift in low speeds |
|
|
Where is the most stable place to stand in a row boat?
|
Bottom center
|
|
|
What is the aerodynamic effect that occurs near the ground?
|
Ground effect
|
|
|
What is camber?
|
curvature at the top of a wing or airfoil
|
|
|
What is the angle of attack?
|
angle formed by the chord line of the wing and the oncoming flow
|
|
|
What is aspect ratio?
|
the ratio of the distance between the wing tips of an airplane to its average wing width
|
|
|
What is fly-by-wire?
|
control linkages between the cockpit and the plane's control surfaces; they are electronic rather than mechanical
|
|
|
What are trim tabs?
|
small control surfaces that permit the pilot to balance control forces in steady flight to relieve pressure on the aircraft's controls and reduce pilot fatigue
|
|
|
What is autorotation?
|
a maneuver used by helicopter pilots to make an emergency landing when he/she has lost engine power during flight
|
|
|
What are the colors of the lights on each side of the ship?
|
starboard = green
port = red |
|
|
What is another name for the NFO (Naval Flight Officer)?
Hint: In the movie Top Gun, what is Goose's job? |
RIO (Radar Intercept Officer)
|
|
|
What is the Bonhomme Richard and what country did it serve?
|
sailing ship, United States
|
|
|
What is compass deviation?
|
The error of a magnetic compass due to local magnetism, as well as the difference between your desired grip or map heading and the heading you must follow on your compass due to local magnetism. It is dependent on your heading.
|
|
|
What is the difference between a spring tide and a neap tide?
|
spring tide = the large rise and fall of the tide at or soon after the new or full moon
neap tide = the tides midway between spring tides that attain the least height |
|
|
When is the moon at its perigee?
|
When it is closest to Earth
|
|
|
If perigee is when the moon is closest to the earth, what is apogee?
|
When it is farthest from the Earth
|
|
|
What is a yawl?
|
double mast sailing vessel (where the mizzen or rear mast is aft of the rudder post)
|
|
|
What is a sloop?
|
single mast sailing vessel
|
|
|
Who is Alan Shepard?
|
the first American in space
|
|
|
Who is John Glen?
|
the first American to orbit the Earth, using Project Mercury Gemini capsule Friendship 7, as well as the first American to fly supersonic across the US
|
|
|
Who is Yuri Gagarin?
|
Russian cosmonaut who was the first human in space
|
|
|
At an airport, what color are the lights that light up the taxi-ways?
|
blue
|
|
|
On an aircraft, long wings compared to shorter wings result in which of the following?
- shallower glide angle - faster roll rate - greater speed |
shallower glide angle
|
|
|
How are runways numbered?
|
By the first two numbers of their compass heading
|
|
|
Which of the following launch vehicles were NOT in the US program?
- Redstone - Atlas - Challenger - Columbia - Delta - Titan |
Delta
|
|
|
Why does a pilot dump fuel prior to an emergency landing?
- fire hazard - maneuverability - to harm the environment - in hope that doing so will correct the problem |
maneuverability
|
|
|
What characteristics describe a warm front?
|
steady, long period of rain and fog
|
|
|
Which is lighter, humid or dry air?
|
humid air
|
|
|
Which is lighter, cold or warm air?
|
warm air
|
|
|
All other things being equal, when is actual airspeed faster than indicated airspeed?
|
at high altitude
|
|
|
If a plane is in straight and level accelerated flight, its:
- propulsion is less than drag - propulsion is equal to drag - propulsion is greater than drag |
propulsion is greater than drag
|
|
|
What is the method called in which you use the surrounding terrain to guide you along your way?
|
terrain association
|
|
|
What is the method called in which you rely solely on your compass for direction?
|
dead reckoning
|
|
|
Why do pilots prefer to land into the wind?
- to have the wind in their hair to remind them of how glamorous being a pilot is - to accelerate just before touching down - to reduce ground speed - to decrease lift |
to reduce ground speed
|
|
|
When is a plane more likely to stall?
- in straight and level flight - in a great degree of bank turn - in a gentle turn - while on the ground idling |
in a great degree of bank turn
|
|
|
When two powered vessels are coming toward each other head on, who has the right of way?
|
both vessels should give way to the starboard (right) side
|
|
|
When two powered vessels are crossing paths, who has the right of way?
|
the vessel on the operator's left gives way to the right; the vessel on operator's right is stand-on and can maintain course
|
|
|
When a powered vessel wishes to overtake another powered vessel, who has right of way?
|
the vessel overtaking has the right of way and should pass on either side; the vessel BEING OVERTAKEN is stand-on and should maintain course
|
|
|
Who has the right of way concerning a powered vessel vs. a sailing vessel?
|
the powered vessel should give way to the sailing vessel; the sailing vessel is stand-on
|
|
|
When it comes to a powered vessel vs. a sailing vessel in one wanting to overtake the other, who has right of way?
|
whichever one is overtaking (powered OR sailing) is give-way and should pass on either side
|
|
|
When it comes to a sailing vessel vs. another sailing vessel, and the wind is on the SAME side, who has right of way?
|
the leeward (downwind) vessel is stand-on and should maintain course
|
|
|
When it comes to a sailing vessel vs. another sailing vessel, and the wind is on DIFFERENT sides, who has right of way?
|
the vessel with wind on its starboard side is stand-on
|
|
|
If operating a power driven vessel, to which other vessels must you give way to?
|
- any vessel not under command
- any vessel restricted in its ability to maneuver - any vessel engaged in commercial fishing - sailing vessels UNLESS they are overtaking |
|
|
If operating a sailing vessel, to which other vessels must you give way to?
|
- any vessel not under command
- any vessel restricted in its ability to maneuver - any vessel engaged in commercial fishing |
|
|
Concerning aircraft, which aircraft ALWAYS has the right of way?
|
aircraft in distress
|
|
|
When aircraft are approaching each other head on, which has the right of way?
|
both aircraft must give way to the right
|
|
|
When one aircraft wishes to overtake another, who has right of way?
|
the overtaking aircraft must pass the slower aircraft to the right and stay well clear
|
|
|
When aircraft of the same category are converging, who has right of way?
|
the aircraft to the other's right has right of way
|
|
|
When two aircraft are converging or approaching from the side, who has right of way?
|
the aircraft to the left must give way to the aircraft on the right
|
|
|
When aircraft of DIFFERENT categories are converging, who has right of way?
|
the least maneuverable aircraft has right of way
|
|
|
Arrange the following in order of least maneuverable aircraft to most maneuverable.
- glider - airplane/rotorcraft - airship - balloon - aircraft refueling |
In order from least maneuverable to most maneuverable:
balloon, glider, aircraft refueling, airship, airplane/rotorcraft |
|
|
When approaching for a landing, which aircraft has right of way?
|
the aircraft of lower altitude has the right of way
ALSO: aircraft in approach for landing has right of way over others in the pattern and those on the ground |
|
|
Where is the longitudinal axis on an airplane?
|
along the fuselage
|
|
|
What does the longitudinal axis do, and what is its movement called?
|
provides lateral stability, movement about: banking
|
|
|
Where is the lateral axis on an airplane?
|
along the wings
|
|
|
What does the lateral axis do, and what is its movement called?
|
provides longitudinal stability, movement about: pitching
|
|
|
Where is the vertical axis located on an airplane?
|
it is a perpendicular axis, and runs through the top and bottom of the fuselage
|
|
|
What is the movement provided by the vertical axis called?
|
yawing
|
|
|
What is the wing span?
|
the length running from wing tip to wing tip
|
|
|
If wing area is doubled, what results?
|
doubled lift and drag
|
|
|
Longer wings compared to short wings result in what?
|
shallower glide angle
|
|
|
What does a headwind do to an aircraft during takeoff?
|
shortens takeoff run, increases angle of climb
|
|
|
What does a tailwind do to an aircraft during takeoff?
|
lengthens takeoff run, decreases angle of climb
|
|
|
One nautical mile is equal to how many statute miles?
|
1 nm = 1.15 statute mile
nautical/statute ratio = 8:7 |
|
|
One nautical mile is equal to how many feet?
|
1 nm = 6076 ft
|
|
|
What is the standard weight for gasoline on an airplane?
|
6 lbs./ US gal
|
|
|
What is the standard weight for oil on an airplane?
|
7.5 lbs./US gal
|
|
|
What is the standard weight for water on an airplane?
|
8.35 lbs./US gal
|
|
|
How does fog form?
|
at night, when warmer air moves over colder water
|
|
|
How can you determine when fog is forming?
|
determined by differences between wet-and-dry bulb temperatures; when the wet-bulb depression is less than 4 degrees
|
|
|
Where is the white light located, and what is its purpose?
|
the white light is located at the stern, it is used to indicate the direction the ship is going
|
|
|
What are yellow lights on a ship used for?
|
special circumstances
|
|
|
What is the freeboard?
|
the section of the boat from water level to the deck
|
|
|
What is the draft?
|
the section of the boat from water level to the bottom of the boat
|
|
|
What is the forecastle?
|
bow half of the deck
|
|
|
What is the fantail?
|
stern half of the deck
|
|
|
What is the keel?
|
the principal structural member of a ship, running lengthwise along the center line from bow to stern, to which frames are attached
|
|
|
What is the lubbers line?
|
the direction of the ship's bow, fore and aft line of the ship
|
|
|
What is the course line?
|
line drawn from the fix in direction in which a ship is moving
|
|
|
Which is lighter, humid or dry air?
|
humid air is lighter than dry air
|
|
|
Which is lighter, warm or cold air?
|
warm air is lighter than cold air
|
|
|
What is dead reckoning?
|
relying solely on your compass for direction
|
|
|
What is terrain association?
|
using the surrounding terrain to guide you along your way
|
|
|
How can you calculate aspect ratio?
|
b^2/s
b = wing span s= surface area of wing |
|
|
What does a high aspect ratio result in?
|
long and skinny wings
|
|
|
What does a low aspect ratio result in?
|
short and stubby wings
|
|
|
What is wing load?
|
ratio of wing surface area to aircraft weight
|
|
|
What is variation?
|
the difference between true bearing and magnetic bearing
|
|
|
At an airport, what do the blue lights illuminate?
|
taxiway
|
|
|
At an airport, what do the white lights illuminate?
|
runway
|
|
|
How are runways numbered?
|
by the first two numbers in their compass heading
e.g. runway 36 is north, not 00 |
|
|
To an aircraft in flight, what does a flashing white light mean?
|
nothing
|
|
|
To an aircraft in flight, what does a steady green light mean?
|
it is cleared to land
|
|
|
To an aircraft in flight, what does a flashing green light mean?
|
it is cleared to approach the airport, or return to land
|
|
|
To an aircraft in flight, what does a steady red light mean?
|
continue circling, give way to other aircraft
|
|
|
To an aircraft in flight, what does a flashing red light mean?
|
airport is unsafe, do not land
|
|
|
To an aircraft in flight, what does an alternating red and green light mean?
|
exercise extreme caution
|
|
|
To an aircraft on the ground, what does a flashing white light mean?
|
return to starting point
|
|
|
To an aircraft on the ground, what does a steady green light mean?
|
cleared for takeoff
|
|
|
To an aircraft on the ground, what does a flashing green light mean?
|
cleared to taxi
|
|
|
To an aircraft on the ground, what does a steady red light mean?
|
stop
|
|
|
To an aircraft on the ground, what does a flashing red light mean?
|
immediately taxi clear of runway in use
|
|
|
To an aircraft on the ground, what does an alternating red and green light mean?
|
exercise extreme caution
|
|
|
To ground vehicles/personnel at an airport, what does a flashing white light mean?
|
return to starting point
|
|
|
To ground vehicles/personnel at an airport, what does a steady green light mean?
|
cleared to cross/proceed
|
|
|
To ground vehicles/personnel at an airport, what does a flashing green light mean?
|
nothing
|
|
|
To ground vehicles/personnel at an airport, what does a steady red light mean?
|
stop
|
|
|
To ground vehicles/personnel at an airport, what does a flashing red light mean?
|
clear the taxiway/runway
|
|
|
To ground vehicles/personnel at an airport, what does an alternating red and green light mean?
|
exercise extreme caution
|
|
|
To all parties at an airport (i.e. aircraft in flight, aircraft on the ground, ground vehicles/personnel), what do blinking runway lights mean?
|
vehicles, planes, and pedestrians immediately clear landing area in use
|
|
|
In which conflict were helicopters first widely used?
|
Korean War
|
|
|
What is an ebb tide?
|
when the tide falls after high tide
|
|
|
Place the following space programs in chronological order:
Gemini Apollo Mercury |
Mercury, Gemini, Apollo
|
|
|
How many types of fuselage are there, and what are they called?
|
2; truss and monocoque
|
|
|
What is a truss fuselage?
|
one that uses steel/aluminum tubing in a series of triangular shapes (trusses) to get the necessary strength and rigidity
|
|
|
What is a monocoque fuselage?
|
one that uses bulkheads, stringers (running the length of the fuselage), and formers (perpendicular to the stringers) of various shapes/sizes to support a stretched or "stressed" skin
|
|
|
What is a planform?
|
the shape of the wing viewed from above
|
|
|
How many wing types are there, and what are they called?
|
3; straight, sweep, and delta
|
|
|
What is a straight wing type?
|
found on small low-speed airplanes, give the most efficient lift at low speeds
|
|
|
What is a sweep wing type?
|
found on high-speed airplanes, creates less drag, more unstable at low speeds
|
|
|
What is a delta wing type?
|
found on airplanes designed for supersonic speeds, has triangle planform with straight trailing edge
|
|
|
What/when was the Apollo 11 mission?
|
US moon landing mission in 1969
|
|
|
Who were the astronauts that conducted the Apollo 11 mission?
|
Neil Armstrong, Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin Jr., and Michael Collins
|
|
|
How many Apollo missions were conducted?
|
17 total Apollo missions
|
|
|
Which American spacecraft was the first to explore the outer solar system?
|
Pioneer 10
|
|
|
Who is Ed White?
|
the first American to walk in space
|
|
|
Arrange the following layers of Earth's atmosphere from lowest to highest:
stratosphere mesosphere troposphere thermosphere exosphere |
- troposphere (from surface to 30000 ft at poles, 56000 ft at equator)
- stratosphere (39000 ft to 164k-180k ft) - mesosphere (160k ft to 260k-280k ft) - thermosphere (260k ft to 1.6m-3.3m ft) - exosphere (>3.3m ft to 33m ft) |
|
|
What is the ionosphere?
|
region of the atmosphere ionized by solar radiation and responsible for auroras; includes the mesosphere, thermosphere, and parts of the exosphere
|
|
|
What is the boundary between the troposphere and stratosphere called?
|
tropopause
|
|
|
Where is the ozone layer located within the atmosphere?
|
at the higher end of the stratosphere
|
|
|
What is air composed of?
|
78% nitrogen
21% oxygen 1% argon trace amounts of carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and other gases |
|
|
When flying, at what altitude would you need oxygen?
|
above 10000 ft
|
|
|
What is the transponder code for hijacking?
|
7500
|
|
|
What is the transponder code for loss of communication?
|
7600
|
|
|
What is the transponder code for emergency?
|
7700
|
|
|
What is the transponder code for military flight/interceptor?
|
7777
|
|
|
What is the condition called in which there is too little oxygen in the bloodstream, resulting in a blackout?
|
hypoxia
|
|
|
What is the condition in which a person feels he/she is constantly moving up and down/feeling turbulence?
|
vertigo
|
|
|
What is Class A airspace?
|
18000 ft (5500 m) mean sea level (MSL) to 60000 ft (18000 m) MSL
alternatively, flight level (FL) 180 to FL 600 |
|
|
What is Class B airspace?
|
surface to 10000 ft (3000 m) MSL, surrounds major airports
|
|
|
What is Class C airspace?
|
surface to 4000 ft (1200 m) above ground level (AGL), surrounds busy airports but in lesser degree than Class B airports
|
|
|
What is Class D airspace?
|
surface to 2500 ft (760 m) AGL, surround airports with operational control tower
|
|
|
What is Class G airspace?
|
surface to 1200 ft or less AGL
|
|
|
What is Class E airspace?
|
any controlled airspace that is not Class A, B, C, or D
|
|
|
How many types of altitude are there, and what are they called?
|
5; indicated, true, absolute, pressure, and density
|
|
|
What is indicated altitude?
|
uncorrected altitude read directly from the altimeter when it is set to the current altimeter setting
|
|
|
What is true altitude?
|
the vertical distance of the airplane above sea level, expressed as feet above MSL
|
|
|
What is absolute altitude?
|
the vertical distance of an airplane above ground level
|
|
|
What is pressure altitude?
|
altitude indicated when the altimeter setting window (barometric scale) is adjusted to 29.92; used to compute density altitude, true altitude, true airspeed, and other performance data
|
|
|
What is density altitude?
|
pressure altitude corrected for variations from standard temperature, directly related to the airplane's performance
|
|
|
What is an altimeter?
|
a flight instrument that measures height above a particular air pressure level, i.e. altitude
|
|
|
What is a vertical speed indicator (VSI)?
|
a flight instrument that indicates whether an airplane is climbing, descending, or level; indicated in feet per minute
|
|
|
What is an airspeed indicator?
|
flight instrument that measures difference between pitot (impact) pressure and static pressure, indicated in mph and/or knots
|
|
|
How many types of airspeed are there, and what are they called?
|
4; indicated, calibrated, equivalent, true
|
|
|
What is indicated airspeed?
|
measures air pressure reading from the pitot tube
|
|
|
What is calibrated airspeed?
|
airspeed calculated after accounting for aircraft mechanical and position errors (attitude)
|
|
|
What is equivalent airspeed?
|
airspeed calculated after compensating for compression effects; usually only needed at speeds over 200 mph
|
|
|
What is true airspeed?
|
airspeed calculated after accounting for temperature and atmospheric pressure changes
|
|
|
What is a turn indicator?
|
flight instrument that indicates turn direction and quality (coordination)
|
|
|
What is an attitude indicator?
|
flight instrument that indicates attitude of airplane (whether banking, pitching, yawing)
|
|
|
What is a heading indicator?
|
flight instrument that supplements the magnetic compass using electronic stabilizing features to indicate magnetic heading of aircraft
|
|
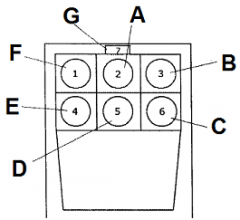
Identify A
|
attitude indicator
|
|
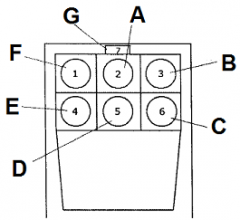
Identify B
|
altimeter
|
|
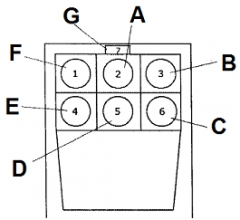
Identify C
|
turn coordinator
|
|
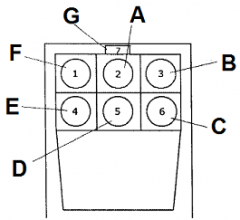
Identify D
|
heading indicator
|
|
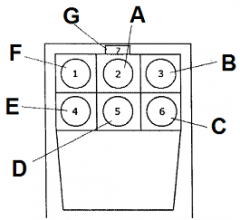
Identify E
|
fuel gauge
|
|
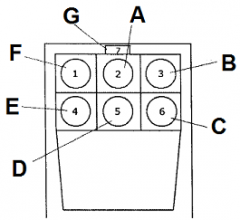
Identify F
|
airspeed indicator
|
|
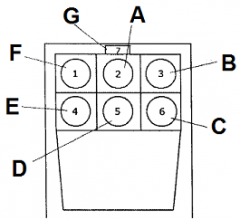
Identify G
|
magnetic compass
|
|
|
At an airport, what color are the taxiway markings?
|
yellow
|
|
|
On the taxiway, how is the centerline represented?
|
solid yellow line
|
|
|
On the taxiway, how are the edges represented?
|
double solid yellow line
|
|
|
On the taxiway, how are the holding lines represented?
|
double solid yellow and double dashed yellow lines across the width of the taxiway
|
|
|
On the taxiway, how is the runway holding position sign represented?
|
red with white characters
|
|
|
On the runway, what is the displaced threshold, and how is it represented?
|
it is the start of the landing portion of the runway, and is a white block with white arrows
|
|
|
On a runway, what are chevrons used for?
|
in case of emergency
|
|
|
On the runway, what does a large white X represent?
|
marks an unusable runway
|
|
|
What color are taxiway lights?
|
blue (on the edge)
|
|
|
What color are runway lights?
|
white (on sidelines), red (at end of runway), green (for threshold)
|
|
|
How are obstructions on the taxiway/runway made known?
|
red lights
|
|
|
What does VASI stand for?
|
visual approach slope indicators
|
|
|
How are VASI lights used?
|
red = low
white/amber = high green = on slope even number of white and red = on slope |
|
|
What does PAPI stand for?
|
precision approach path indicators
|
|
|
How is a 4-Unit PAPI display used?
|
4 white lights = too high
3 white, 1 red light = slightly high 2 white, 2 red = on slope 1 white, 3 red = slightly low 4 red lights = too low |
|
|
How is a 2-Unit PAPI display used?
|
2 white lights = high
1 white, 1 red = on slope 2 red lights = low |
|
|
At what height is a normal air traffic pattern flown?
|
1000 ft AGL
|
|
|
What are the 5 legs of a normal traffic pattern?
|
(in order) upwind leg, crosswind leg, downwind leg, base leg, final approach
|
|
|
For any helicopter, the higher the density altitude, __________
|
the less the rate of climb
|
|
|
What happens as air density increases?
|
lift and drag increase
|
|
|
What is the Beaufort Scale?
|
estimates wind speed
|
|
|
What is a fathometer?
|
electronic device used in making deep-sea soundings
|
|
|
What is a sextant?
|
precision instrument used in celestial navigation to measure angles
|
|
|
What is a capstan?
|
an apparatus used for hoisting weights, consisting of a vertical spool-shaped cylinder that is rotated manually or by machine and around which a cable is wound
|
|
|
What are 4 methods of determining position?
|
piloting, dead reckoning, celestial navigation, electronic navigation
|
|
|
Concerning docks, how can you identify a pier?
|
right angle to the shore
|
|
|
Concerning docks, how can you identify a wharf?
|
parallel to the shore
|
|
|
Concerning docks, what is a slip?
|
space between adjacent piers
|
|
|
What is a cumulus cloud?
|
Latin for "heap", it is a low-lying cloud that looks like a heap of cotton balls; they can develop into the storm cloud cumulonimbus
|
|
|
What is a stratus cloud?
|
Latin for "covering" or "blanket", stratus clouds look like grey flat blankets
|
|
|
What is a cirrus cloud?
|
Latin for "curl", cirrus clouds are high level clouds made out of ice crystals and are wispy in appearance
|
|
|
Which clouds are considered high level clouds (above 18000-20000 ft)?
|
cirrus, cirrocumulus, cirrostratus
|
|
|
Which clouds are considered middle level clouds (above 6500 ft)?
|
altocumulus, altostratus, nimbostratus
|
|
|
Which clouds are considered low level clouds (below 6000 ft)?
|
stratocumulus, stratus, cumulus, nimbostratus
|
|
|
What is a land breeze?
|
at night the land cools faster than the water, therefore the air above it cools and descends; the air over the sea rises; surface air moves to sea; higher air moves inland
|
|
|
What is a sea breeze?
|
during the day, more common on hot sunny days; the land heats and causes the air over the land to rise; the air above the water is cooler and moves in over land and creates a circular pattern
|
|
|
What does "windward" mean?
|
toward the wind
|
|
|
What does "leeward" mean?
|
away from the wind (downwind)
|
|
|
What are the three stages of a thunderstorm?
|
(in order) cumulus stage, mature stage, dissipating stage
|
|
|
What happens in the cumulus stage of a thunderstorm?
|
warm air rises in cumulus clouds, strong updrafts
|
|
|
What happens in the mature stage of a thunderstorm?
|
precipitation begins, typically lasts 20-30 minutes
|
|
|
What happens in the dissipating stage of a thunderstorm?
|
downdrafts of cold air overcome rising warm air, the temperature in the clouds warm to match that of the surrounding environment
|
|
|
If atmospheric temperature is higher than standard, what happens to true altitude compared to indicated altitude?
|
true altitude will be higher than your indicated altitude
|
|
|
If atmospheric temperature is colder than standard, what happens to true altitude compared to indicated altitude?
|
true altitude will be lower than indicated altitude
|
|
|
What is temperature at mean sea level?
|
+15 degrees Celsius
|
|
|
What is pressure at mean sea level?
|
29.92 inches Hg (mercury)
|
|
|
What does it mean if an engine is considered "high performance"?
|
it has more than 200 horsepower
|
|
|
What happens to an engine in thin air conditions?
|
1. the horsepower output is decreased due to fuel-air mixture being reduced
2. the propeller develops less thrust because the blades, as airfoils, are less efficient in thin air 3. the wings develop less lift because thin air exerts less force on the airfoils 4. take-off distance is substantially increased, climb performance is substantially reduced, even nonexistent in extreme conditions |
|
|
What happens to an engine in high humidity conditions?
|
the high level of water vapor in the air reduces the amount of air available for combustion and results in an enriched mixture and reduced power
|
|
|
If you fly from high pressure to low pressure without resetting altimeter, what happens?
|
indicated altitude will read higher than true altitude
|
|
|
If you fly from low pressure to high pressure, what happens?
|
true altitude will be higher than indicated altitude
|
|
|
Choose:
Actual air speed is faster/slower than indicated air speed at high/low altitudes, where the air is more/less dense. |
faster / high / less
|
|
|
Choose:
The higher/lower you go, the more/less dense the air. This means more/less lift, but also more/less drag. |
higher / less / less / less
|
|
|
In what conditions do you get the best lift?
|
dry air, low altitude, cold temperature (all affect density)
|
|
|
Through which physical principle do airfoils work?
|
Bernoulli effect
the air that passes above the airfoil is accelerated back and takes a lower path and thus exerts less pressure, whereas the air that passes below the airfoil moves slower and thus exerts a larger pressure on the wing surface and generates lift |
|
|
How does the Bernoulli effect work?
|
a faster flowing fluid exerts a lower pressure on its surroundings than a slower flowing fluid
|
|
|
What is form/pressure drag?
|
drag caused by the air that is flowing over the aircraft/airfoil; results from the turbulent wake caused by the separation of airflow from the surface of the structure
|
|
|
How can you reduce form/pressure drag?
|
streamline the aircraft; parts of an aircraft that do not lend themselves to streamlining are enclosed in covers called fairings, or a cowling for an engine
|
|
|
Which airplane components produce form/pressure drag?
|
the wing and wing flaps, the fuselage, tail surfaces, nacelles, landing gear, wing tanks and external stores, and engines
|
|
|
What is skin friction drag?
|
drag created by the actual contact of the air particles against the surface of the aircraft
|
|
|
How can you reduce skin friction drag?
|
by keeping an aircraft's surface highly polished and clean
|
|
|
What is parasite drag?
|
the mathematical sum of form drag and skin friction drag, i.e.:
parasite drag = form drag + skin friction drag |
|
|
What is induced drag?
|
drag created by the vortices at the tip of an aircraft's wing; drag due to lift; the high pressure underneath the wing causes the airflow at the tips of the wings to curl around from bottom to top in a circular motion, resulting in a trailing vortex
|
|
|
Induced drag increases in direct proportion to what?
|
increases in angle of attack
the greater the angle of attack up to critical angle, the greater the amount of lift and greater the induced drag |
|
|
Jet propulsion is similar to what action?
|
the release of an inflated balloon
|
|
|
What types of jet engine are commonly used, and which is the simplest?
|
ramjet, turbojet, turbofan
ramjet is the simplest jet engine, but not efficient at low speeds; must be working at supersonic |
|
|
How does a ramjet engine work?
|
1. air enters inlet and is compressed; air pressure is raised
2. air arrives at the combustion chamber, fuel is added and an electric spark is generated 3. a controlled explosion is then created that raises the temperature and air pressure 4. the hot, high pressure air "jets" out of the nozzle of the engine, providing forward thrust |
|
|
How does a turbojet engine work?
|
1. air flows into the engine through the inlet; the inlet design makes the air slow down and raises the pressure
2. the air then goes through the compressor where sets of blades compress the air more and raises the pressure more 3. the air then enters the combustion chamber where fuel is added and ignited 4. the very hot, high pressure air rushes past the turbine blades making them spin very fast; the turbine blades are connected back to the compressor blades by a shaft 5. the turbine blades take some of the energy from the air and returns it to the compressor 6. the hot, high pressure air that gets past the turbine "jets" out the exhaust nozzle, thrusting the engine forward |
|
|
What is an afterburner?
|
a device built into an engine to increase thrust
|
|
|
How does an afterburner work?
|
fuel is dumped into the hot exhaust gas exiting the nozzle causing another controlled explosion
|
|
|
How does a turbofan engine work?
|
1. a large set of fan blades is set right in front of the inlet; the fan works like a propeller, thrusting the engine forward and pushing a large amount of air backwards
2. as the air is pushed back by the fan, some of it goes into the engine and some bypasses the engine; the engine that sits behind the fan is basically a turbojet 3. the air that goes into this engine receives the same treatment as air that goes through the turbojet 4. the air "jets" out the back of the engine |
|
|
What is a turboprop engine?
|
a turbofan engine where the fan is replaced by a propeller
|
|
|
Why must an airplane using a turboprop engine be kept well below the speed of sound?
|
the speed of the propeller approaches the speed of sound faster than the plane, which increases drag
|
|
|
What is total drag?
|
parasite drag + induced drag
|
|
|
When was the Navy founded?
|
October 13, 1775
|
|
|
What was the Ader Eole?
|
first true aeroplane, steam powered
|
|
|
Who developed the Ader Eole, and when?
|
Clement Ader, 1890
|
|
|
What is the name of the first zeppelin?
|
LZ1
|
|
|
When was the first flight of the LZ1, and how long was it?
|
July 2, 1900; flight was 18 minutes long
|
|
|
What was the LZ127?
|
first aircraft to circumnavigate the globe; 21 days, 5 hours, 31 minutes
|
|
|
What was the Wright Flyer?
|
first successful powered and piloted aircraft; flight was 12 seconds, for 120 ft
|
|
|
Who developed the Wright Flyer, and when?
|
Wilbur and Orville Wright, December 17, 1903
|
|
|
What was the FW-61, and when was it built?
|
first functional helicopter, built 1936
|
|
|
What was the aircraft that flew the first nonstop flight across the Atlantic, and when?
|
Vickers Vimmy IV, flown by Alcock and Brown, in June 14, 1919
|
|
|
Who flew the first solo nonstop flight across the Atlantic?
|
Charles Lindbergh Jr., in May 20-21, 1927
|
|
|
Who was Amelia Earhart?
|
first woman to receive the Distinguished Flying Cross, fly solo across the Atlantic (twice), fly nonstop across the US, and fly nonstop from Hawaii to the continental US
|
|
|
What was the first jet to fly combat missions?
|
Messerschmitt ME-262, in 1944
|
|
|
Who was the first man to break the sound barrier, and when?
|
Chuck Yeager in Bell X-1 rocketplane, 1947
|
|
|
Who was Eugene Ely?
|
first person to complete a ship takeoff and landing, on the USS Pennsylvania, 1911
|
|
|
When did the attack on Pearl Harbor occur?
|
December 7, 1941
|
|
|
When was D-Day?
|
June 6, 1944
|
|
|
Name and date the two atomic bomb drops on Japan.
|
Hiroshima, August 6, 1945
Nagasaki, August 9, 1945 |

